We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1063
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
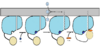
| - | The FadD13 enzyme functions to activate lipids before going into metabolic pathways. This is done by ATP/AMP binding to the <scene name='69/694230/Atp_and_amp_binding_region/4'>ATP and AMP binding region</scene>. Once ATP/AMP is bound the long lipid chain up to 26 carbons may bind in the hydrophobic portion of the enzyme. Upon binding of the substrate, the C terminal swings up to close off the tunnel. From | + | The FadD13 enzyme functions to activate lipids before going into metabolic pathways. This is done by ATP/AMP binding to the <scene name='69/694230/Atp_and_amp_binding_region/4'>ATP and AMP binding region</scene>. Once ATP/AMP is bound, the long lipid chain up to 26 carbons may bind in the hydrophobic portion of the enzyme. Upon binding of the substrate, the C terminal swings up to close off the tunnel. From there CoA can bind to produce the final product, an acyl-CoA Thioester. The lipid can now move transversely throughout the membrane and throughout the rest of the cell. Below is the proposed mechanism for ACSVL proteins<ref> Andersson, C.S., Lundgren, C.A.K., Magnusdottir, A., Ge, C., Weislander, A., Molina, D., Hogbom, M. (2012)The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: structural Basis for Housing lipid Substrates longer than the Enzyme. Cell Press,1062-1070 </ref>. |
[[Image:Proposed Mechanism.png|100 px|thumb|left|Proposed Mechanism]] | [[Image:Proposed Mechanism.png|100 px|thumb|left|Proposed Mechanism]] | ||
Revision as of 04:05, 8 April 2015
FadD13
| |||||||||||