Mycobacterium tuberculosis ArfA Rv0899
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
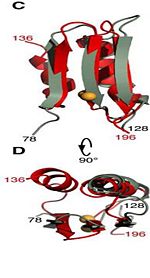
| - | The C domain <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/1'>(residues 201-326)</scene> has homology to the OmpA-C-like superfamily of periplasmic peptidoglycan-binding sequences, found in several types of bacterial membrane proteins.The C domain of wild-type ArfA <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/3'></scene> <scene name='61/612805/C_domain_1/1'> folds </scene> into four β-strands and four α-helices.Three parallel (β1, β2, β3) and one antiparallel (β4) β-strands form a four-stranded β-sheet (β1–β4-β2–β3) that packs against three α-helices (α1, α2, α3), while a fourth helix (α4) extends from the N-terminus of β4. A disulfide bond between C208 and C250 connects the N-terminus of α1 to the C-terminus of α2 and stabilizes the structure. | + | The C domain <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/1'>(residues 201-326)</scene> has homology to the OmpA-C-like superfamily of periplasmic peptidoglycan-binding sequences, found in several types of bacterial membrane proteins.The C domain of wild-type ArfA <scene name='61/612805/C_domain/3'></scene> <scene name='61/612805/C_domain_1/1'> folds </scene> into four β-strands and four α-helices.Three parallel (β1, β2, β3) and one antiparallel (β4) β-strands form a four-stranded β-sheet (β1–β4-β2–β3) that packs against three α-helices (α1, α2, α3), while a fourth helix (α4) extends from the N-terminus of β4. A disulfide bond between C208 and C250 connects the N-terminus of α1 to the C-terminus of α2 and <scene name='61/612805/C_domain_stabilization/1'>hydrophobic bonds between side chains and hydrogen </scene> stabilizes the structure. |
==Putative functions== | ==Putative functions== | ||
| - | 1. Acquisition of Zn(2+): | + | 1. Acquisition of Zn(2+) ions: |
Using [[NMR]] chemical shift perturbation and isothermal calorimetric titration assays, Rv0899 was able to interact with <scene name='61/612805/Binding-site_for_zn/1'>Zn(2+) ions</scene>, which may indicate a role for Rv0899 in the process of Zn(2+) acquisition. | Using [[NMR]] chemical shift perturbation and isothermal calorimetric titration assays, Rv0899 was able to interact with <scene name='61/612805/Binding-site_for_zn/1'>Zn(2+) ions</scene>, which may indicate a role for Rv0899 in the process of Zn(2+) acquisition. | ||
<ref>PMID: 22108166 </ref> | <ref>PMID: 22108166 </ref> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
<scene name='61/612805/Positive-negativ_aa/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | <scene name='61/612805/Positive-negativ_aa/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='61/612805/C_domain_stabilization/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
Revision as of 16:36, 21 January 2015
| |||||||||||