User:Michael Roberts/BIOL115 CaM
From Proteopedia
m |
(Undo revision 2394006 by Michael Roberts (Talk)) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| - | '''SECONDARY STRUCTURE''': This is shown more clearly by a <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Structure_plus_c/ | + | '''SECONDARY STRUCTURE''': This is shown more clearly by a <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Structure_plus_c/2'>ribbon diagram</scene>. The computer calculates where regions of secondary structure occur and draws them in cartoon-style 'ribbons'. |
The α-helical region is now clearly defined, and there are also regions of β-structure. | The α-helical region is now clearly defined, and there are also regions of β-structure. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
In each EF hand loop, the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions are bound by amino acid residues in and near the loops. | In each EF hand loop, the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions are bound by amino acid residues in and near the loops. | ||
| - | The structure shown here has four <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Structure_plus_c/ | + | The structure shown here has four <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Structure_plus_c/3'>calcium ions</scene> bound. In this condition, the protein adopts the extended structure shown. The EF hand-forming helices are bent away from the long linking helix, revealing hydrophobic residues and exposing the linking chain. |
'''CO-ORDINATING RESIDUES''': | '''CO-ORDINATING RESIDUES''': | ||
| - | To illustrate how Ca<sup>2+</sup> is bound, this display shows the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Co-ordination/ | + | To illustrate how Ca<sup>2+</sup> is bound, this display shows the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Co-ordination/1'>residues that take part in binding</scene> one of the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions. |
| - | <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Co-ordination/ | + | <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Co-ordination/2'>Zoom in</scene> to see this more clearly. |
'''CO-ORDINATING ATOMS''': | '''CO-ORDINATING ATOMS''': | ||
| - | To highlight the atoms that co-ordinate the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ion, we can now enlarge those that are close (within 2.7 Å). This shows that <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Co-ordination/ | + | To highlight the atoms that co-ordinate the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ion, we can now enlarge those that are close (within 2.7 Å). This shows that <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Co-ordination/3'>seven oxygen</scene> atoms form the calcium co-ordination shell. Five are contributed by the side chain carboxyl groups of Asp and Glu and a sixth by the peptide carbonyl of Gln. The seventh oxygen is provided by an associated water molecule. |
Revision as of 11:36, 13 April 2015
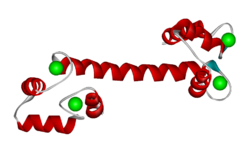
Sequence and structure of EF hands
The EF hand motif is present in a many proteins and it commonly bestows the ability to bind Ca2+ ions. It was first identified in parvalbumin, a muscle protein. Here we'll have a look at the Ca2+-binding protein calmodulin, which possesses four EF hands. Calmodulin and its isoform, troponinC, are important intracellular Ca2+-binding proteins.
The structure below, obtained by X-ray crystallography, represents the Ca2+-binding protein calmodulin. It has a dumbell-shaped structure with two identical lobes connected by a central alpha-helix. Each lobe comprises three α-helices joined by loops. A helix-loop-helix motif forms the basis of each EF hand.
Click on the 'green links' in the text in the scrollable section below to examine this molecule in more detail.
| |||||||||||
External Resources. You can view a nice animation of the conformational change undergone by calmodulin upon calcium binding by following this link [1].
