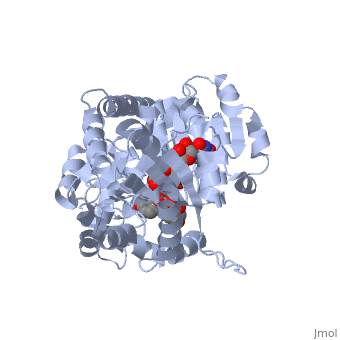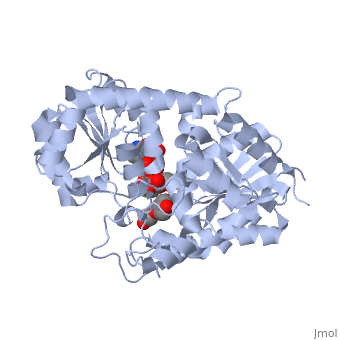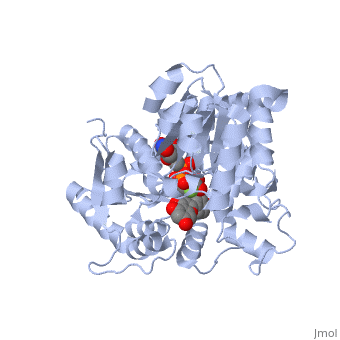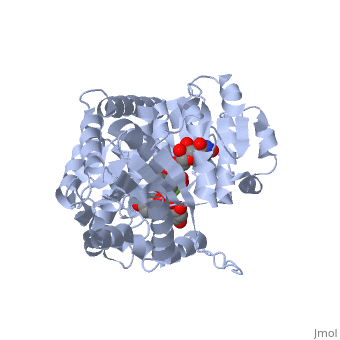
Vitis vinifera Flavonoid 3-O-Glucosyltransferase (Vv3GT) is involved in the modification of grape anthocyanins and thus could affect their color stability. The color plays a significant role in the in agricultural produce, such as table grapes and wine.
Introduction
Vv3GT belongs to Glycosyltransferases (GTs), a large family of enzymes involved in the transfer of sugar residues from a sugar donor to various substrates. Glycosylation of metabolites in plants is usually catalyzed by glycosyltransferases (GTs) belonging to the GT1 sub-family (as classified by the CAZy database [1], which use UDP-activated sugars as the major donor molecule and are thus referred to as UGTs.
Relevance
Structural highlights
Despite low primary sequence similarity, the secondary and tertiary structures of GTs are highly conserved. [1]
GT-B
Plant glycosyltransferases assume one of two folds, GT-A or GT-B. Vv3GT is a GT-B enzyme. GT-B enzymes consists of two β/α/β Rossmann-like domains. The two domains are associated and face each other with the active-site lying between them. These domains are associated with the donor and acceptor substrate binding sites.
The , linked by a flexible loop and α-helix with a hinge region. The linker could be important for sugar donor binding. This linker region holds the UDP-sugar donor next to the C-terminal PSPG motif. The C-terminal domain is highly conserved and binds the UDP sugar donor (e. g. UDP-Glc). On the other hand, the N-terminal domain is not conserved it binds the substrate and provides catalytically active amino acids.
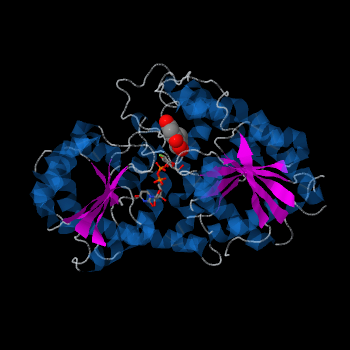
Vv3GT with the two Rossmann-like domains
PSPG
The plant UGTs are characterized by sharing a highly conserved 44 amino acid motif referred to as the
motif (Plant Secondary Product Glycosyltransferase motif). Amino acids of the PSPG motif provide most of the interactions with the sugar donor molecule.
Three conserved motifs involved in sugar binding are present in Vv3GT. The first, a motif (Thr 141; Ala 142) involved in sugar binding. The second, a (Trp 354; Asn 355; Ser 356) motif residues are involved in binding UDP phosphates. The third, motif residues also involved in sugar binding (Asp 374; Gln 375). The WNS and D/EQ motifs are part of the highly conserved PSPG region.
Quiz