We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
RiAFP
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Image:Fig4_D.jpg|frame|alt=Puzzle globe|Fig. 3. Ice-binding surface]] | [[Image:Fig4_D.jpg|frame|alt=Puzzle globe|Fig. 3. Ice-binding surface]] | ||
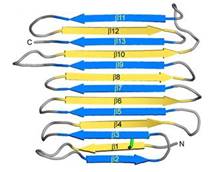
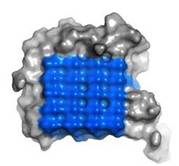
IBS of RiAFP contains five expanded <scene name='60/607864/Ibs/1'>TXTXTXT motifs</scene> within the top β–sheet. These motifs are remarkably regular, allowing any rows/columns of TXTXTXT motifs to be exactly superposed onto any other rows/columns. Threonine residuses are crucial for maintaining antifreeze activity. It was found in other AFPs that mutations of the Thrs within these motifs decrease the thermal hysteresis. The Thr hydroxyls define a large flat IBS of 420 Å2, which correlates with high antifreeze activity (see Figure 3). | IBS of RiAFP contains five expanded <scene name='60/607864/Ibs/1'>TXTXTXT motifs</scene> within the top β–sheet. These motifs are remarkably regular, allowing any rows/columns of TXTXTXT motifs to be exactly superposed onto any other rows/columns. Threonine residuses are crucial for maintaining antifreeze activity. It was found in other AFPs that mutations of the Thrs within these motifs decrease the thermal hysteresis. The Thr hydroxyls define a large flat IBS of 420 Å2, which correlates with high antifreeze activity (see Figure 3). | ||
| - | |||
== Molecular Basis for Ice Binding == | == Molecular Basis for Ice Binding == | ||
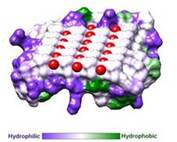
| - | [[Image:Fig2_C.jpg|frame|alt=Puzzle globe|Fig. 2. Hydrophobicity of RiAFP]]IBS is less hydrophilic than the other β–sheet, which is consistent with its role of interacting with the ice(see Figure 2). | + | [[Image:Fig2_C.jpg|frame|alt=Puzzle globe|Fig. 2. Hydrophobicity of RiAFP]]IBS is less hydrophilic than the other β–sheet, which is consistent with its role of interacting with the ice (see Figure 2). Adsorption of the AFP ice-binding surface to ice is facilitated by the flatness of the IBS of the AFP.The Sc (shape complementarity) values between RiAFP and ice interfaces range from 0.75-0.78, where 1.0 indicates perfect match. For comparison, antigen-antibody complexes usually have their Sc values in the range of 0.64–0.68. |
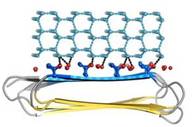
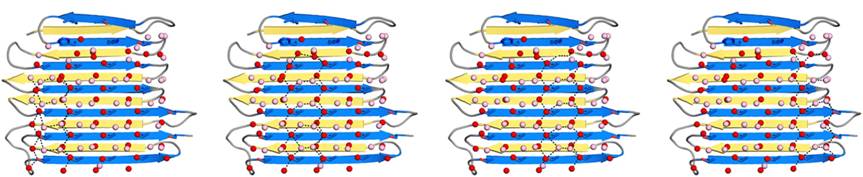
| - | Adsorption of the AFP ice-binding surface to ice is facilitated by the flatness of the IBS of the AFP.The Sc (shape complementarity) values between RiAFP and ice interfaces range from 0.75-0.78, where 1.0 indicates perfect match. For comparison, antigen-antibody complexes usually have their Sc values in the range of 0.64–0.68 . | + | [[Image:Fig5_A.jpg|frame|alt=Puzzle globe|Fig. 4. Docking of RiAFP to the primery prism plane of a hexagonal ice lattice]]Thr hydroxyls bind 3 ranks of 6 water molecules with equivalent spacing between the 4 ranks of Thr side chains. These water molecules are bound tightly, they have lost both translational and rotational freedom and resemble those in an ice lattice. The waters observed in the simulation appear to be organized in an ice-like formation, with close matches to the primary prism and basal planes of ice. IBS is responsible for ordering an ice-like array of anchored “clathrate” water molecules to promote adsorption to ice.(see Figure 4). |
| + | |||
<scene name='60/607864/Isosurface/3'>Ice binding surface</scene> | <scene name='60/607864/Isosurface/3'>Ice binding surface</scene> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 23:43, 24 January 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of antifreeze protein
References
- ↑ Jia Z, Davies PL. Antifreeze proteins: an unusual receptor-ligand interaction. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002 Feb;27(2):101-6. PMID:11852248
- ↑ Chantelle J. Capicciotti, Malay Doshi and Robert N. Ben (2013). Ice Recrystallization Inhibitors: From Biological Antifreezes to Small Molecules, Recent Developments in the Study of Recrystallization, Prof. Peter Wilson (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-0962-4, InTech doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/54992
- ↑ Drori R, Celik Y, Davies PL, Braslavsky I. Ice-binding proteins that accumulate on different ice crystal planes produce distinct thermal hysteresis dynamics. J R Soc Interface. 2014 Sep 6;11(98):20140526. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0526. PMID:25008081 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2014.0526
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82234-2
- ↑ Hakim A, Nguyen JB, Basu K, Zhu DF, Thakral D, Davies PL, Isaacs FJ, Modis Y, Meng W. Crystal structure of an insect antifreeze protein and its implications for ice binding. J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 26;288(17):12295-304. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.450973. Epub, 2013 Mar 12. PMID:23486477 doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.450973