We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 951
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
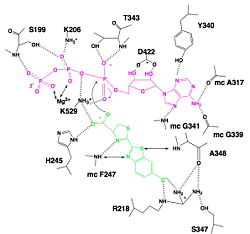
This reaction uses similar reaction but instead of taking luciferin as ligand, it takes fatty acids. Using ATP-Mg2+, it firstly forms fatty-acyl-AMP. And then, CoA-SH attacks the carboxylic group of fatty-acyl-AMP and so forms fatty-acyl-CoA. | This reaction uses similar reaction but instead of taking luciferin as ligand, it takes fatty acids. Using ATP-Mg2+, it firstly forms fatty-acyl-AMP. And then, CoA-SH attacks the carboxylic group of fatty-acyl-AMP and so forms fatty-acyl-CoA. | ||
=====Luciferin & Coenzyme A===== | =====Luciferin & Coenzyme A===== | ||
| - | It has been found that the reaction between luciferin and CoA is possible, forming in a first step luciferin-AMP and then luciferin-CoA. This reaction leads to an interesting biological phenomenon : when this reaction occurs in parallel of light emission reaction, we don't have a flash of light but a continuous light emission. This is because luciferin-AMP is a competitive inhibitor of the reaction whereas the luciferin-CoA is not. So the inhibition is deleted and the reaction continue to occur.<ref>PMID:18949818</ref> | + | It has been found that the reaction between luciferin and CoA is possible, forming in a first step luciferin-AMP and then luciferin-CoA. This reaction leads to an interesting biological phenomenon : when this reaction occurs in parallel of light emission reaction, we don't have a flash of light but a continuous light emission. This is because luciferin-AMP is a competitive inhibitor of the reaction whereas the luciferin-CoA is not. So the inhibition is deleted and the reaction continue to occur.<ref name="third">PMID:18949818</ref> |
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
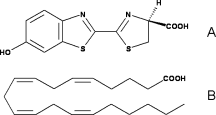
Fatty acids are highly similar to luciferin. Therefore, luciferase can use the luciferin binding site to bind fatty acids. That is why they can be used as substrates by luciferase and then, very high similar reaction as for luciferin occurs. | Fatty acids are highly similar to luciferin. Therefore, luciferase can use the luciferin binding site to bind fatty acids. That is why they can be used as substrates by luciferase and then, very high similar reaction as for luciferin occurs. | ||
[[Image:Luciferin_fatty-acid.gif|250px|left|thumb|Comparison of the chemical structures of (A) firefly | [[Image:Luciferin_fatty-acid.gif|250px|left|thumb|Comparison of the chemical structures of (A) firefly | ||
| - | D-LH2 and (B) arachidonic acid,<ref>PMID:18949818</ref>]] | + | D-LH2 and (B) arachidonic acid,<ref name="third">PMID:18949818</ref>]] |
====Color modulation==== | ====Color modulation==== | ||
Revision as of 18:47, 9 January 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Welsh DK, Kay SA. Bioluminescence imaging in living organisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005 Feb;16(1):73-8. PMID:15722018 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2004.12.006
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Conti E, Franks NP, Brick P. Crystal structure of firefly luciferase throws light on a superfamily of adenylate-forming enzymes. Structure. 1996 Mar 15;4(3):287-98. PMID:8805533
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Marques SM, Esteves da Silva JC. Firefly bioluminescence: a mechanistic approach of luciferase catalyzed reactions. IUBMB Life. 2009 Jan;61(1):6-17. PMID:18949818 doi:10.1002/iub.134
- ↑ Conti E, Franks NP, Brick P. Crystal structure of firefly luciferase throws light on a superfamily of adenylate-forming enzymes. Structure. 1996 Mar 15;4(3):287-98. PMID:8805533
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Photobiology
- ↑ Hosseinkhani S. Molecular enigma of multicolor bioluminescence of firefly luciferase. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Apr;68(7):1167-82. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0607-0. Epub, 2010 Dec 28. PMID:21188462 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0607-0
- ↑ Inouye S. Firefly luciferase: an adenylate-forming enzyme for multicatalytic functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Feb;67(3):387-404. Epub 2009 Oct 27. PMID:19859663 doi:10.1007/s00018-009-0170-8