This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1074
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== '''Structure''' == | == '''Structure''' == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
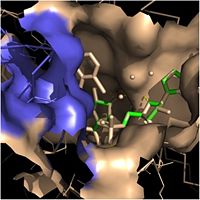
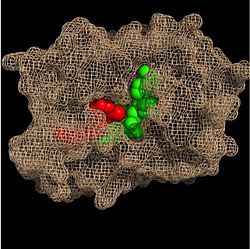
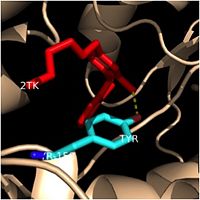
Crystal structures of InhA reveal a <scene name='69/694241/Homotetramer_subunits_labeled/1'>homotetramer</scene> (each subunit featured with a different color) in aqueous solution with separate ligand binding sites in each subunit. Each <scene name='69/694241/Monomer_subunit_no_ligands/1'>monomer</scene> subunit is composed of 289 residues and features a typical [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rossmann_fold] containing a single NADH binding site. The <scene name='69/694241/Secondary_structure/1'>secondary structure</scene> of InhA is made up of several alpha helices (pink), beta sheets (gold), and beta turns (white). This enzyme also features a fatty acyl binding crevice that accommodates the long-chain fatty acyl substrate (2TK) needed to synthesize mycolic acid precursors. The <scene name='69/694241/Helix6_helix7_updated/1'>alpha-6 and alpha-7 helices</scene> of the InhA form one side of the fatty acyl binding crevice, referred to as the <scene name='69/694241/Monomer_subunit_196_219/1'> substrate binding loop (residues 196-219)</scene>. | Crystal structures of InhA reveal a <scene name='69/694241/Homotetramer_subunits_labeled/1'>homotetramer</scene> (each subunit featured with a different color) in aqueous solution with separate ligand binding sites in each subunit. Each <scene name='69/694241/Monomer_subunit_no_ligands/1'>monomer</scene> subunit is composed of 289 residues and features a typical [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rossmann_fold] containing a single NADH binding site. The <scene name='69/694241/Secondary_structure/1'>secondary structure</scene> of InhA is made up of several alpha helices (pink), beta sheets (gold), and beta turns (white). This enzyme also features a fatty acyl binding crevice that accommodates the long-chain fatty acyl substrate (2TK) needed to synthesize mycolic acid precursors. The <scene name='69/694241/Helix6_helix7_updated/1'>alpha-6 and alpha-7 helices</scene> of the InhA form one side of the fatty acyl binding crevice, referred to as the <scene name='69/694241/Monomer_subunit_196_219/1'> substrate binding loop (residues 196-219)</scene>. | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 7 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Enoyl-ACP Reductase InhA from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
| |||||||||||