We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1066
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
= Mechanism = | = Mechanism = | ||
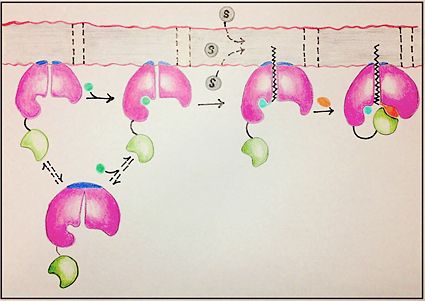
[[Image:FadD13 edited image.jpg|425 px|left|thumb|Figure 1: Mechanism for the activation of fatty acids (C24-C26) by FadD13. The N terminal domain (pink) is embedded in the membrane with the arginine rich lid-loop (dark blue), while the flexile linker (black) connects the C terminal domain (green) to the rest of the enzyme. Activation requires the binding of ATP (blue) which induces structural changes that promote the binding of the fatty acid chain. Formation of an acyl-adenylate intermediate induces a 140° rotation of the C terminal domain and the binding of CoA (orange). ]] | [[Image:FadD13 edited image.jpg|425 px|left|thumb|Figure 1: Mechanism for the activation of fatty acids (C24-C26) by FadD13. The N terminal domain (pink) is embedded in the membrane with the arginine rich lid-loop (dark blue), while the flexile linker (black) connects the C terminal domain (green) to the rest of the enzyme. Activation requires the binding of ATP (blue) which induces structural changes that promote the binding of the fatty acid chain. Formation of an acyl-adenylate intermediate induces a 140° rotation of the C terminal domain and the binding of CoA (orange). ]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='69/694233/Lys_487/2'>Lys 487</scene> results in a 95% loss of function of FadD13. <ref name="residue paper">PMID: 20027301</ref> | ||
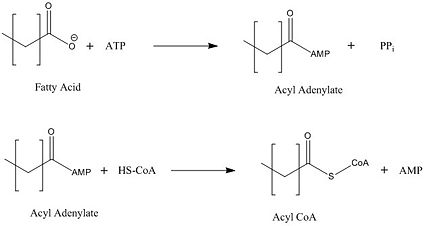
[[Image:acyl coa synthetase.jpg|425 px|left|thumb|Figure 2: Representation of the two-step reaction catalyzed by FadD13]] | [[Image:acyl coa synthetase.jpg|425 px|left|thumb|Figure 2: Representation of the two-step reaction catalyzed by FadD13]] | ||
Revision as of 01:24, 9 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis very-long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Andersson CS, Lundgren CA, Magnusdottir A, Ge C, Wieslander A, Molina DM, Hogbom M. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: Structural Basis for Housing Lipid Substrates Longer than the Enzyme. Structure. 2012 May 2. PMID:22560731 doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.03.012
- ↑ Jatana N, Jangid S, Khare G, Tyagi AK, Latha N. Molecular modeling studies of Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (FadD13) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis--a potential target for the development of antitubercular drugs. J Mol Model. 2011 Feb;17(2):301-13. doi: 10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3. Epub 2010 May, 8. PMID:20454815 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Khare G, Gupta V, Gupta RK, Gupta R, Bhat R, Tyagi AK. Dissecting the role of critical residues and substrate preference of a Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase (FadD13) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2009 Dec 21;4(12):e8387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008387. PMID:20027301 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008387
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Jatana N, Jangid S, Khare G, Tyagi AK, Latha N. Molecular modeling studies of Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (FadD13) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis--a potential target for the development of antitubercular drugs. J Mol Model. 2011 Feb;17(2):301-13. doi: 10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3. Epub 2010 May, 8. PMID:20454815 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0727-3
Similar Proteopedia Pages
Thioesterase Do we have anything like this?
External Resources
Tuberculosis Wikipedia page
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Wikipedia page
Coenzyme A Wikipedia page
Acyl CoA Wikipedia Page
Mycolic Acid Wikipedia page