We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Andrea Bauer/Sandbox 956
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| - | Isoprene Synthase is supposed to be a dimeric enzyme which consists of 595 amino acids and has a molecular mass of 68,386 Da. The protein is made up of alpha-helices which form two alpha-helical domains. | + | Isoprene Synthase is supposed to be a dimeric enzyme which consists of 595 amino acids and has a molecular mass of 68,386 Da. The protein is made up of alpha-helices which form two alpha-helical domains.<ref name:"Koch"> PMID:20624401 </ref> |
| - | The <scene name='68/686749/N-terminal_domain/1'>N-terminal domain</scene> of the protein chain is folded similar to class II terpenoid synthases that are made up of (𝛼𝛼)6 barrels <ref> PMID:9519404 </ref>. | + | The <scene name='68/686749/N-terminal_domain/1'>N-terminal domain</scene> of the protein chain is folded similar to class II terpenoid synthases that are made up of (𝛼𝛼)6 barrels <ref name="Went"> PMID:9519404 </ref>. |
Up to now there is no catalytic activity known for this domain. Quite the contrary regarding the <scene name='68/686749/C-terminal_domain/1'>C-terminal domain</scene> of the isoprene synthase: This domain shows up an 𝛼-helical class I terpenoid synthase fold and contains the active site which is surrounded by five 𝛼-helices. The active site of the enzyme is located in a deep hydrophobic pocket which ensures a protection of the reaction intermediate from water. | Up to now there is no catalytic activity known for this domain. Quite the contrary regarding the <scene name='68/686749/C-terminal_domain/1'>C-terminal domain</scene> of the isoprene synthase: This domain shows up an 𝛼-helical class I terpenoid synthase fold and contains the active site which is surrounded by five 𝛼-helices. The active site of the enzyme is located in a deep hydrophobic pocket which ensures a protection of the reaction intermediate from water. | ||
== Catalyzed Reaction == | == Catalyzed Reaction == | ||
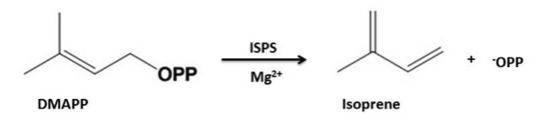
| - | The Isoprene Synthase catalyses the production of isoprene from the substrate dimethylallyl-diphosphate (DMAPP)[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimethylallyl_pyrophosphate]. During the reaction inorganic pyrophosphate is eliminated leading to the reaction products isoprene and inorganic pyrophosphate. The release of the pyrophosphate group leads to the generation of an allylic carbocation which is typical of class I terpenoid | + | The Isoprene Synthase catalyses the production of isoprene from the substrate dimethylallyl-diphosphate (DMAPP)[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimethylallyl_pyrophosphate]. During the reaction inorganic pyrophosphate is eliminated leading to the reaction products isoprene and inorganic pyrophosphate. The release of the pyrophosphate group leads to the generation of an allylic carbocation which is typical of class I terpenoid syntheses<ref name="Went"/>. The occuring elimination mechanism is syn-periplanar and the leaving diphpsphate group acts as general base. The characteristic DDXXD-sequence motif of class I terpenoid synthases that binds to the diphosphate leaving group via Mg2+-ions facilitates the release of the pyrophosphate group. |
[[Image:Isoprene_formation.jpg | thumb | upright=3]] | [[Image:Isoprene_formation.jpg | thumb | upright=3]] | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 9 January 2015
Structure of Isoprene Synthase from Grey Poplar Leaves (Populus x canescens)
| |||||||||||