Introduction
NrdH is a redox protein and is part of a family of redox proteins. The other proteins that maintain the redox balance of NrdH are three thioredoxin and three glutaredoxins-like proteins. Prokaryotes typically maintain redox homeostasis through low-molecular weight thiols (glutathione) and through proteins involved in disulfide exchange (thioredoxins). NrdH is found in many types of bacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This bacteria causes the disease tuberculosis, which is a fatal disease if not treated properly. Tuberculosis was the leading cause of death in the United States in the past, and it can be spread through the air from one person to another by coughing, sneezing, or speaking [1].
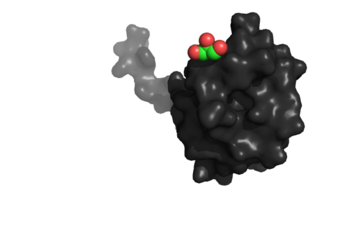
Binding site specific for aromatic amino acids. The hole that is located in the center of this image of NrdH shows the binding site.
The of NrdH has a thioredoxin fold with 79 residues with a glutaredoxin-like sequence. Unlike glutaredoxins, NrdH of Mycobacterium tuberculosis can accept electrons from thioredoxin reductase[2]. It contains two bound ligands, three alpha helices, and four beta sheets. The two ligands are colored by element, red representing oxygen and gray representing carbon. The binding site of NrdH is specific for aromatic amino acids. The image on the left shows the specific binding site. The specificity for aromatic amino acids is vital because aromatic-aromatic interactions have shown to have great importance for protein folding, ligand binding, and protein stability [3].
Function
NrdH redoxins are small reductases, and they contain similar amino acid sequences to glutaredoxins and mycoredoxins. However, NrdH redoxins are different because of their thioredoxin-like activity. Their main function is to act as the electron donor for class 1b ribonucleotide reductases, which are important for the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides [4]. The process of ribonucleotide reduction is one of the most fundamental biochemical processes that is required for the existence of DNA-based life. It is the only de novo pathway to synthesize deoxyribonucleotides. Deoxyribonucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and are synthesized from ribonucleotides by reducing the 2’OH in a radical based reaction. The deoxyribonucleotides are then used as precursors for the process of DNA synthesis. This reaction is catalyzed by ribonucleotide reductases [2].
Ribonucleotide Reductases (RNRs)
All RNRs are related because they are necessary for all living cells, with the exception of a couple types of parasites and obligate endosymbionts. This is evident due to the catalytic core, which is structurally conserved across all extant RNRs. RNRs are essential for the processes of DNA replication and repair [5].
There are three classes of RNRs. These classes are divided based on the mechanism of radical generation in the reaction.
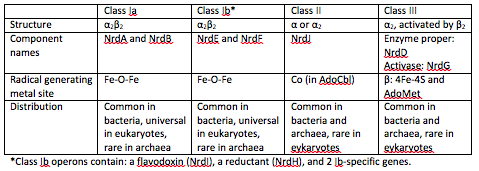
Class I enzymes reduce nucleotide 5’-diphosphates, while the other 2 classes reduce ribonucleotide 5’-triphosphates [2]. Class I RNRs are oxygen-dependent enzymes that contain a di-iron cluster [4].
Class 1 RNRs generate a tyrosyl radical in another subunit, which is NrdB for class 1a and NrdF in class 1b. The tyrosyl radical is then transferred to the catalytic subunit, which is NrdA in class Ia and NrdE in class 1b [5].
At the end of each cycle of ribonucleotide reduction, the ribonucleotide reductase needs to be reduced in order to be ready for the next reduction cycle. For a class 1a RNR, an external cofactor, such as a glutaredoxin or thioredoxin, performs this reduction step. For class 1b RNRs, this cofactor is known as NrdH. NrdH contains a glutaredoxin-like sequence but behaves like a thioredoxin [2].
Structure
NrdH has a typical thioredoxin fold and is a monomer that has the ability to form a stable dimer when there is a high concentration of protein. The thioredoxin fold composes three alpha helices with four beta sheets.
Conserved Motifs
Members of the NrdH family are typically characterized by CVQC and WSGFRP
The , is an active site and it is located at the N terminus of the first alpha helix.
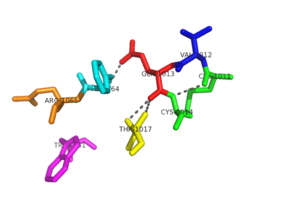
the amide oxygen of glutamine residue is firmly hydrogen bonded with the peptidyl nitrogen of Phe-44. The amide nitrogen of glutamine is then available for further hydrogen bonding. The carbonyl oxygen of Val-12 hydrogen bonds with peptidyl nitrogen of Ala-16. This hydrogen bonding leads to stability within the redox active site of NrdH. The N-terminal cysteine of the CVQC motif acts as a nucleophile, whereas the C-terminal cysteine acts as the resolving cysteine. The residues between the two cysteines are known to affect redox potentials and pKa values. Also, by changing the target proteins, in turn, they regulate the function [2].
The is stabilized by glutamine of the CVQC motif and phenylalanine is exposed to the solvent. Phe-64 and Val-12 with Ala-16 and Ala-20 create a distinct hydrophobic patch that is exposed to the solvent. This patch is of functional significance that could potentially interact with the C-terminus of RNR. This hydrogen bonding network lends to the stability of the redox active site [2].
A highly conserved residue in all members of the NrdH family is Arg-68. This residue hydrogen bonds with the main carbonyl oxygen of His-60. The His-60 is located before the WSGFRP motif, which suggests that the interaction between Arg-68 and His-60 may be of structural significance. In an alternate conformation of Arg-68, the guanidinyl group of Arg-68 forms a salt bridge with Asp-59. The hydrogen bonds and salt bridge work together to stabilize the WSGFRP motif [2].
A buried water molecule binds with the WSGFRP motif. This water is believed to be one of the structural signatures of NrdH proteins. The hydrogen bonding network of the CVQC and WSGFRP motifs also involves the water molecule, and this may suggest that this region is important in the evolution of NrdH [2].
Function
The main function is to act as a reducing partner of class 1B ribonucleotide reductase and for ribonucleotide reduction (RR), it is thought to supply electrons for this biochemical reaction. RR is one of the most fundamental biochemical processes that is required for DNA based life form to exist. Ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs) produce deoxyribonucleotides. These are precursors for DNA synthesis [2].
Chemical Processes
NrdH is able to accept electrons from M. tuberculosis thioredoxin reductase and is able to reduce the disulfide bonds that are present in insulin [2].
Disease
Tuberculosis, also known as TB, is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis which normally attacks the lungs. TB bacteria attack the lungs, kidneys, spine, and the brain as well. This disease is fatal if not treated properly and was the leading cause of death in the United States in the past. It can be spread through the air from one person to another by coughing, sneezing, or speaking [6].
Latent TB infections can live inside the human body in a dormant state and therefore will not get sick and will not be contagious. When the immune system cannot support the latent TB bacteria anymore, it will become active and contagious. This can be treated with several drugs taken for 6-9 months [7].
Sequence alignment of NrdH from
Mycobacterium tuberculosis,
Corynebacterium glutamicum, and
Echerichia coliGenes that encode for NrdE and NrdF are essential for growth, and RR might be an attractive biochemical pathway for antimycobacterial drug discovery. Organisms that depend solely on class 1B RNR could potentially contain the essential genes and serve as potential drug targets for treating tuberculosis [2].
References
- ↑ Gomez JE, McKinney JD. M. tuberculosis persistence, latency, and drug tolerance. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2004;84(1-2):29-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2003.08.003. PMID:14670344 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2003.08.003
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Phulera S, Mande SC. The Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NrdH at 0.87 A Suggests a Possible Mode of Its Activity. Biochemistry. 2013 May 28. PMID:23675692 doi:10.1021/bi400191z
- ↑ Lanzarotti E, Biekofsky RR, Estrin DA, Marti MA, Turjanski AG. Aromatic-aromatic interactions in proteins: beyond the dimer. J Chem Inf Model. 2011 Jul 25;51(7):1623-33. doi: 10.1021/ci200062e. Epub 2011, Jun 27. PMID:21662246 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci200062e
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Van Laer K, Dziewulska AM, Fislage M, Wahni K, Hbeddou A, Collet JF, Versees W, Mateos LM, Tamu Dufe V, Messens J. NrdH-redoxin of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Corynebacterium glutamicum dimerizes at high protein concentration and exclusively receives electrons from thioredoxin reductase. J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 28. PMID:23362277 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.392688
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Lundin D, Gribaldo S, Torrents E, Sjoberg BM, Poole AM. Ribonucleotide reduction - horizontal transfer of a required function spans all three domains. BMC Evol Biol. 2010 Dec 10;10:383. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-383. PMID:21143941 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-383
- ↑ Gomez JE, McKinney JD. M. tuberculosis persistence, latency, and drug tolerance. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2004;84(1-2):29-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2003.08.003. PMID:14670344 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2003.08.003
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention