We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 996
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
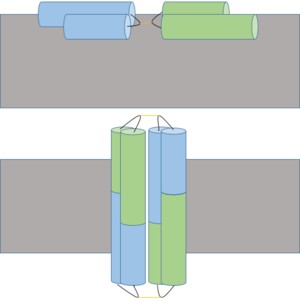
| - | [[Image:Possible_Ectatomin_Mechanism_3.png|300px|left|thumb| A proposed | + | [[Image:Possible_Ectatomin_Mechanism_3.png|300px|left|thumb| A proposed insertion (above) and dimerization mechanism to form cation channel (below) of Ectatomin in the cell membrane (gray). Insertion occurs when the α and β subunits open at the hairpin hinge region (shown in black with yellow disulfide bonds), exposing internal hydrophobic residues which interact with hydrophobic lipid tails of the cell membrane. Pore formation occurs after dimerization, allowing ions to freely cross the membrane.]] |
Ectatomin has several proposed mechanisms of action. The primary proposed mechanism involves the formation of a nonselective cation channel. In this mechanism, the α and β subunits open up, exposing the internal hydrophobic residues. The protein flattens while remaining attached at the hairpin hinge region. The now exposed hydrophobic residues nonselectively insert into plasma membranes. The inserted protein dimerizes, eventually forming a nonselective cation channel. | Ectatomin has several proposed mechanisms of action. The primary proposed mechanism involves the formation of a nonselective cation channel. In this mechanism, the α and β subunits open up, exposing the internal hydrophobic residues. The protein flattens while remaining attached at the hairpin hinge region. The now exposed hydrophobic residues nonselectively insert into plasma membranes. The inserted protein dimerizes, eventually forming a nonselective cation channel. | ||
Revision as of 00:08, 11 March 2015
Ectatomin (1eci)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Arseniev AS, Pluzhnikov KA, Nolde DE, Sobol AG, Torgov MYu, Sukhanov SV, Grishin EV. Toxic principle of selva ant venom is a pore-forming protein transformer. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 27;347(2-3):112-6. PMID:8033986
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Pluzhnikov K, Nosyreva E, Shevchenko L, Kokoz Y, Schmalz D, Hucho F, Grishin E. Analysis of ectatomin action on cell membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1999 Jun;262(2):501-6. PMID:10336635
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Nolde DE, Sobol AG, Pluzhnikov KA, Grishin EV, Arseniev AS. Three-dimensional structure of ectatomin from Ectatomma tuberculatum ant venom. J Biomol NMR. 1995 Jan;5(1):1-13. PMID:7881269
- ↑ Touchard A, Labriere N, Roux O, Petitclerc F, Orivel J, Escoubas P, Koh JM, Nicholson GM, Dejean A. Venom toxicity and composition in three Pseudomyrmex ant species having different nesting modes. Toxicon. 2014 Sep;88:67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.05.022. Epub 2014 Jun 11. PMID:24929139 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.05.022