|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | <StructureSection load='2l26' size='350' side='right' caption='NMR structure of uncharacterized protein Rv0899 (PDB code [[2l26]])' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='2l26' size='350' side='right' caption='NMR structure of uncharacterized protein Rv0899 (PDB code [[2l26]])' scene=''> |
| | | | |
| - | | + | == Structural highlights == |
| - | == Function == | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2l26]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2L26 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2L26 FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | Protein Rv0899 from '''''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''''' [http://he.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis] belongs to the OmpA (outer membrane protein A) family of outer membrane proteins.The deletion of this gene impairs the uptake of some water-soluble substances, such as serine, glucose, and glycerol.Using [[NMR]] chemical shift perturbation and isothermal calorimetric titration assays, Rv0899 was able to interact with <scene name='61/612805/Binding-site_for_zn/1'>Zn(2+) ions</scene>, which may indicate a role for Rv0899 in the process of Zn(2+) acquisition.
| + | </td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2l26 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2l26 OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2l26 RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2l26 PDBsum]</span></td></tr> |
| - | <ref>PMID: 22108166 </ref> | + | </table> |
| - | ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' ArfA (Rv0899) is a membrane protein encoded by an ammonia release facilator operon that is necessary for rapid ammonia secretion, pH neutralization and adaptation to acidic environments in vitro. Its C-terminal domain (C domain) shares significant sequence homology with the OmpA-like family of peptidoglycan-binding domains, suggesting that its physiological function in acid stress protection may be related to its interaction with the mycobacterial cell wall. It exhibits pH-dependent conformational dynamics (with significant heterogeneity at neutral pH and a more ordered structure at acidic pH), which could be related to its acid stress response. The C domain associates tightly with polymeric peptidoglycan isolated from ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. Its functions in acid stress protection and <scene name='61/612805/The_peptidoglycan_binding_site/1'>peptidoglycan binding</scene> suggest a link between the acid stress response and the physicochemical properties of the mycobacterial cell wall.<ref>PMID: 22206986 </ref>. | + | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> |
| | | | |
| | ==Structure Section== | | ==Structure Section== |
| | The 326-residue protein contains three domains: an N-terminal domain (residues 1-72) that includes a sequence of 20 hydrophobic amino acids required for membrane translocation. | | The 326-residue protein contains three domains: an N-terminal domain (residues 1-72) that includes a sequence of 20 hydrophobic amino acids required for membrane translocation. |
| | [[Image:N-ter domain.jpg|210px]] | | [[Image:N-ter domain.jpg|210px]] |
| | + | |
| | <scene name='61/612805/N-c_rainbow/1'>Residues 73-326</scene> | | <scene name='61/612805/N-c_rainbow/1'>Residues 73-326</scene> |
| | form a mixed alpha/beta-globular structure, encompassing two independently folded modules corresponding to the B and C domains connected by a flexible linker. | | form a mixed alpha/beta-globular structure, encompassing two independently folded modules corresponding to the B and C domains connected by a flexible linker. |
| Line 16: |
Line 17: |
| | [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/IPR014004]. | | [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/IPR014004]. |
| | <scene name='61/612805/Surface/1'>The core is hydrophobic, while the exterior is polar and predominantly acidic</scene>. | | <scene name='61/612805/Surface/1'>The core is hydrophobic, while the exterior is polar and predominantly acidic</scene>. |
| - | | |
| | The C domain <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/1'>(residues 201-326)</scene> has homology to the OmpA-C-like superfamily of periplasmic peptidoglycan-binding sequences, found in several types of bacterial membrane proteins. | | The C domain <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/1'>(residues 201-326)</scene> has homology to the OmpA-C-like superfamily of periplasmic peptidoglycan-binding sequences, found in several types of bacterial membrane proteins. |
| | | | |
| | + | = Function == |
| | + | Protein Rv0899 from '''''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''''' [http://he.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis] belongs to the OmpA (outer membrane protein A) family of outer membrane proteins.The deletion of this gene impairs the uptake of some water-soluble substances, such as serine, glucose, and glycerol.Using [[NMR]] chemical shift perturbation and isothermal calorimetric titration assays, Rv0899 was able to interact with <scene name='61/612805/Binding-site_for_zn/1'>Zn(2+) ions</scene>, which may indicate a role for Rv0899 in the process of Zn(2+) acquisition. |
| | + | <ref>PMID: 22108166 </ref> |
| | + | ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' ArfA (Rv0899) is a membrane protein encoded by an ammonia release facilator operon that is necessary for rapid ammonia secretion, pH neutralization and adaptation to acidic environments in vitro. Its C-terminal domain (C domain) shares significant sequence homology with the OmpA-like family of peptidoglycan-binding domains, suggesting that its physiological function in acid stress protection may be related to its interaction with the mycobacterial cell wall. It exhibits pH-dependent conformational dynamics (with significant heterogeneity at neutral pH and a more ordered structure at acidic pH), which could be related to its acid stress response. The C domain associates tightly with polymeric peptidoglycan isolated from ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. Its functions in acid stress protection and <scene name='61/612805/The_peptidoglycan_binding_site/1'>peptidoglycan binding</scene> suggest a link between the acid stress response and the physicochemical properties of the mycobacterial cell wall.<ref>PMID: 22206986 </ref>. |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Line 33: |
Line 37: |
| | == Relevance == | | == Relevance == |
| | | | |
| - | == Structural highlights == | |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2l26]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2L26 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2L26 FirstGlance]. <br> | |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2l26 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2l26 OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2l26 RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2l26 PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | |
| - | </table> | |
| - | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
|
Structural highlights
Structure Section
The 326-residue protein contains three domains: an N-terminal domain (residues 1-72) that includes a sequence of 20 hydrophobic amino acids required for membrane translocation.
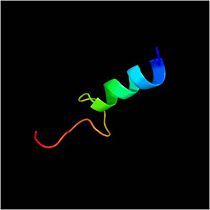
form a mixed alpha/beta-globular structure, encompassing two independently folded modules corresponding to the B and C domains connected by a flexible linker.
The central B domain ( ) folds with .
The B domain has homology with conserved putative
[1].
.
The C domain has homology to the OmpA-C-like superfamily of periplasmic peptidoglycan-binding sequences, found in several types of bacterial membrane proteins.
Function =
Protein Rv0899 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis [2] belongs to the OmpA (outer membrane protein A) family of outer membrane proteins.The deletion of this gene impairs the uptake of some water-soluble substances, such as serine, glucose, and glycerol.Using NMR chemical shift perturbation and isothermal calorimetric titration assays, Rv0899 was able to interact with , which may indicate a role for Rv0899 in the process of Zn(2+) acquisition.
[1]
Mycobacterium tuberculosis ArfA (Rv0899) is a membrane protein encoded by an ammonia release facilator operon that is necessary for rapid ammonia secretion, pH neutralization and adaptation to acidic environments in vitro. Its C-terminal domain (C domain) shares significant sequence homology with the OmpA-like family of peptidoglycan-binding domains, suggesting that its physiological function in acid stress protection may be related to its interaction with the mycobacterial cell wall. It exhibits pH-dependent conformational dynamics (with significant heterogeneity at neutral pH and a more ordered structure at acidic pH), which could be related to its acid stress response. The C domain associates tightly with polymeric peptidoglycan isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Its functions in acid stress protection and suggest a link between the acid stress response and the physicochemical properties of the mycobacterial cell wall.[2].
Disease
The membrane protein Rv0899 of M. tuberculosis encoded by gene Rv0899 has been proposed to act as an outer membrane porin and to contribute to the bacterium's adaptation to the acidic environment of the phagosome[3] during infection.
The protein is restricted to pathogenic Mycobacteria associated with TB and, thus, is an attractive candidate for the development of anti-TB chemotherapeutic agents.Two M. tuberculosis H37Rv genes (Rv0900 and Rv0901) adjacent to Rv0899 also encode putative membrane proteins, and are found exclusively in association with Rv0899 in the same pathogenic mycobacteria, suggesting that the three may constitute an operon dedicated to a common function.
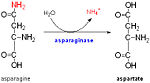
The amino acid pair Asn111-Gly112,located at the end of α1 and preceding L3, undergoes in-vitro deamidation, a pH-dependent reaction whereby Asn is converted to Asp and ammonia is released. Asparagine residues preceding glycine, and situated in conformationally flexible regions of proteins, are frequently deamidated, with potentially significant consequences for protein regulation and function. In the case of Rv0899, deamidation and the concomitant release of ammonia could have important consequences for the acid adaptation function of the protein. The gene is restricted to pathogenic mycobacteria and, thus, is an attractive candidate for the development of anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy. [3]
Probably plays a role in ammonia secretion that neutralizes the medium at pH 5.5,and preceded exponential growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, although it does not play a direct role in ammonia transport.[ARFA_MYCTU]. The ompATb operon is necessary for rapid ammonia secretion and adaptation of M. tuberculosis to acidic environments in vitro but not in mice.
[4]
Image:Bdomain.jpg
Relevance
References
- ↑ Li J, Shi C, Gao Y, Wu K, Shi P, Lai C, Chen L, Wu F, Tian C. Structural Studies of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0899 Reveal a Monomeric Membrane-Anchoring Protein with Two Separate Domains. J Mol Biol. 2011 Nov 15. PMID:22108166 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.016
- ↑ Yao Y, Barghava N, Kim J, Niederweis M, Marassi FM. Molecular Structure and Peptidoglycan Recognition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ArfA (Rv0899). J Mol Biol. 2012 Feb 17;416(2):208-20. Epub 2011 Dec 21. PMID:22206986 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.12.030
- ↑ Teriete P, Yao Y, Kolodzik A, Yu J, Song H, Niederweis M, Marassi FM. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0899 Adopts a Mixed alpha/beta-Structure and Does Not Form a Transmembrane beta-Barrel. Biochemistry. 2010 Mar 10. PMID:20199110 doi:10.1021/bi100158s
- ↑ Song H, Huff J, Janik K, Walter K, Keller C, Ehlers S, Bossmann SH, Niederweis M. Expression of the ompATb operon accelerates ammonia secretion and adaptation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to acidic environments. Mol Microbiol. 2011 May;80(4):900-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07619.x. Epub, 2011 Mar 16. PMID:21410778 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07619.x
|


