Introduction
This scene is of the within the Kappa Opioid Receptor by Group 3.
-"Kappa-Opioid receptors mediate the regulation of pain, respiratory drive, mood"
-"structure reveals important features of the ligand-binding pocket that contribute to the high affinity and subtype selectivity of JDTic for the human kappa-OR"
-consequences of stress as well as depression/anxiety
-hallucinogenic effects
-talk about mu and kappa OR
-intro to kappa-OR subtype selectivity
Overall Structure
Copy and paste the following line where you want the scene link to appear (scroll down if needed) and edit the TextToBeDisplayed:
The Kappa opioid receptor is a dimmer composed of two sub units. This can be seen here. The extracellular side is home to the proteins primary . These two units will span the length for the cell membrane to form the basis of the receptor molecule. The each subunit is attached to the other by the I, II and VIII alpha helices. This can be seen where helices I (shown in the light blue) and helices VIII (show in the dark blue). This area will make up the basis for the intermembrane surface area. A distinguishing feature that separates the Kappa receptor from other receptors, is the large beta Hairpin,, located near the main active site of the protein. It is believed that its function is to cap the active site of the receptor. Although in general, this protein is primarily composed of alpha helices, not beta sheets (Compare to here). This evidence reinforces the idea that this protein is a transmembrane protein rather than one found inside the cytosol. In general transmembrane protein are composed almost entirely of alpha helices (or beta sheets arranged in special fashion called a beta barrel), in order to have maximum stability inside the membrane. Another interesting feature of the Kappa opioid receptor is the formed by Cys131 and Cys210 which is conserved across all opioid receptors.
Binding Interactions
Active Site of kappa Opioid Receptors
The human kappa opioid receptor (hKOR) ligand binding pocket displays a unique combination of key characteristics both shared with and distinct from those in the chemokine and aminergic receptor families [2].
Common Ligands of Opioid Receptors
The majority of endogenous opioid peptides have a defined preference to specific subtypes, for example, endorphins act via DORs and MORs, whereas dynorphins preferentially activate KORs. Several KOR selective partial agonists and antagonists have been developed as potential antidepressants, anxiolytics, and anti-addiction medications, whereas a widely abused, naturally occurring hallucinogen Salvinorin A (SalA) was also found to be a highly selective KOR agonist. The elucidation of a large binding cavity with a multitude of potential anchoring points begins to explain both the extreme structural diversity of hKOR drugs and differences in their receptor interaction modes, as supported by differential effects of various site-directed mutations on the binding properties of chemically diverse ligands [2] [5] [7].
[See Reference 6 for list of ligands.]
Agonists Salvinorin A - Mechanisms, Structure, and Effects
Salvinorin A (SalA), a naturally occurring diterpene from the widely abused hallucinogenic plant Salvia divinorum represents an exceedingly potent and selective KOR agonist. It has been found that the 2-acetoxy moiety on SalA interacts with Cys315. SalA also displayed hydrogen bonds with binding site residues Gln115, His291, and Leu212, but it has more flexibility than JDTic [2] [4].
[See reference 7 for more information.]
Antagonists JDTic - Mechanisms, Structure, and Effects
JDTic, has exceptionally high affinity (Ki = 0.32 nM), potency, long duration of action and amore than 1000 fold selectivity for hKOR as compared to other Opioid receptor (OR) subtypes. The protonated amines in both piperidine and isoquinoline moieties of the ligand form salt bridges to the Asp 138 3.32 side chain. The piperidine amine is essential for binding. The isoquinoline nitrogen can be replaced by carbon, oxygen or sulfur atoms with only ~10 to 50 fold reduction in affinity. A “V” shaped conformation was found in the crystal structure of JDTic by itself and which showed its amino groups coordinating a water molecule. The anchoring-type interaction of two amino groups with Asp138 likely fixes the ligand in this characteristic V-shape. The distal hydroxyl groups on both the piperidine and isoquinoline moieties of JDTic when removed result in a 100 fold reduction of affinity. JDTic interacts with four residues of the binding pocket that differ in other closely related ORs, which are thought to contribute to the subtype selectivity of JDTic and other KOR-selective ligands [2] [4].
Val 108, Val 118, Ile 294 and Tyr 312
The isopropyl group from JDTic reaches deep in the orthosteric pocket to form a hydrophobic interaction with a conserved Trp 287 side chain, possibly playing a critical role in the pharmacological properties of this ligand. Analysis of the ligand-receptor interactions has revealed important molecular details responsible for the exceptionally high affinity and subtype selectivity of JDTic-a small molecule antagonist with a broad therapeutic potential [2] [5].
[See reference 2 for more information.]
Figures
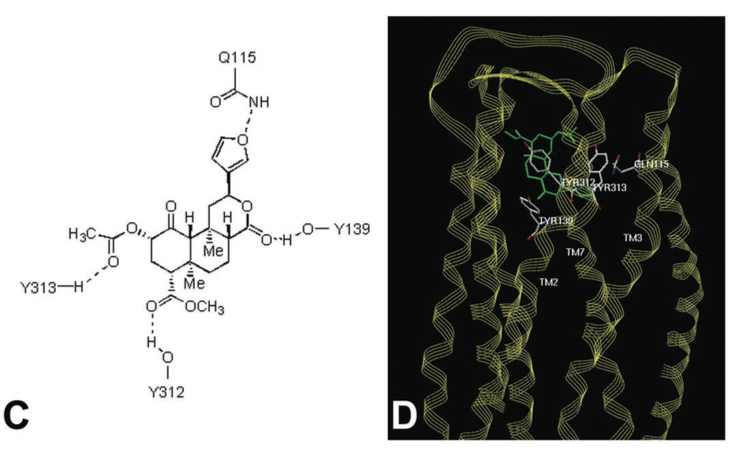
Below Figure C shows potential residues on the KOR identified by molecular modeling, which might interact with Salvinorin A, and D shows a model of Salvinorin A’s interactions with the KOR [From Reference 7].
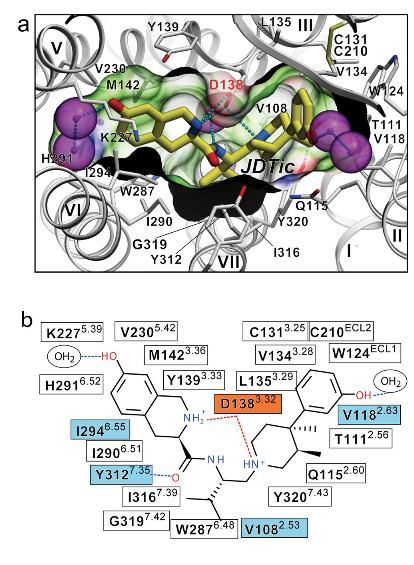
Conformation of the binding pocket with JDTic shown by sticks with yellow carbons. The protein is displayed in cartoon representation looking down from the extracellular side, with the 22 contact residues within 4.5 A ̊ from the ligand shown by white sticks. The pocket surface is shown as a semitransparent surface coloured according to binding properties (green: hydrophobic; blue: hydrogen-bond donor; red: hydrogen-bond acceptor). Salt bridges and hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines. Structured water molecules are shown as large magenta spheres. b, Diagram of ligand interactions in the binding pocket side chains at 4.5 A ̊ cut-off. Salt bridges are shown in red and direct hydrogen bonds in blue dashed lines. Ballesteros–Weinstein numbering is shown as superscript. Residues that vary among the m-OR, d-OR and k-OR subtypes are highlighted in cyan, and residue Asp 1383.32 implicated in k-OR-ligand binding by mutagenesis data, is highlighted orange. [From Reference 2].
Additional Features
The k-opioid receptor is a protein, with inter-membrane alpha helices displayed in red.

A hydropathy plot for this receptor reinforces this fact, with a large span of the molecule shown again as trans-membrane alpha helices.
Based on the Ramachandran plot for the general case showing the standard phi and psi angle, it can be inferred that the majority of the secondary structure is composed , with the alpha helices shown in purple and the beta sheets shown in yellow.
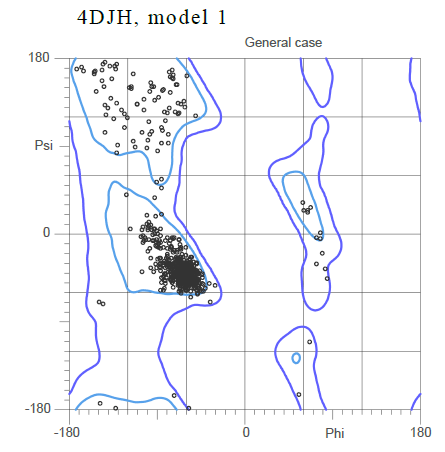
The large cluster of dots shown close to the origin of the plot corresponds to small angles that imply an alpha helix.
Quiz Question 1
Why might the , highlighted in blue, be located here in the protein? (Explain how its location and other properties of the protein maintain binding specificity.) What basic conformational changes may the protein undergo while binding to ligands?
Quiz Question 2
What properties and functional groups would a substrate binding to the active site of the Kappa-opioid receptor probably possess? Explain your reasoning.
See Also
Credits
Introduction - Patrick Harney
Overall Structure - Matthew Long
Drug Binding Site - Brandon Kittredge
Additional Features - Jacob Kellet
Quiz Question 1 - Leah Caffrey
Quiz Question 2 - Bridget Kilkenny
References
1. Chavkin C., The Therapeutic Potential of κ-Opioids for Treatment of Pain and Addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:369–370.
2. Wu H., Wacker D., Mileni M., Structure of the human kappa opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature. 2012;485:327-332. PMID:22437504
3. Martinez-Mayorga K., Byler K., Yongye A., et al. Ligand/kappa-opioid Receptor Ineractions: Insights from the X-Ray Crystal Structure. Eur J. Med. Chem. 2013; 66: 114-121.
4. Leonis, Georgios, Aggelos Avramopoulos, Ramin Ekhteiari Salmas, Serdar Durdagi, Mine Yurtsever, and Manthos G. Papadopoulos. "Elucidation of Conformational States, Dynamics, and Mechanism of Binding in Human κ‐Opioid Receptor Complexes." Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (n.d.): n. pag. ACS. Web.
5. Aldrich, Jane V., and Jay P. Mclaughlin. "Peptide Kappa Opioid Receptor Ligands: Potential for Drug Development." The AAPS Journal 11.2 (2009): 312-22. Web.
6.Henriksen, G., and F. Willoch. "Imaging of Opioid Receptors in the Central Nervous System." Brain 131.5 (2007): 1171-196. Web.
7.Roth, B. L. "Salvinorin A: A Potent Naturally Occurring Nonnitrogenous Kappa Opioid Selective Agonist." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 99.18 (2002): 11934-1939. Web.



