User:Michael Roberts/BIOL115 CaM
From Proteopedia
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
== Binding to target proteins == | == Binding to target proteins == | ||
'''ACTIVE & INACTIVE CALMODULIN:''' | '''ACTIVE & INACTIVE CALMODULIN:''' | ||
| - | At resting levels of cytosolic Ca<sup>2+</sup> (~100 nM), calmodulin exists predominantly in the calcium-free form. This is called <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Inactive_calmodulin/1'>apo-calmodulin</scene> and its structure is more compact than the structure we saw earlier <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Structure_plus_c/3'>with bound calcium | + | At resting levels of cytosolic Ca<sup>2+</sup> (~100 nM), calmodulin exists predominantly in the calcium-free form. This is called <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Inactive_calmodulin/1'>apo-calmodulin</scene> and its structure is more compact than the structure we saw earlier <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Structure_plus_c/3'>with bound calcium</scene>. Note the extended α-helix linking the two EF-hand-containing domains in the Ca-bound structure, which is interrupted in the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_CaM/Inactive_calmodulin/1'>Ca-free form</scene>. Here, the terminal helices are folded down concealing their hydrophobic surfaces and the central chain, which is not now α-helical along its whole length, is not exposed. |
Current revision
Sequence and structure of EF hands
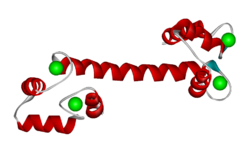
The EF hand motif is present in a many proteins and it commonly bestows the ability to bind Ca2+ ions. It was first identified in parvalbumin, a muscle protein. Here we'll have a look at the Ca2+-binding protein calmodulin, which possesses four EF hands. Calmodulin and its isoform, troponinC, are important intracellular Ca2+-binding proteins.
The structure below, obtained by X-ray crystallography, represents the Ca2+-binding protein calmodulin. It has a dumbell-shaped structure with two identical lobes connected by a central alpha-helix. Each lobe comprises three α-helices joined by loops. A helix-loop-helix motif forms the basis of each EF hand.
Click on the 'green links' in the text in the scrollable section below to examine this molecule in more detail.
| |||||||||||
External Resources. You can view a nice animation of the conformational change undergone by calmodulin upon calcium binding by following this link [1].
