Overview
Mycobacterium tuberculosis NrdH (MtNrdH)is a small glutaredoxin-like protein involved in the electron transport chain in ribonucleotide reduction. Therefore, it is extremely important in DNA production and replication because it helps supply cells with deoxyribonucleotides. Reduction of MtNrdH results in the breaking of an internal disulfide bond at the active site, allowing it to accept electrons and pass them on downstream. Because of its imperative role in ribionucleotide reduction, MtNrdH is thought to be essential to the reproductive integrity of M. tuberculosis, suggesting its role in infectivity and leading to its identification as a possible drug target.[1]
Background
Mycobacterium tuberculosisresides in the lungs of a host and upon becoming active, results in a Tuberculosis infection (TB) and the ensuing symptoms of chest pain, weakness, and intense coughing. Left untreated and unmanaged, TB can lead to death (1.5 million in 2013).[2] The disease has a high co-morbidity with HIV/AIDS due to its immunocompromising tendencies. TB is one of the most heavily studied diseases today. With over 9 million infections worldwide per year, the necessity for antimicrobial agents to combat emerging multi-drug resistant strands is imperative.[2]
Structure
The structure of M. tuberculosis as determined by x-ray crystallography has 79 residues in a single polypeptide chain. . The active site (shown in green) is dominated by a disulfide bond between Cys-11 and Cys-14, which serves as the site of reduction by theirodoxin reductase. [3]
Many thioredoxin-like proteins have a similar active site region, denoted as the thioredoxin fold, which occurs directly before the disulfide bond. The residues in this region, denoted by letters CVQC, are the most highly conserved of all areas of the protein across multiple species. Exactly how this structure relates to function is somewhat debated. A threonine-7 reside directly across the thioredoxin fold from the disulfide bond has been suggested to adopt two different conformations which differentially affect the redox abilities of the protein. In the , the alcohol of the threonine side chain points towards the disulfide bond, engaging an ionic interaction between the two that prevents thioredoxin reductase from binding. Alternatively, in the , the alcohol points in the opposite direction, allowing sufficient space for the ligand to bind and reduction to occur.[4]
The active site of the protein is stabilized through a involving the two highly conserved residues, CVQC (green) and WSGFRP (yellow). The crystal structure shows that interactions with one water molecule is necessary for the proper coordination between the conserved motifs to occur. These hydrogen bonds orient the important residues in the most optimal position to promote oxidation and reduction.[5]

Weblogo diagram showing highly conserved CVQC region of NrdH.
Another highly conserved residue is the WSGFRP sequence. This nonpolar sequence is found on the surface of the molecule and is exposed to solvent.
[6] [7] For this reason, it has been hypothesized that this sequence plays a role in the binding of thioredoxin reductase.
[8]
Arg-68 is responsible for the stabilization of the hydrophobic region of NrdH. Arg-68 has two distinct conformations. In the , Arg-68 is hydrogen bonded to His- 60 and Asp-59. When Arg-68 shifts to its
, it breaks its hydrogen bond with Asp-59. [9] This reduction in hydrogen bonding gives the hydrophobic region more flexibility and is thought to occur when NrdH is in its inactive state.
Function
MtNrdH has been identified as an electron carrier protein in ribonuleotide reduction. Ribonucleotide reduction uses an enzyme called ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) to make deoxyribonucleotides, which act as precursors to DNA synthesis. Three classes of RNRs have been identified; each class differs in cofactor requirement, structure, and oxygen dependence, but the general catalytic mechanism is conserved in all three classes.[10] Mycobacterium tuberculosis uses class I ribonucleotide reductase.
Class I RNR is further subdivided into class Ia and Ib. Both Ia and Ib reduce ribonucleotide 5’ diphosphate to deoxyribonucleotide 5’ diphosphate (NDP to dNDP). After ribonucleotide reductase performs the first round of reduction, RNR must be reduced again to reset the cycle. In class Ib, RNR is reduced by either glutadoxin or thioredoxin, which are first reduced by glutadoxin reductase and thioredoxin reductase, respectively.[11] In class Ib, RNR is reduced by NrdE, which is first reduced by NrdH. An important distinction between Ia and Ib is that Ia is present in eukaryotes, eubacteria, bacteriophages, and virus, but Ib is only present in eubacteria. [12]
[13]
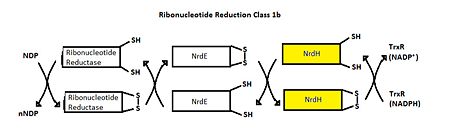
Ribonucleotide Reduction Class Ib general mechanism. The role of NrdH is highlighted.
Relevance
Like most NrdHs, MtNrdH is similar in sequence to glutaredoxins, but structurally similar to thioredoxins. MtNrdH also accepts electrons from thioredoxin reductase, a characteristic of thioredoxins, but not glutaredoxins.
[14] 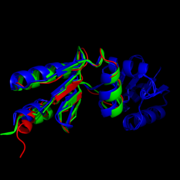
Structural comparison of NrdHs with "thioredoxin folds":
E. Coli NrdH (green),
C. ammoniagenes NrdH (blue),
M. tuberculosis NrdH (red)
Similar structures of NrdH have been isolated in other primitive species including E. coli, S. pyogenes, S. typhimurium, D. deserti, S. flexneri 2457T, and S. dysenteriae. In higher order multi-cellular organisms, however the NrdH protein is replaced by more complex glutaredoxins or thioredoxins. This observation leads some to speculate that NrdH is one of the very first ancestors in the ribonucleotide reduction pathway. [17] If this is true, NrdH can be seen as a critical protein that allowed for the development of DNA-based life since deoxyribonucleotides could not have existed without the ribonucleotide reduction pathway. A better understanding of the evolutionary timeline of NrdH and similar proteins could shed greater light onto the RNA Wold Hypothesis, specifically describing the time frame of emergence of DNA based life.
Possible Drug Target
MtNrdH can serve as a potential drug target to treat tuberculosis. The genes encoding NrdE and NrdF2, a cofactor in class 1b ribonucleotide reduction, are essential for growth of M. tuberculosis in vitro.[18] This suggest that M. tuberculosis relies solely on class Ib ribonucleotide reduction. If that is the case, NrdH may be an essential gene as well. Since NrdH is not found in humans, a drug that targets NrdH would be able to damage M. tuberculosis cells without hurting the human host.
References
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) The Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NrdH at 0.87Å Suggests a Possible Mode of Its Activity. Biochemistry 52, 4056-4065.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Tuberculosis." Media Centre. World Health Organization, Web. 16 Mar. 2015. Media Centre. <http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs104/en/>.
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) The Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NrdH at 0.87Å Suggests a Possible Mode of Its Activity. Biochemistry 52, 4056-4065.
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) The Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NrdH at 0.87Å Suggests a Possible Mode of Its Activity. Biochemistry 52, 4056-4065.
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) The Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NrdH at 0.87Å Suggests a Possible Mode of Its Activity. Biochemistry 52, 4056-4065.
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) 4060.
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) 4057.
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) 4056.
- ↑ Nelson, David L., and Michael M. Cox. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. 5th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman, 2008. 888-889.
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) 4056.
- ↑ Makhlynets, O., Boal, A. K., Rhodes, D. V., Kitten, T., Rosenzweig, A. C., & Stubbe, J. (2014). Streptococcus sanguinis Class Ib Ribonucleotide Reductase: HIGH ACTIVITY WITH BOTH IRON AND MANGANESE COFACTORS AND STRUCTURAL INSIGHTS. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289(9), 6259–6272. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.533554.
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) 4057.
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) The Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NrdH at 0.87Å Suggests a Possible Mode of Its Activity. Biochemistry 52, 4056-4065.
- ↑ Swastik, Phulera and Mande, Shekhar C. (2013) 4057.



