Introduction
Tuberculosis, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is a respiratory infection still prevalent throughout the world. During the last decade, the emergence of multi-drug resistant strains of M. tuberculosis has given rise to the need for the development of new antibiotics in order to combat the infection[1]. In order to develop an efficacious antibiotic, the drug must be able to target a unique aspect of the bacteria, such as a protein, that is critical for its full virulence and survival. MgtC, an integral protein embedded in the extracellular membrane of M. tuberculosis, has recently been hypothesized as a novel drug target to resolve tuberculosis infections. The targeting of MgtC was a result of observing that upon deletion of the protein from M. tuberculosis, the bacteria are no longer able to survive due to inhibition of intramacrophage growth. [2]
Structure
Based on its tertiary structure, this protein has been placed into a larger group of proteins known as the MgtC superfamily. The overall structure of MgtC is constituted by two domains: an N-terminal domain and a C-terminal domain. Each of these domains have striking similarities and differences with other MgtC-like proteins.[2]
N-terminal Domain
The N-terminal domain of MgtC is highly-conserved between orthologues of the MgtC super family. This domain is largely hydrophobic and serves as the main component of MgtC that allows its embedment in the extracellular membrane. While this domain is highly conserved amongst orthologues, a crystal structure is not yet available, but the sequence available has determined it to be largely hydrophobic. [2]
C-terminal Domain
This domain of MgtC, in contrast, is highly variable in comparison to several orthologues, as presented by Yang et al. However, through a sequence alignment of five known functional MgtC orthologues from pathogens that survive inside macrophages (M. tuberculosis, B. melitensis, B. cenocepacia, Y. pestis, and S. Typhimurium), seven strictly conserved residues were found to be scattered along the whole sequence of the relatively hydrophilic and soluble C-terminal domain. [2]
A large hydrophobic core has conserved residues .
The opposite side of the protein has a small cluster of conserved residues .
Additionally, there is a crystal structure available for this domain. When comparing the crystal structure of the C-terminal domain to other protein structures, there are striking similarities between this domain and a class of proteins known as ACT domains. [2]
Function
Collectively, because there is not a crystal structure available for the entire protein and the high variability of the C-terminal domain, it has been difficult to characterize the biochemical function performed by MgtC within M. tuberculosis. Several roles have been proposed, including magnesium uptake, the binding of amino acids and metals, as well as facilitating dimerization with various proteins. [2]
Magnesium Transport
A role for MgtC as a magnesium transporter has been debated since its discovery. Several publications have produced data indicating that this protein is critical for the uptake of magnesium in magnesium-deprived medium, while other literature has shown that this protein plays an insignificant role in this process.
Support for a role in magnesium transport is supported by: 1) Mutants of MgtC are unable to survive in low-magnesium environment; 2) Expression of the gene encoding for MgtC is highly-induced in low magnesium environment; 3) Genes adjacent to the MgtC gene encode for known magnesium transporters. Very recent evidence against MgtC playing a role in magnesium transport showed that RT-PCR experiments gave consistent levels of MgtC expression despite changes in the concentration of extracellular magnesium. [2]
Potential for Binding Amino Acids
The exploration of this role for MgtC was first considered because of the ACT domain-like structure of the C-terminal domain.
ACT domains commonly bind small amino acids within the cell as a form of regulation. Yang et al. showed that the structure
of the C-terminal domain overlaps significantly with the structure of SerA (PDB: 3LGH), a known amino acid-binding ACT domain from E. coli
Figure 1A shows the overlap of these two proteins; the blue protein represents MgtC and the orange protein represents SerA.
However, the glycine that is critical for the binding of amino acids in these ACT domains has been substituted in MgtC with a
tyrosine, likely abolishing any potential amino acid binding activity [2]
Potential for Chelation
As with the potential for binding amino acids, this role was also explored because of the structural similarity of the C-terminal domain with ACT domains, as ACT domains also serve as excellent chelators to sequester cations within the cell. Yang et al. also compared the structure of the C-terminal domain of MgtC with an ACT domain of a known chelator, NikR. These structures overlapped quite well, indicating that MgtC may serve as a chelator. Figure 1B highlights the significant overlap between these residues; the blue protein represents MgtC and the orange protein represents NikR. However, the two histidine residues and the cysteine residue present in NikR that serve as the chelating residues are modified to threonine, proline, and isoleucine respectively. These substitutions likely prevent any chelating activity by MgtC. [2]
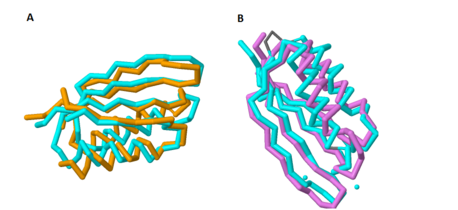
Figure 1. Overlap of the C-terminal Domain of MgtC with ACT domains of known function. 1A shows the significant overlap of the C-terminal of MgtC with SerA, an ACT domain that has been established to bind amino acids. 1B shows the overlap of the C-terminal domain of MgtC with NikR, a known chelating ACT domain.
Role in Dimerization
The potential for dimerization was another aspect of MgtC which was studied to see if this protein forms complexes with proteins of known function. A Bacterial Two-Hybrid (BACTH) assay was performed to study the potential for the entire protein to dimerize with itself and the potential for individual domains to dimerize. The results of this assay showed that the entire MgtC protein likely dimerizes, but the individual domains do not. This dimerization could serve as a critical component to the biochemical function of MgtC, although the exact implications have not yet been discerned [2]. Frantz et al proposed a role for MgtC to form dimers with MgtR, a protein that serves to promote the degradation of MgtC. This has huge implications in the overall clinical relevance of how MgtC could be targeted to develop new-generation antibiotics. [3]
Clinical Relevance
The development of an antibiotic which targets and inhibits MgtC could come from exploitation and enhancement of the process which promotes its degradation within Mycobacterium tuberculosis. MgtR, a hydrophobic peptide, promotes the degradation of MgtC upon high expression with the bacteria. As previously stated, inadequate levels of MgtC within M. tuberculosis results in an inability to growth and survive. [3] It is quite reasonable that analogues of MgtR could be developed, injected (subcutaneously) into infected patients, and resolve the tuberculosis infection by promoting degradation of MgtC and impairing growth of M. tuberculosis.
Future Work
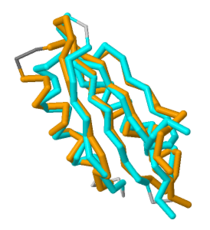
Figure 2. Overlap of MgtC C-terminal domain with the ACT domain of a GTP pyrophosphokinase. This figure demonstrates the significant overlap between the C-terminal domain of MgtC and the ACT domain of a GTP pyrophosphokinase.
Since so little is known about MgtC, future work should involve both crystallizing the entire MgtC protein and characterizing its biochemical function. Because the sequence of amino acids in a protein dictates structure, and structure typically determines the protein's function, further sequencing and structural analysis should be performed with MgtC to discern its function. Shown in Figure 2 is an overlap of MgtC with the ACT domain of a GTP pyrophosphokinase. This overlap shows even more extensive similarity than the aforementioned SerA and NikR ACT domains. Structural similarity analysis could aid in resolving the biochemical function of MgtC.
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.


