We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1066
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
This is the <scene name='69/698726/Overall_structure_cartoon/1'>overall structure of FadD13</scene> | This is the <scene name='69/698726/Overall_structure_cartoon/1'>overall structure of FadD13</scene> | ||
| - | FadD13 is composed of 503 amino acid residues divided into three main regions: The <scene name='69/694233/Domains/1'>N-terminal domain</scene> (residues 1-395) and <scene name='69/694233/C-terminal_domain/1'>C-terminal domain</scene> (residues 402-503) which are connected via a flexible linker (residues 396-401).<ref name="Our Paper"/> | + | FadD13 is composed of 503 amino acid residues divided into three main regions: The <scene name='69/694233/Domains/1'>N-terminal domain</scene> (residues 1-395) and <scene name='69/694233/C-terminal_domain/1'>C-terminal domain</scene> (residues 402-503) which are connected via a flexible <scene name='69/694232/Linker_section/2'>linker</scene> (residues 396-401).<ref name="Our Paper"/> |
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
== Active Site == | == Active Site == | ||
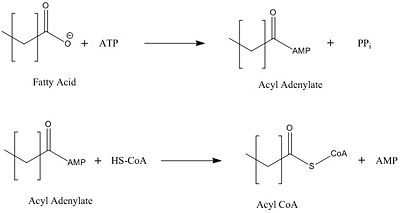
| - | The active site on FadD13 is composed of two conserved regions, one of which serves as the binding site for ATP and the other for CoA. The | + | The active site on FadD13 is composed of two conserved regions, one of which serves as the binding site for ATP and the other for CoA. The adenine of ATP is bound to a group of <scene name='69/694232/Adenine_binding_group/2'>six amino acids (300-305)</scene> that is structurally identically to other acyl-CoA synthetases (Citation for original paper). |
= Disease = | = Disease = | ||
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' is the causative agent involved in the disease '''tuberculosis'''. | ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' is the causative agent involved in the disease '''tuberculosis'''. | ||
Revision as of 18:38, 3 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis very-long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Andersson CS, Lundgren CA, Magnusdottir A, Ge C, Wieslander A, Molina DM, Hogbom M. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: Structural Basis for Housing Lipid Substrates Longer than the Enzyme. Structure. 2012 May 2. PMID:22560731 doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.03.012
- ↑ Jatana N, Jangid S, Khare G, Tyagi AK, Latha N. Molecular modeling studies of Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (FadD13) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis--a potential target for the development of antitubercular drugs. J Mol Model. 2011 Feb;17(2):301-13. doi: 10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3. Epub 2010 May, 8. PMID:20454815 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3
Similar Proteopedia Pages
Thioesterase Do we have anything like this?
External Resources
Tuberculosis Wikipedia page
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Wikipedia page
Coenzyme A Wikipedia page
Mycolic Acid Wikipedia page