This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Ubc9
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | - | |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | + | - | |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | + | - | |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | - | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
1. Reverter, D., & Lima, C. D. (2005). Insights into E3 ligase activity revealed by a SUMO-RanGAP1-Ubc9-Nup358 complex. Nature, 435(June), 687–692. doi:10.1038/nature03588 | 1. Reverter, D., & Lima, C. D. (2005). Insights into E3 ligase activity revealed by a SUMO-RanGAP1-Ubc9-Nup358 complex. Nature, 435(June), 687–692. doi:10.1038/nature03588 | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 05:09, 22 February 2015
|
Contents |
Structure
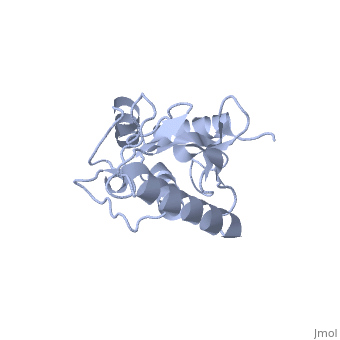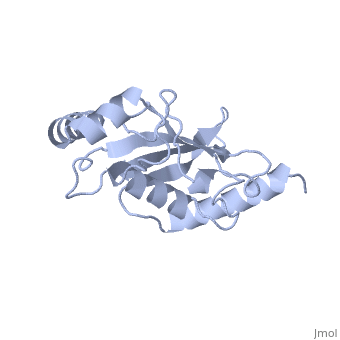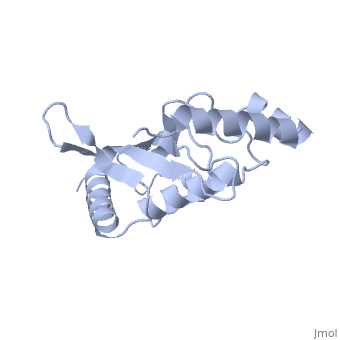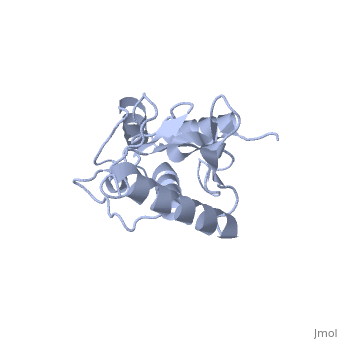
Ubc9 exhibits a single domain structure consisting of both alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets. C93 has been identified as the active residue and is located on a non-secondary structured loop of amino acids (78-108) between beta sheet four and alpha helix two ^1^ .
Function
-
Disease
-
Relevance
-
Structural highlights
-
References
1. Reverter, D., & Lima, C. D. (2005). Insights into E3 ligase activity revealed by a SUMO-RanGAP1-Ubc9-Nup358 complex. Nature, 435(June), 687–692. doi:10.1038/nature03588