We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 951
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
====The N-terminal domain==== | ====The N-terminal domain==== | ||
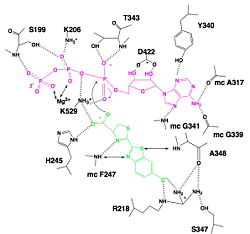
| - | The sequence of amino acids of C-terminal domain is composed of non-contiguous residues. It falls into three subdomains (<scene name='60/604470/Domain_a/1'>the subdomain A</scene>,<scene name='60/604470/Domain_b/1'>the subdomain B</scene>, and <scene name='60/604470/Domain_c/1'>the subdomain C</scene>). The subdomains A and B corresponds to two β sheets, which are framed by <scene name='60/604470/Alpha_helices/1'>α helices</scene>. Each of the two β sheets subdomains are composed of 8 β strands and 6 helices. The β sheet A has <scene name='60/604470/A_beta_strands/1'>5 parallel and 3 antiparallel β strands</scene>. The β sheet B has <scene name='60/604470/A_beta_strands/1'>6 parallel and 2 antiparallel β strands</scene>. Those β sheets create a groove, closed on one end by the subdomain C, which is an antiparallel <scene name='60/604470/Beta_barrel/3'>β barrel</scene>. <ref name = | + | The sequence of amino acids of C-terminal domain is composed of non-contiguous residues. It falls into three subdomains (<scene name='60/604470/Domain_a/1'>the subdomain A</scene>,<scene name='60/604470/Domain_b/1'>the subdomain B</scene>, and <scene name='60/604470/Domain_c/1'>the subdomain C</scene>). The subdomains A and B corresponds to two β sheets, which are framed by <scene name='60/604470/Alpha_helices/1'>α helices</scene>. Each of the two β sheets subdomains are composed of 8 β strands and 6 helices. The β sheet A has <scene name='60/604470/A_beta_strands/1'>5 parallel and 3 antiparallel β strands</scene>. The β sheet B has <scene name='60/604470/A_beta_strands/1'>6 parallel and 2 antiparallel β strands</scene>. Those β sheets create a groove, closed on one end by the subdomain C, which is an antiparallel <scene name='60/604470/Beta_barrel/3'>β barrel</scene>. <ref name ="first">PMID:8805533</ref> |
Revision as of 18:45, 9 January 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Welsh DK, Kay SA. Bioluminescence imaging in living organisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005 Feb;16(1):73-8. PMID:15722018 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2004.12.006
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Conti E, Franks NP, Brick P. Crystal structure of firefly luciferase throws light on a superfamily of adenylate-forming enzymes. Structure. 1996 Mar 15;4(3):287-98. PMID:8805533
- ↑ Marques SM, Esteves da Silva JC. Firefly bioluminescence: a mechanistic approach of luciferase catalyzed reactions. IUBMB Life. 2009 Jan;61(1):6-17. PMID:18949818 doi:10.1002/iub.134
- ↑ Conti E, Franks NP, Brick P. Crystal structure of firefly luciferase throws light on a superfamily of adenylate-forming enzymes. Structure. 1996 Mar 15;4(3):287-98. PMID:8805533
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Photobiology
- ↑ Marques SM, Esteves da Silva JC. Firefly bioluminescence: a mechanistic approach of luciferase catalyzed reactions. IUBMB Life. 2009 Jan;61(1):6-17. PMID:18949818 doi:10.1002/iub.134
- ↑ Hosseinkhani S. Molecular enigma of multicolor bioluminescence of firefly luciferase. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Apr;68(7):1167-82. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0607-0. Epub, 2010 Dec 28. PMID:21188462 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0607-0
- ↑ Inouye S. Firefly luciferase: an adenylate-forming enzyme for multicatalytic functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Feb;67(3):387-404. Epub 2009 Oct 27. PMID:19859663 doi:10.1007/s00018-009-0170-8