Sandbox Reserved 431
From Proteopedia
(→Overall Structure) |
(→Overall Structure) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Overall Structure== | ==Overall Structure== | ||
| - | <Structure load='4c9x' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Basic Structure of MTH1/S-crizotinib' scene='48/483888/Basic/1' /> | + | <Structure load='4c9x' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Basic Structure of MTH1/S-crizotinib 4c9x' scene='48/483888/Basic/1' /> |
| - | <br> MTH1/S-crizotinib is a member of a protein family of phosphorohydrolases known as the Nudix family (2). Proteins in the Nudix family are used to hydrolyze nucleoside phosphates; they also act as catalysts for the same reaction. Proteins in the Nudix family consist of two unique parts: <scene name='48/483888/Different_backbone_components/1'>a Nudix fold, and a Nudix motif</scene> (2). The Nudix fold is the secondary structure, or backbone, of the protein; the backbone has an α/β/α structure, meaning that the backbone consists of mixed beta sheet | + | <br> MTH1/S-crizotinib is a member of a protein family of phosphorohydrolases known as the Nudix family (2). Proteins in the Nudix family are used to hydrolyze nucleoside phosphates; they also act as catalysts for the same reaction. Proteins in the Nudix family consist of two unique parts: <Structure load='4c9x' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='The Nudix fold and Nudix motif of the MTH1/S-crizotinib protein 4c9x' scene name='48/483888/Different_backbone_components/1'>a Nudix fold, and a Nudix motif</scene> (2). The Nudix fold is the secondary structure, or backbone, of the protein; the backbone has an α/β/α structure, meaning that the backbone consists of mixed beta sheet (gold) with an alpha helix on each end (magenta) (2). |
| - | The second component of proteins in the Nudix family, such as MTH1/S-crizotinib, is the Nudix motif, which is different for every protein. The Nudix motif in MTH1/S-crizotinib is made up of 23 amino acid sequence that orient into a small alpha helix | + | The second component of proteins in the Nudix family, such as MTH1/S-crizotinib, is the Nudix motif, which is different for every protein. The Nudix motif in MTH1/S-crizotinib is made up of 23 amino acid sequence that orient into a small alpha helix (dark purple) (5,6). This helix attached to one of the main alpha helices in MTH1/S-crizotinib’s backbone. The amino acids that catalyze the hydrolysis reactions are located in this alpha helix (2,5,6). All of these components establish the <Structure load='4c9x' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='The polarity of MTH1/S-crizotinib (4c9x) where the magenta represents the polar aspects of the protein and gray symbolizes the non-polar parts' scene name='48/483888/Polarity_of_mth1-s-crizotinib/1'>polarity</scene> of the protein; the outer parts of the helices and beta sheet are polar and hydrophilic (purple), while the inner parts and non polar and hydrophobic (gray). |
| - | MTH1/S-crizotinib also has an <scene name='48/483888/Active_site_of_mth1/1'>active site pocket</scene> that is formed between the beta sheet and one of the alpha helices (2). This pocket is built out of the residues Leu9 | + | MTH1/S-crizotinib also has an <Structure load='4c9x' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='The different components of the active site in MTH1/S-crizotinib (4c9x) are highlighted in this structure' scene name='48/483888/Active_site_of_mth1/1'>active site pocket</scene> that is formed between the beta sheet and one of the alpha helices (2). This pocket is built out of the residues Leu9 (aqua), Phe27 (violet), Phe72 (magenta), Met81 (lime green), Val83 (brown), Trp117 (orange), Trp123 (gold), and Phe139 (salmon). Furthermore, the amino acid <Structure load='4c9x' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='The Glu100 amino acid in MTH1/S-crizotinib (4c9x)' scene name='48/483888/4c9x-_the_glu_100_amino_acid/1'>Glu100</scene> is used to coordinate metal-binding in the protein and is located outside the alpha helix motif (2). |
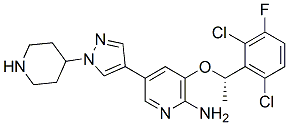
| - | MTH1/S-crizotinib has three different types of ligands attached to it: one chloride ligand, five sulfate ligands, and the <scene name='48/483888/S-crizotinib_ligand/1'>S-crizotinib ligand</scene>. Crizotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and its molecular structure is C21H22Cl2FN5O. The stereochemistry of the crizotinib determines if this inhibitor prevents MTH1 from carrying out its purpose in cancer cells; the S-crizotinib stops MTH1 from working while the R-crizotinib has no effect on the protein (3,7). | + | MTH1/S-crizotinib has three different types of ligands attached to it: one chloride ligand, five sulfate ligands, and the <Structure load='4c9x' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='The S-crizotinib ligand in MTH1/S-crizotinib (4c9x)' scene name='48/483888/S-crizotinib_ligand/1'>S-crizotinib ligand</scene>. Crizotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and its molecular structure is C21H22Cl2FN5O. The stereochemistry of the crizotinib determines if this inhibitor prevents MTH1 from carrying out its purpose in cancer cells; the S-crizotinib stops MTH1 from working while the R-crizotinib has no effect on the protein (3,7). |
| - | |||
| - | Val83- brown | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 12:52, 5 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from January 19, 2016, through August 31, 2016 for use for Proteopedia Team Projects by the class Chemistry 423 Biochemistry for Chemists taught by Lynmarie K Thompson at University of Massachusetts Amherst, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 425 through Sandbox Reserved 439. |
MTH1/crizotinib
Introduction
|
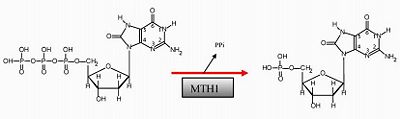
MTH1 is known as 7,8-dihydro-8-oxuguanine triphosphate (2). MTH1 is a protein in the human body encoded by the NUDT1 gene. In general, MTH1 is often synonymous for the gene NUDT1.
It is a protein that belongs to the Nudix hydrolase family and is characterized by a conserved of 23 – residue sequence segment. Since, MTH1 is part of the Nudix hydrolyse family, it has the typical Nudix structure, fold, structure arranged as a mixed of with one on each side. MTH1 is a protein prevents the misincorporation of oxidized nucleotides into DNA. Hydrolysis of a triphosphate nucleotide to a monophosphate nucleotide prevents this incorporation.The hydrolysis of the triphosphate nucleotide 8-oxo-dGTP to the monophosphate nucleotide 8-oxo-dGMP will not be recognized by DNA polymerase, preventing its incorporation into DNA (1).Specifically, the hydrolysis of the triphosphate nucleotide 8-oxo-dGTP to the monophosphate nucleotide 8-oxo-dGMP will not be recognized by DNA polymerase, preventing its incorporation into DNA.Cancer cells frequently overexpress MTH1. In order to slow down cancerous tumor growth, suppressing this protein could cause an increase in DNA misincorporations and induce cell death.
MTH1 is inhibited by Crizotinib has an aminopyridine structure and functions as a protein kinase inhibitor because it binds with the ATP – binding pocket of target kinase (3). Crizotinib has a high impact in drug designer because it causes tumors to shrink or stabilize. When (S)-Crizotinib inhibits MTH1, it increases the DNA single – strand to break, it activates DNA repair in colon carcinoma cells. When (S)-crizotinib inhibits MTH1, the protein can longer function as a nucleotide ‘healer’, and impairment rate of the nucleotide pool is increased. MTH1 is broadly used in drug production because based on researched made, it is proved that it helps fighting tumors. This because a loss of function of MTH1 impaires growth of KRAS tumor cells and an overexpression of MTH1 mitigates the cancer cells(4). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced as byproducts from cellular metabolism can cause damage to DNA and free nucleotides. Misincorporation of oxidized nucleoside triphosphates into DNA and RNA is one cause of mutation during transcription and replication that can result in DNA damage and ultimately cell death . This misincorporation of oxidized nucleotides could be used as a tool to combat tumor growth. Also, MTH1 assists in eliminating RAS – induced oxidative damage to prevent induction of senescence, so any inhibitors of MTH1 increase the amount of RAS induced oxidative damage and make cancer cells to enter pre – mature senescence which reduces cancer growth.
Overall Structure
|
MTH1/S-crizotinib is a member of a protein family of phosphorohydrolases known as the Nudix family (2). Proteins in the Nudix family are used to hydrolyze nucleoside phosphates; they also act as catalysts for the same reaction. Proteins in the Nudix family consist of two unique parts:
| |||||||||||