This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 976
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
The tissue-type Plasminogen Activator is a 69-kDa multidomain glycoprotein, which consists in a single polypeptide chain of 527-530 amino acids <ref name=vivien/>. There is three types of domain: F1 (homologous to fibronectin type I), G (epidermal growth-factor like) and kringle.<ref name=smith>Smith BO, Downing AK, Driscoll PC, Dudgeon TJ, Campbell ID (1995) The solution structure ans backbone dynamics of the fibronectin type I and epidermal growth factor-like pair of modules of tissue-type plasminogen activator. Structure, 3 : 823-833</ref> | The tissue-type Plasminogen Activator is a 69-kDa multidomain glycoprotein, which consists in a single polypeptide chain of 527-530 amino acids <ref name=vivien/>. There is three types of domain: F1 (homologous to fibronectin type I), G (epidermal growth-factor like) and kringle.<ref name=smith>Smith BO, Downing AK, Driscoll PC, Dudgeon TJ, Campbell ID (1995) The solution structure ans backbone dynamics of the fibronectin type I and epidermal growth factor-like pair of modules of tissue-type plasminogen activator. Structure, 3 : 823-833</ref> | ||
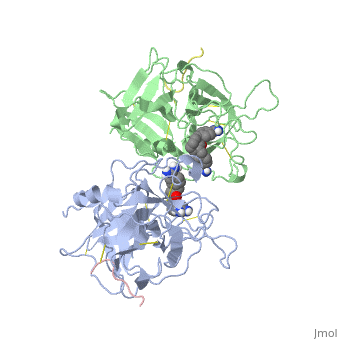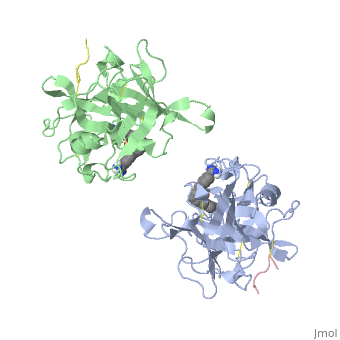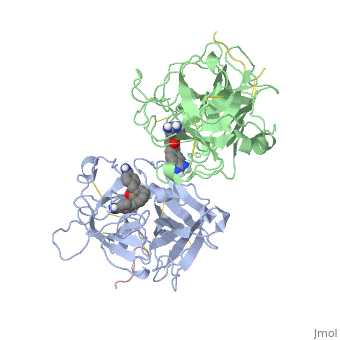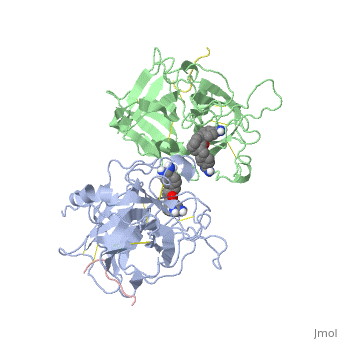
| - | The structures described below correspond to the structure of the catalytic domain of humain tPA in complex with a Bis-Benzamidine. The catalytic domain of a protein is the part of the enzyme that reacts with the substrate to induce the enzymatic reaction and benzamidine is an organic compound often used as an inhibitor | + | The structures described below correspond to the structure of the catalytic domain of humain tPA in complex with a Bis-Benzamidine. <scene name='68/686810/Newscene/1'>The catalytic domain of a protein is the part of the enzyme that reacts with the substrate to induce the enzymatic reaction and benzamidine</scene> is an organic compound often used as an inhibitor. Thus, the complexation of t-PA with bis-benzamidine revealed a strong structural similarities to other trypsin-like serine proteases, as alpha-chymotrypsine. tPA is known for its high specificity : tPA recognizes complexes or multiple elements on the surface of plasminogen, even distant form its cleavage site. In vivo, the tPA cleavage site is a single bond of plasminogen formed by the residues Arg560-Val561 <ref name=renatus >Renatus M, Bode W, Huber R, Stürzebecher J, Prasa D, Fisher S, Kohnert U, Stubbs MT (1997) Structural Mapping of the Active Site Specificity Determinants of Human Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator. The Journal of Biological Chemestry, 272 : 21712-21719</ref>. |
Few t-PA-specific inhibitors are known. Synthetic inhibitors for t-PA-like proteins has been based on Arginin and Lysin residues derivatives and the structurally related benzamidines. | Few t-PA-specific inhibitors are known. Synthetic inhibitors for t-PA-like proteins has been based on Arginin and Lysin residues derivatives and the structurally related benzamidines. | ||
Revision as of 22:03, 11 January 2015
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-PA)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Vivien D, Gauberti M, Montagne A, Defer G and Touzé E (2011) Impact of tissue plaminogen activator on the neurovascular unit : from clinical data to experimental evidence. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 31 : 2119-2134.
- ↑ Maithili Sashindranath,1 Eunice Sales,1 Maria Daglas,1 Roxann Freeman, (2012) The tissue-type plasminogen activator–plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 complex promotes neurovascular injury in brain trauma: evidence from mice and humans. Brain 2012: 135; 3251–3264
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Role of Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator in Ischemic Stroke, Yasuhiro Suzuki 1, (2010) J Pharmacol Sci 113, 203 – 207 (2010)
- ↑ Thrombolytic Therapy for the Treatment of Prosthetic Heart Valve Thrombosis in Pregnancy With Low-Dose, Slow Infusion of Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator (2013). Mehmet Özkan, Beytullah Çakal, Süleyman Karakoyun, Ozan Mustafa Gürsoy, doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001145 Circulation. 2013;128:532-540; originally published online June 28, 2013
- ↑ Smith BO, Downing AK, Driscoll PC, Dudgeon TJ, Campbell ID (1995) The solution structure ans backbone dynamics of the fibronectin type I and epidermal growth factor-like pair of modules of tissue-type plasminogen activator. Structure, 3 : 823-833
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Renatus M, Bode W, Huber R, Stürzebecher J, Prasa D, Fisher S, Kohnert U, Stubbs MT (1997) Structural Mapping of the Active Site Specificity Determinants of Human Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator. The Journal of Biological Chemestry, 272 : 21712-21719