Mycobacterium tuberculosis ArfA Rv0899
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='2l26' size='350' side='right' caption='NMR structure of uncharacterized protein Rv0899 (PDB code [[2l26]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2l26' size='350' side='right' caption='NMR structure of uncharacterized protein Rv0899 (PDB code [[2l26]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:Bdomain.jpg|150px]] | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 13: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:N-ter domain.jpg|210px]] | [[Image:N-ter domain.jpg|210px]] | ||
| - | A central B domain ( <scene name='61/612805/Bon_domains/1'>residues 73-200</scene> ) with homology to the conserved putative lipid-binding BON (bacterial OsmY and nodulation) superfamily[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/IPR014004] ,<scene name='61/612805/with conserved_g95_and_g164_in_bon/1'>with conserved G95 and G164 in BON superfamily</scene> | + | A central B domain ( <scene name='61/612805/Bon_domains/1'>residues 73-200</scene> ) with homology to the conserved putative lipid-binding BON (bacterial OsmY and nodulation) superfamily[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/IPR014004] ,<scene name='61/612805/with conserved_g95_and_g164_in_bon/1'>with conserved G95 and G164 in BON superfamily</scene>.The B domain folds with <scene name='61/612805/Sheet_and_helix/1'> three parallel/antiparallel alpha-helices packed against six parallel/antiparallel beta-strands that form a flat beta-sheet</scene>. <scene name='61/612805/Surface/1'>The core is hydrophobic, while the exterior is polar and predominantly acidic</scene>. |
| + | A C domain (residues 201-326) with homology to the OmpA-C-like superfamily of periplasmic peptidoglycan-binding sequences, found in several types of bacterial membrane proteins. | ||
| + | Residues 73-326 form a mixed alpha/beta-globular structure, encompassing two independently folded modules corresponding to the B and C domains connected by a flexible linker. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
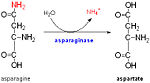
Probably plays a role in ammonia secretion that neutralizes the medium at pH 5.5,and preceded exponential growth of ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', although it does not play a direct role in ammonia transport.[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P9WIU5 ARFA_MYCTU]]. The ompATb operon is necessary for rapid ammonia secretion and adaptation of M. tuberculosis to acidic environments in vitro but not in mice. | Probably plays a role in ammonia secretion that neutralizes the medium at pH 5.5,and preceded exponential growth of ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', although it does not play a direct role in ammonia transport.[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P9WIU5 ARFA_MYCTU]]. The ompATb operon is necessary for rapid ammonia secretion and adaptation of M. tuberculosis to acidic environments in vitro but not in mice. | ||
<ref>PMID: 21410778 </ref> | <ref>PMID: 21410778 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Bdomain.jpg|150px]] | ||
[[Image:Asparaginase-reaction.jpg|150px]] | [[Image:Asparaginase-reaction.jpg|150px]] | ||
Revision as of 19:49, 13 January 2015
| |||||||||||