This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
2qjm
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:2qjm.gif|left|200px]] | + | [[Image:2qjm.gif|left|200px]] |
| - | + | ||
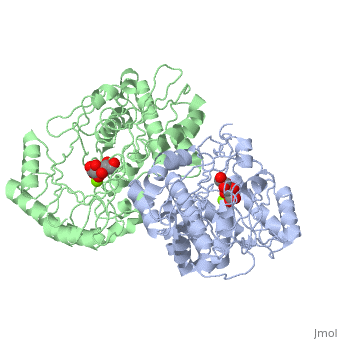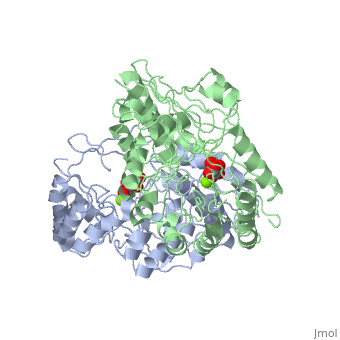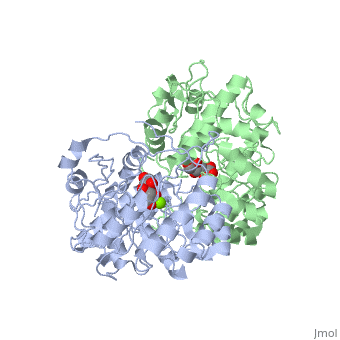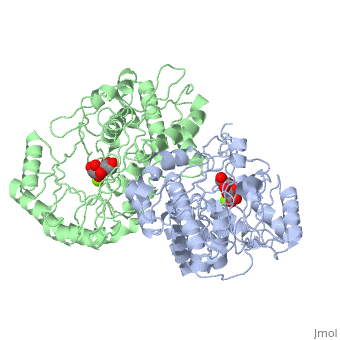
| - | '''Crystal structure of the K271E mutant of Mannonate dehydratase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans complexed with Mg and D-mannonate''' | + | {{Structure |
| + | |PDB= 2qjm |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>2qjm</scene>, resolution 2.20Å | ||
| + | |SITE= | ||
| + | |LIGAND= <scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene> and <scene name='pdbligand=CS2:D-MANNONIC ACID'>CS2</scene> | ||
| + | |ACTIVITY= | ||
| + | |GENE= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Crystal structure of the K271E mutant of Mannonate dehydratase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans complexed with Mg and D-mannonate''' | ||
| + | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 16: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 2QJM is a [ | + | 2QJM is a [[Single protein]] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Novosphingobium_aromaticivorans Novosphingobium aromaticivorans]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2QJM OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| - | Evolution of enzymatic activities in the enolase superfamily: D-Mannonate dehydratase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans., Rakus JF, Fedorov AA, Fedorov EV, Glasner ME, Vick JE, Babbitt PC, Almo SC, Gerlt JA, Biochemistry. 2007 Nov 13;46(45):12896-908. Epub 2007 Oct 18. PMID:[http:// | + | Evolution of enzymatic activities in the enolase superfamily: D-Mannonate dehydratase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans., Rakus JF, Fedorov AA, Fedorov EV, Glasner ME, Vick JE, Babbitt PC, Almo SC, Gerlt JA, Biochemistry. 2007 Nov 13;46(45):12896-908. Epub 2007 Oct 18. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17944491 17944491] |
[[Category: Novosphingobium aromaticivorans]] | [[Category: Novosphingobium aromaticivorans]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category: lyase]] | [[Category: lyase]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Mar 20 18:26:30 2008'' |
Revision as of 16:26, 20 March 2008
| |||||||
| , resolution 2.20Å | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | and | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
Crystal structure of the K271E mutant of Mannonate dehydratase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans complexed with Mg and D-mannonate
Overview
The d-mannonate dehydratase (ManD) function was assigned to a group of orthologous proteins in the mechanistically diverse enolase superfamily by screening a library of acid sugars. Structures of the wild type ManD from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans were determined at pH 7.5 in the presence of Mg2+ and also in the presence of Mg2+ and the 2-keto-3-keto-d-gluconate dehydration product; the structure of the catalytically active K271E mutant was determined at pH 5.5 in the presence of the d-mannonate substrate. As previously observed in the structures of other members of the enolase superfamily, ManD contains two domains, an N-terminal alpha+beta capping domain and a (beta/alpha)7beta-barrel domain. The barrel domain contains the ligands for the essential Mg2+, Asp 210, Glu 236, and Glu 262, at the ends of the third, fourth, and fifth beta-strands of the barrel domain, respectively. However, the barrel domain lacks both the Lys acid/base catalyst at the end of the second beta-strand and the His-Asp dyad acid/base catalyst at the ends of the seventh and sixth beta-strands, respectively, that are found in many members of the superfamily. Instead, a hydrogen-bonded dyad of Tyr 159 in a loop following the second beta-strand and Arg 147 at the end of the second beta-strand are positioned to initiate the reaction by abstraction of the 2-proton. Both Tyr 159 and His 212, at the end of the third beta-strand, are positioned to facilitate both syn-dehydration and ketonization of the resulting enol intermediate to yield the 2-keto-3-keto-d-gluconate product with the observed retention of configuration. The identities and locations of these acid/base catalysts as well as of cationic amino acid residues that stabilize the enolate anion intermediate define a new structural strategy for catalysis (subgroup) in the mechanistically diverse enolase superfamily. With these differences, we provide additional evidence that the ligands for the essential Mg2+ are the only conserved residues in the enolase superfamily, establishing the primary functional importance of the Mg2+-assisted strategy for stabilizing the enolate anion intermediate.
About this Structure
2QJM is a Single protein structure of sequence from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Evolution of enzymatic activities in the enolase superfamily: D-Mannonate dehydratase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans., Rakus JF, Fedorov AA, Fedorov EV, Glasner ME, Vick JE, Babbitt PC, Almo SC, Gerlt JA, Biochemistry. 2007 Nov 13;46(45):12896-908. Epub 2007 Oct 18. PMID:17944491
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Mar 20 18:26:30 2008