Mycobacterium tuberculosis ArfA Rv0899
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Using [[NMR]] chemical shift perturbation and isothermal calorimetric titration assays, Rv0899 was able to interact with <scene name='61/612805/Binding-site_for_zn/1'>Zn(2+) ions</scene>, which may indicate a role for Rv0899 in the process of Zn(2+) acquisition. | Using [[NMR]] chemical shift perturbation and isothermal calorimetric titration assays, Rv0899 was able to interact with <scene name='61/612805/Binding-site_for_zn/1'>Zn(2+) ions</scene>, which may indicate a role for Rv0899 in the process of Zn(2+) acquisition. | ||
<ref>PMID: 22108166 </ref> | <ref>PMID: 22108166 </ref> | ||
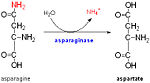
| - | ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' ArfA (Rv0899) is a membrane protein encoded by an ammonia release facilator operon that is necessary for rapid ammonia secretion, pH neutralization and adaptation to acidic environments in vitro. Its C-terminal domain (C domain) shares significant sequence homology with the OmpA-like family of peptidoglycan-binding domains, suggesting that its physiological function in acid stress protection may be related to its interaction with the mycobacterial cell wall. It exhibits pH-dependent conformational dynamics<scene name='61/612805/Hydrophobic_region_of_d236a/1'>Hydrophobic region of mutant ArfA-c (D236A)</scene> <scene name='61/612805/The_peptidoglycan_binding_site/1'>The peptidoglycan binding site</scene> (with significant heterogeneity at neutral pH and a more ordered structure at acidic pH), which could be related to its acid stress response. The C domain associates tightly with polymeric peptidoglycan isolated from ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. Its functions in acid stress protection and <scene name='61/612805/The_peptidoglycan_binding_site/1'>peptidoglycan binding</scene> suggest a link between the acid stress response and the physicochemical properties of the mycobacterial cell wall <scene name='61/612805/Hydrophobic_region_of_d236a/3'>Pept+H</scene> .<ref>PMID: 22206986 </ref>. | + | ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' ArfA (Rv0899) is a membrane protein encoded by an ammonia release facilator operon that is necessary for rapid ammonia secretion, pH neutralization and adaptation to acidic environments in vitro. Its C-terminal domain (C domain) shares significant sequence homology with the OmpA-like family of peptidoglycan-binding domains, suggesting that its physiological function in acid stress protection may be related to its interaction with the mycobacterial cell wall. It exhibits pH-dependent conformational dynamics<scene name='61/612805/Hydrophobic_region_of_d236a/1'> Hydrophobic region of mutant ArfA-c (D236A)</scene> <scene name='61/612805/The_peptidoglycan_binding_site/1'>The peptidoglycan binding site</scene> (with significant heterogeneity at neutral pH and a more ordered structure at acidic pH), which could be related to its acid stress response. The C domain associates tightly with polymeric peptidoglycan isolated from ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. Its functions in acid stress protection and <scene name='61/612805/The_peptidoglycan_binding_site/1'>peptidoglycan binding</scene> suggest a link between the acid stress response and the physicochemical properties of the mycobacterial cell wall <scene name='61/612805/Hydrophobic_region_of_d236a/3'>Pept+H</scene> .<ref>PMID: 22206986 </ref>. |
[[Image:Pep-gl.jpg|210px]] | [[Image:Pep-gl.jpg|210px]] | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 15 January 2015
| |||||||||||