We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1063
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
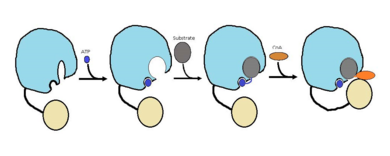
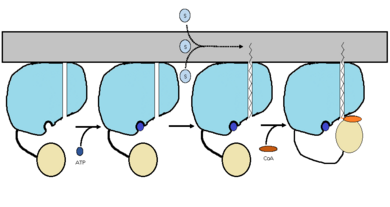
The FadD13 enzyme functions to activate lipids. Once the lipids are activated, they can continue on into metabolic pathways. This is done by ATP/AMP binding to the <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/12'>ATP/AMP binding region</scene>. Once ATP/AMP is bound, the long lipid chain up to 26 carbons may bind in the <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/13'>hydrophobic tunnel</scene> of the enzyme. Upon binding of the substrate, the C terminal swings up to close off the tunnel. From there CoA can bind to produce the final product, an acyl-CoA Thioester. The lipid can now move transversely throughout the membrane and throughout the rest of the cell. Below is the proposed mechanism for ACSVL proteins. | The FadD13 enzyme functions to activate lipids. Once the lipids are activated, they can continue on into metabolic pathways. This is done by ATP/AMP binding to the <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/12'>ATP/AMP binding region</scene>. Once ATP/AMP is bound, the long lipid chain up to 26 carbons may bind in the <scene name='69/694230/Fadd13_subunits/13'>hydrophobic tunnel</scene> of the enzyme. Upon binding of the substrate, the C terminal swings up to close off the tunnel. From there CoA can bind to produce the final product, an acyl-CoA Thioester. The lipid can now move transversely throughout the membrane and throughout the rest of the cell. Below is the proposed mechanism for ACSVL proteins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Relevant Pages== | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
Revision as of 18:02, 21 April 2015
FadD13
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Watkins PA, Maiguel D, Jia Z, Pevsner J. Evidence for 26 distinct acyl-coenzyme A synthetase genes in the human genome. J Lipid Res. 2007 Dec;48(12):2736-50. Epub 2007 Aug 30. PMID:17762044 doi:http://dx.doi.org/M700378-JLR200
- ↑ Kochan G, Pilka ES, von Delft F, Oppermann U, Yue WW. Structural snapshots for the conformation-dependent catalysis by human medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM2A. J Mol Biol. 2009 May 22;388(5):997-1008. Epub 2009 Apr 1. PMID:19345228 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.03.064
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Andersson CS, Lundgren CA, Magnusdottir A, Ge C, Wieslander A, Molina DM, Hogbom M. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase: Structural Basis for Housing Lipid Substrates Longer than the Enzyme. Structure. 2012 May 2. PMID:22560731 doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.03.012
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Khare G, Gupta V, Gupta RK, Gupta R, Bhat R, Tyagi AK. Dissecting the role of critical residues and substrate preference of a Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase (FadD13) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2009 Dec 21;4(12):e8387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008387. PMID:20027301 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008387