We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1063
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Structural Highlights == | == Structural Highlights == | ||
| - | There are many portions of the FadD13 enzyme the play very pivotal roles in its function. The first important structural point of note is that there are two subunits, the larger N-terminal subunit (<scene name='69/694230/N-terminal_domain/5'>residues 1-395</scene>) and the smaller C-terminal subunit (<scene name='69/694230/C-terminal_domain/1'>residues 402-503</scene>) held together by a six amino acid linker (<scene name='69/694230/Residues_396-401/1'>residues 396-401</scene>).The <scene name='69/694230/Atp_and_amp_binding_region/4'>ATP and AMP binding region</scene> allows for either ATP or AMP to bind and activate FadD13. The next major region of note is the hydrophobic tunnel which allows for lipid binding up to 26 carbons in length and extends from the ATP and AMP binding region. The hydrophobic tunnel is capped by an arginine and aromatic-rich surface patch which is involved in membrane binding of the protein. | + | There are many portions of the FadD13 enzyme the play very pivotal roles in its function. The first important structural point of note is that there are two subunits, the larger N-terminal subunit (<scene name='69/694230/N-terminal_domain/5'>residues 1-395</scene>) and the smaller C-terminal subunit (<scene name='69/694230/C-terminal_domain/1'>residues 402-503</scene>) held together by a six amino acid linker (<scene name='69/694230/Residues_396-401/1'>residues 396-401</scene>).The <scene name='69/694230/Atp_and_amp_binding_region/4'>ATP and AMP binding region</scene> allows for either ATP or AMP to bind and activate FadD13. The next major region of note is the hydrophobic tunnel which allows for lipid binding up to 26 carbons in length and extends from the ATP and AMP binding region. The hydrophobic tunnel is capped by an arginine and aromatic-rich surface patch which is involved in membrane binding of the protein<ref> [http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/3r44/ 3R44] </ref>. |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
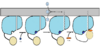
| - | The FadD13 enzyme functions to activate lipids before going into metabolic pathways. This is done by ATP/AMP binding to the <scene name='69/694230/Atp_and_amp_binding_region/4'>ATP and AMP binding region</scene>. Once ATP/AMP is bound the long lipid chain up to 26 carbons may bind in the hydrophobic portion of the enzyme. Upon binding of the substrate, the C terminal swings up to close off the tunnel. From There CoA can bind to produce the final product, an acyl-CoA Thioester. The lipid can now move transversely throughout the membrane and throughout the rest of the cell. Below is the proposed mechanism for ACSVL proteins<ref> | + | The FadD13 enzyme functions to activate lipids before going into metabolic pathways. This is done by ATP/AMP binding to the <scene name='69/694230/Atp_and_amp_binding_region/4'>ATP and AMP binding region</scene>. Once ATP/AMP is bound the long lipid chain up to 26 carbons may bind in the hydrophobic portion of the enzyme. Upon binding of the substrate, the C terminal swings up to close off the tunnel. From There CoA can bind to produce the final product, an acyl-CoA Thioester. The lipid can now move transversely throughout the membrane and throughout the rest of the cell. Below is the proposed mechanism for ACSVL proteins<ref> Andersson, C.S., Lundgren, C.A.K., Magnusdottir, A., Ge, C., Weislander, A., Molina, D., Hogbom, M. (2012)The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: structural Basis for Housing lipid Substrates longer than the Enzyme. Cell Press,1062-1070 </ref>. |
[[Image:Proposed Mechanism.png|100 px|thumb|left|Proposed Mechanism]] | [[Image:Proposed Mechanism.png|100 px|thumb|left|Proposed Mechanism]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| - | * Andersson, C.S., Lundgren, C.A.K., Magnusdottir, A., Ge, C., Weislander, A., Molina, D., Hogbom, M. (2012)The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: structural Basis for Housing lipid Substrates longer than the Enzyme. Cell Press,1062-1070 </ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | * [http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/3r44 3R44] | ||
Revision as of 13:47, 7 April 2015
FadD13
| |||||||||||