Structure
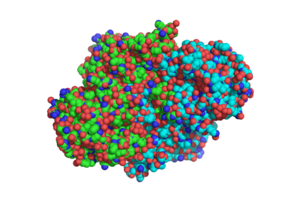
Overall structure of
1SJ2, showing that the structure is a
homodimer.
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Catalase Peroxidase (mtCP) is a homodimer with each monomer consisting of two domains. The overall structure is stabilized by 703 water molecules.
The two domains of each monomer are primarily alpha helical and have similar foldings. The similar foldings suggests that the monomer results from a gene duplication event; however, the C-terminal domain does not contain the heme b prosthetic group, while the does. The active site is therefore located within the N-terminal domain. The two monomers interact through an interlocking hook formed by the N-terminal domains that stabilizes the formation of the dimer (1).
The N-terminal is formed through hydrophobic interactions between residues Tyr-28 and Tyr-197 and residues Trp-38 and Trp-204. This interlocking loop region is also found in similar conformations of other catalase peroxidase structures such as: hmCP and bpCP.
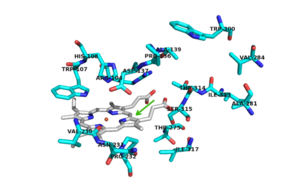
Active Site
There are 6 conserved key active site residues that surround the . These residues are Arg 104, Trp 107, His 108, His 270, Asp 381 (1).
In hmCP, which share 55% and 69% identity with mtCP, the heme is buried inside HmCP-N, and substrate access to the active site is through a narrow channel that prevents access of a large substrate (3). The location of the binding site for isoniazid (INH) is located near the δ meso heme edge, about 3.8 Å away from the heme iron. This binding site is found within what is considered to be the usual substrate access channel of peroxidases. The reaction between INH and the enzyme must occur from interaction in a binding site intended for the natural substrate (2). Asp 137 plays a key role in the activation and binding of INH. Asp 137 creates energetically favorable interactions due to its ability to make hydrogen-bond interactions between its carboxylic acid side chain and the pyridinyl N1 of INH.
Catalase Peroxidases
Catalase-peroxidases are enzymes that degrade hydrogen peroxide. Catalase converts two equivalents of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen via a two-step reaction cycle in which H202 alternately oxidizes and reduces the heme iron at the active site. Within peroxidases, oxidation of heme iron involves a H202 molecules, similar to that in the catalase-catalyzed reaction. Reduction of the heme iron, however, involves hydrogen donors such as NADH, not a second H202 molcule (3). Catalase-Peroxidases that have been characterized are either homodimers or homotetramers and contain a single heme b cofactor at the active site. Usually, the primary struture of the subunit can be divided into two halves that have a high level of sequence similarity, most likely due to a gene duplication event.
Clinical Applications
Isoniazid Structure
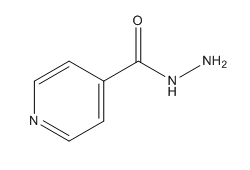
Chemical Structure of Isoniazid (INH)
Isoniazid Role
INH is a prodrug susceptible to oxidative reactions catalyzed by KatG (4). INH action against mycobacteria requires catalase-peroxidase (KatG) function.
Mechanism
Formation of IN-NAD Adduct
Activation or oxidation of INH by KatG has recently been measured in the terms of production of an IN-NAD adduct molecule that serves as a tight binding inhibitor of InhA. InhA is an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of mycolic acids, which are components of the mycobacterial cell wall. Therefore, inhibition of InhA alone is sufficient enough to inhibit mycolic acid biosynthesis and induce cell lysis after exposure of bacteria to INH (4).
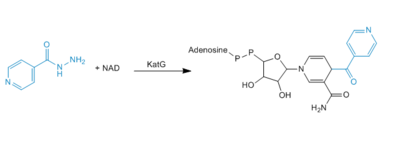
Mechanism of adduct formation
Mutations
Resistance to INH is a continuing problem in the development of effective therapeutic regimes designed to eliminate infections from M. tuberculosis. Resistance to INH is due to deletions or mutations in this KatG catalase peroxidase enzyme. There are many possible mutations in this peroxidase that can play a role in the resistance of INH. The most commonly occurring mutation occurs at Ser 315. A mutation at this amino acid can result in up to a 200 fold increase in the minimum inhibitory concentration for INH. Ser 315 has been reported to mutate to asparagine, isoleucine, glycine, and most frequently, threonine. A S315T mutant has the ability to reduce the affinity of the enzyme for INH by increasing steric hindrance and reducing access to the substrate binding site (1). Mutation of Ser315 to a Thr in mtCP results in a loss of the activation to the anti-tuberculosis drug (INH) with no loss of either peroxidase or catalase activity (3). Any of the other mutations at this site, except for glycine, would also increase steric hindrance and decrease the accessibility to the binding site.
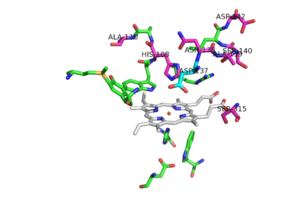
Pink residues represent the location of possible mutations. Green residues represent the active site. Asp 137 is shown in blue.
Of the active site residues that are involved in enzyme catalyzed activation of INH, only His 108 has been a site for mutations that can increase resistance to INH. His 108 has been reported to mutate to glutamic acid and glutamine. These mutations reduce the affinity for INH but the hydrogen bond donor/acceptor groups of glutamine would still allow INH to bind. However, glutamine wouldn't be able to act as proton shuttle in the way His 108 does in the enzyme-catalyzed activation pathway.
No known mutants have been reported to occur at Asp 137, although a few mutants nearby could cause local conformational changes and thereby altering the orientation of the Asp 137 side chain, making it less effective in binding and activation of INH (1).
References
1) Bertrand, T.; Eady, N. A. J.; Jones, J. N.; Jesmin, Nagy, J. M.; Jamart-Gregorie, B.; Raven. E. L.; Brown, K. A. Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium Tubercuosis Catalase-Peroxidase. The J. of Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 38991-38999.
2) Carpena, X.; Loprasert, Suvit,; Mongkolsuk, S.; Switala, J.; Loewen, P. C.; Fita, I. Catalase-peroxidase KatG of Burkholderia pseudomallei at 1.7 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 327, 475-489.
3) Yamada, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Sato, T.; Igarashi, N.; Tanaka, N. The 2.0 Å crystal structure of catalase-peroxidase from Haloarcula marismortui Natur Structural Biol. 2002, 9, 691-695.
4) Zhao, X.; Yu, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, F.; Sacchettini, J. C.; Magliozzo, R. S.; Hydrogen Peroxide-Mediated Isoniazid Activation Catalyzed by Mycobacterium tuberculosis Catalase-Peroxidase (KatG) and Its S315T Mutant. Biochemistry. 2006, 45, 4131-4140.