Sandbox Reserved 958
From Proteopedia
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
This process leads to an Imunnodeficiency that can indirectly undergo death by an opportunic infection. | This process leads to an Imunnodeficiency that can indirectly undergo death by an opportunic infection. | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | The HIV-1 integrase is a 288-amino acids length of 32 kDa expressed by the ''Pol'' gene. It leads to the synthesis of a polyprotein named Gag-Pol which will be cleaved by the HIV-protease and produced several proteins including integrase. | + | The HIV-1 integrase is a 288-amino acids length of 32 kDa expressed by the ''Pol'' gene. It leads to the synthesis of a '''polyprotein named Gag-Pol''' which will be cleaved by the HIV-protease and produced several proteins including integrase. |
This structure consists of two catalytic core domain monomers. Each monomer is composed of <scene name='60/604477/Sheets/1'>five beta sheets</scene> surrounded by <scene name='60/604477/Helix/1'>five alpha-helix</scene>. | This structure consists of two catalytic core domain monomers. Each monomer is composed of <scene name='60/604477/Sheets/1'>five beta sheets</scene> surrounded by <scene name='60/604477/Helix/1'>five alpha-helix</scene>. | ||
This protein is divided in three main domains: the N-terminal, the central and the C-terminal domain. | This protein is divided in three main domains: the N-terminal, the central and the C-terminal domain. | ||
Revision as of 10:57, 9 January 2015
Dimer of HIV-1 integrase catalytic core domain is the active form of the 3'-Processing reaction that occurs in patients cells suffering from AIDS. The catalytic core domain is just one of three parts composing the HIV-1 integrase. This enzyme performs mainly two specific reactions : the 3'-processing and the integration of the viral DNA into the host genome. In vivo we can find this protein in several forms such as monomer, dimers and tetramers[1].
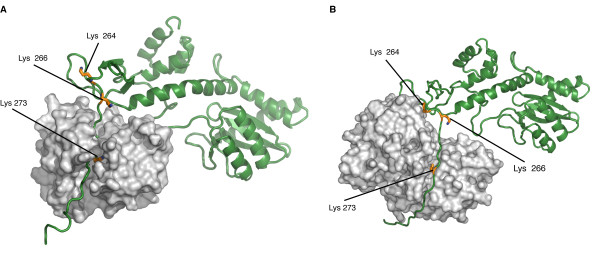
Biological roleAcquired Immune Defficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a human disease caused by the Human Imunnodeficiency Virus (HIV) which is part of the retroviral virus family. This virus infects immune system's cells (Lymphocytes, Macrophages or Dendritic Cells,...) and provoke their destruction by highjacking the cellular machinery. In the first step the virus penetrates the cell through specific membrane receptors then the Retrotranscriptase transforms the viral RNA into a double strand DNA. Further, it will be integrated into the cellular DNA by association with the integrase and other viral and cellular proteins to form the Pre-Integration Complex (PIC). In the last step several viral proteins will be expressed and new virions will be formed by packaging viral and cellular proteins but also the viral RNA [2]. This process leads to an Imunnodeficiency that can indirectly undergo death by an opportunic infection. StructureThe HIV-1 integrase is a 288-amino acids length of 32 kDa expressed by the Pol gene. It leads to the synthesis of a polyprotein named Gag-Pol which will be cleaved by the HIV-protease and produced several proteins including integrase. This structure consists of two catalytic core domain monomers. Each monomer is composed of surrounded by . This protein is divided in three main domains: the N-terminal, the central and the C-terminal domain. The N-terminal domain (1-49) presents a HHCC motif which is a pseudo zinc-finger complexing with zinc ions. The zinc ejection impedes the 3'-processing process and pertubs the integrase multimerisation[3]. Therefore the presence of this ion is necessary for the virus life cycle. The central domain (50-213) which corresponds to the catalytic domain contains the by association of two aspartates and one glutamate residues that coordinate bivalent ions, Cd++ in this structure but Mg++ or Mn++ in vivo [4]. There is also an analogy of structure with the transposase core domain and help to interact with DNA by contact the major groove of viral and cellular DNA[5]. This domain contains between the 170-180 position involved in the packaging of the Uracil DNA glycosylase (UNG2)[6] essential for the viral replication. The flexible elbow (195-220) is a 26-aa alpha-helix called helix links the C-ter domain to the catalytic core domain. It can be see like a flexible elbow because it offers conformation changes of the two previous domains during integration. Another property of this intermediary domain is the ability to contact the DNA phosphate backbone thanks to three main residues : K211, K215 and K219[5]. The C-terminale domain (214-288) is a domain composed of five beta-sheets. It allows the DNA binding in a non-specific manner, HIV-1 IN dimer-dimer contacts, has a tethering role for DNA during the integration process and is also involved in the stability of the complex with DNA[7]. DNA bindingThe recognition of the viral DNA, specifically the Long-Terminal Repeat (LTR) found at either end of proviral DNA, is an important step for the 3' processing reaction. One of the key elements which performs the specific binding between the integrase and the cognate viral DNA is the that is situated at the catalytic core surface[8]. In order to have a tight binding, the integrase-DNA interaction requires optimal number of contacts such as hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces and ionic interactions between DNA elements (bases, phosphates and sugars) and amino acid chains. Among the alpha4 helix residues, have a main role in the specific binding of integrase to DNA by forming bidentate hydrogen bonds which are higher specific than single hydrogen bonds[8]. Moreover, by being positively charged, the lysine side chain provides ionic interactions as well. In addition, Lys-rich sequence implicated in this specific interaction include these two lysines. It has also be shown that contacts on adenine and cytosine of the 5' AC overhang in processed LTR[8]. It also seems that there is a different sensitivity to the viral DNA sequence (LTR) depending on the presence of Mg++ or Mn++ suggesting that specific contacts between the integrase and the viral DNA extremity are more favored in a Mg++ containing environment[3]. FunctionIntegrase is the most conserved protein of the HIV, it means that this enzyme is essential for its life cycle. It has many functions during a cell infection : - in vivo it catalyzes the transport the viral DNA into the nucleus, it interacts with many proteins (VPR, VBP1, HIV-matrix,...) and DNA to form the Pre-Integration Complex (PIC) and allow the integration of the viral DNA into host genome and this mechanism can be divided in two reactions, the 3'-Processing and the Strand Transfer[1] - in vitro researchers proved that two more reactions can be catalyzed by the integrase, the disintegration of the viral DNA and also a possible DNA polymerase activity[4] to repair mismatches during integration. 3'-ProcessingThe 3'-processing is a reaction where the integrase and most precisely, the catalytic core by association with the N-ter domain catalyze the excision of two 3'-terminal nucleotides on both strands of the DNA due to a nucleophilic attack using water. Indeed it is a specific cleavage where two nucleotides on the 3' viral DNA extremities are excised, after that the two newly 3'-OH are used for a second reaction : the strand transfer. To make it possible, integrase needs Mg++ or Mn++ and also zinc ions. Moreover dimers of IN are formed to induce this reaction, then these two dimers are linked on the viral DNA extremities to form a tetramer of IN[3]. The 3' processing reaction occurs before the PIC penetration in the nucleus. Strand TransferThe strand transfer is the really integration step, it provokes the integration of the viral DNA into the host genome by two sequential transesterifications. The integration site is a palindromic and symmetric sequence composed of five nucleotides. This sequence is cleaved to allow the fusion of the LTR extremities of the viral DNA. Afterwards two 3' nucleotides are excised and the joining strand of the five nucleotides is full-filed[9]. The structure that permits this transfer is the intasome (viral DNA + integrase) by association with the Lens Epithelium-derived Growth factor (LEDGF) and the p75 protein that has a cofactor activity for integrase and is a tethering site for chromatin binding. Posttranslationnal ModificationsStudies have prooved that 4 different kinds of Post Translationnal Modifications (PTMs) affect the HIV-1 integrase : ubiquitination, SUMOylation, acetylation and phosphorylation. Furthermore, there are proteins that counteract or facilitate these PTMs implantation, for instance p300 and GCN5 can acetylate IN mostly on its C-ter domain on three different Lys residues (K264, K266 and K273). In contrary Ku70 reduces the ubiquitination level of the N-ter domain (K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48 and K63). Another study also found that IN contains three ψ-K-x-D/E motifs, which can be SUMOylated at three Lys residues, K46, and K244 [10]. InhibitorsSince few years, HIV-1 is an important therapeutic target. Actually there are two kind of inhibitors: the Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors (INSTIs ) and the INtegrase DNA-Binding Inhibitors (INBIs). Over the past 5 years, INSTIs have been shown significant results as antiviral compounds with in 2007, the licensing of the first integrase inhibitor called raltegravir, which target the integrase active site and thus, inhibit DNA strand transfer. However, resistance to this compound emerges which in turn confers the same effect to the second licensed INSTI, elvitegravir[11]. Recent advances allow the discovery of a new inhibitor class which acts in a dissimilar way from that of INSTIs. These compounds exert their inhibitory effect by binding to a highy conserved allosteric pocket on the catalytic core domain dimer (CCD-CCD dimer) mediated through the alpha helice 1 and 5[11]. In a normal HIV-1 life cycle, the cellular co-factor LEDGF/p75 engages the enzyme at the CCD-CCD dimer via its Integrase Binding Domain (IBD). By binding this allosteric pocket, LEDGF/p75 stimulates both concerted integration and strand transfer. It has also be shown that LEDGF-integrase complex exhibits a better solubility profiles compared to the free integrase. This co-factor increases the tetrameric stability of integrase in order to tether the viral DNA to active genes[1]. LEDGF/p75 contacts on one integrase subunit via hydrogen bonds between the cofactor residue Asp366 and the primary amino groups of integrase residues . LEDGF/p75 residue Ile365 contacts on the other integrase subunit by nesting into a hydrophobic pocket which consists of residues [11]. This new class of inhibitor, by engaging this allosteric pocket, prevents the binding of LEDGF/p75 and inhibits the integrase activity by enhancing the formation of integrase multimers, which impedes the intasome assembly[11]. Among these inhibitors, is a investigational new drug that has a distinct mechanism from that of raltegravir and elvitegravir. Indeed, by binding this conserved allosteric pocket on integrase, BI 224436 is the first Non-Catalytic site INtegrase Inhibitor (NCINI)[12].
References
| ||||||||||||||