Binding site of AChR
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
The overly of the first 12 residues of the 13-mer HAP on AChBP residues 182-193 shows that the HAP has almost the same conformation with the loop 182-193 of AChBP(Fig 1), in the figure the red one is 13-mer little peptide and the blue one is loop 182-193 of AChBP. | The overly of the first 12 residues of the 13-mer HAP on AChBP residues 182-193 shows that the HAP has almost the same conformation with the loop 182-193 of AChBP(Fig 1), in the figure the red one is 13-mer little peptide and the blue one is loop 182-193 of AChBP. | ||
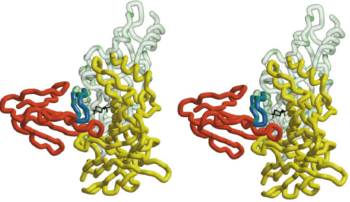
| - | The figure 2 shows that the <scene name='68/688431/Btx_complex_with_two_subunits/1'>superposition of the HAP on loop 182-193</scene> the α-BTX to fit exquisitely into the interface of two subunits of the pentameric AChBP. it shows the stereo view of the combined model of α-BTX-HAP(Red) and AChBP structure with subunit A in green and subunit B in yellow showing the insertion of loop 2 of the toxin into the interface of the to subunits. In order to identify more clearly that the little 13-mer peptide is actually have almost the same structure with the 182-193 loop with AChBP, we compare two structures: <scene name='68/688431/Btx_complex_with_two_subunits/5'>removing</scene> the HAP form the structure and <scene name='68/688431/Btx_complex_with_two_subunits/6'> | + | The figure 2 shows that the <scene name='68/688431/Btx_complex_with_two_subunits/1'>superposition of the HAP on loop 182-193</scene> the α-BTX to fit exquisitely into the interface of two subunits of the pentameric AChBP. it shows the stereo view of the combined model of α-BTX-HAP(Red) and AChBP structure with subunit A in green and subunit B in yellow showing the insertion of loop 2 of the toxin into the interface of the to subunits. The blue little peptide is HAP, which superimpose on the loop 182-193 of AChBP. In order to identify more clearly that the little 13-mer peptide is actually have almost the same structure with the 182-193 loop with AChBP, we compare two structures: <scene name='68/688431/Btx_complex_with_two_subunits/5'>removing</scene> the HAP form the structure and <scene name='68/688431/Btx_complex_with_two_subunits/6'> |
superposition</scene> the HAP on the AChBP. | superposition</scene> the HAP on the AChBP. | ||
| - | So that the little peptide has almost the same structure with the loop of AChBP binding to α-BTX, which means it can be used as a model to study the binding site of AChR. | + | So that the little peptide(HAP) has almost the same structure with the loop of AChBP binding to α-BTX, which means it can be used as a model to study the binding site of AChR. |
It is noteworthy that the positively charged <scene name='68/688431/Hepes_black/2'>HEPES</scene> molecule shows the location of the acetylcholine binding site and the blockage of passage to this site caused by the toxin. So the ACh binding site in AChBP is assigned by the localization of HEPES. | It is noteworthy that the positively charged <scene name='68/688431/Hepes_black/2'>HEPES</scene> molecule shows the location of the acetylcholine binding site and the blockage of passage to this site caused by the toxin. So the ACh binding site in AChBP is assigned by the localization of HEPES. | ||
Revision as of 09:29, 2 February 2015
| |||||||||||
Quiz
References
- ↑ Purves, Dale, George J. Augustine, David Fitzpatrick, William C. Hall, Anthony-Samuel LaMantia, James O. McNamara, and Leonard E. White (2008). Neuroscience. 4th ed. Sinauer Associates. pp. 156–7. ISBN 978-0-87893-697-7.
- ↑ Gonzalez-Gutierrez G, Cuello LG, Nair SK, Grosman C. Gating of the proton-gated ion channel from Gloeobacter violaceus at pH 4 as revealed by X-ray crystallography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Oct 28. PMID:24167270 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1313156110
- ↑ Bocquet N, Nury H, Baaden M, Le Poupon C, Changeux JP, Delarue M, Corringer PJ. X-ray structure of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel in an apparently open conformation. Nature. 2009 Jan 1;457(7225):111-4. Epub 2008 Nov 5. PMID:18987633 doi:10.1038/nature07462
- ↑ Harel M, Kasher R, Nicolas A, Guss JM, Balass M, Fridkin M, Smit AB, Brejc K, Sixma TK, Katchalski-Katzir E, Sussman JL, Fuchs S. The binding site of acetylcholine receptor as visualized in the X-Ray structure of a complex between alpha-bungarotoxin and a mimotope peptide. Neuron. 2001 Oct 25;32(2):265-75. PMID:11683996
- ↑ Brejc K, van Dijk WJ, Klaassen RV, Schuurmans M, van Der Oost J, Smit AB, Sixma TK. Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature. 2001 May 17;411(6835):269-76. PMID:11357122 doi:10.1038/35077011
- ↑ Harel M, Kasher R, Nicolas A, Guss JM, Balass M, Fridkin M, Smit AB, Brejc K, Sixma TK, Katchalski-Katzir E, Sussman JL, Fuchs S. The binding site of acetylcholine receptor as visualized in the X-Ray structure of a complex between alpha-bungarotoxin and a mimotope peptide. Neuron. 2001 Oct 25;32(2):265-75. PMID:11683996
- ↑ Brejc K, van Dijk WJ, Klaassen RV, Schuurmans M, van Der Oost J, Smit AB, Sixma TK. Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature. 2001 May 17;411(6835):269-76. PMID:11357122 doi:10.1038/35077011
- ↑ Brejc K, van Dijk WJ, Klaassen RV, Schuurmans M, van Der Oost J, Smit AB, Sixma TK. Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature. 2001 May 17;411(6835):269-76. PMID:11357122 doi:10.1038/35077011
- ↑ Harel M, Kasher R, Nicolas A, Guss JM, Balass M, Fridkin M, Smit AB, Brejc K, Sixma TK, Katchalski-Katzir E, Sussman JL, Fuchs S. The binding site of acetylcholine receptor as visualized in the X-Ray structure of a complex between alpha-bungarotoxin and a mimotope peptide. Neuron. 2001 Oct 25;32(2):265-75. PMID:11683996
- ↑ Harel M, Kasher R, Nicolas A, Guss JM, Balass M, Fridkin M, Smit AB, Brejc K, Sixma TK, Katchalski-Katzir E, Sussman JL, Fuchs S. The binding site of acetylcholine receptor as visualized in the X-Ray structure of a complex between alpha-bungarotoxin and a mimotope peptide. Neuron. 2001 Oct 25;32(2):265-75. PMID:11683996
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicotinic_acetylcholine_receptor
- ↑ Samson AO, Levitt M. Inhibition mechanism of the acetylcholine receptor by alpha-neurotoxins as revealed by normal-mode dynamics. Biochemistry. 2008 Apr 1;47(13):4065-70. doi: 10.1021/bi702272j. Epub 2008 Mar 8. PMID:18327915 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi702272j
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ma Zhuang, Zicheng Ye, Angel Herraez, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel