We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Michael Roberts/BIOL115 Myo
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
'''SECONDARY STRUCTURE''': This next view simplifies things, and just shows a <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Secondary_structure/9'>cartoon representation </scene>of the secondary structure of the protein. | '''SECONDARY STRUCTURE''': This next view simplifies things, and just shows a <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Secondary_structure/9'>cartoon representation </scene>of the secondary structure of the protein. | ||
You see how the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Hbonds/1'>hydrogen bonds</scene> (yellow) that maintain the main secondary structure of the protein are arranged in this next view. | You see how the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Hbonds/1'>hydrogen bonds</scene> (yellow) that maintain the main secondary structure of the protein are arranged in this next view. | ||
| - | Some amino acids have specific effects on secondary structure. This next view shows the locations of the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Secondary_structure/11'>PROLINE</scene> residues in myoglobin. You can see that they all fall at the end of a stretch of helix. This is | + | Some amino acids have specific effects on secondary structure. This next view shows the locations of the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Secondary_structure/11'>PROLINE</scene> residues in myoglobin. You can see that they all fall at the end of a stretch of helix. This is because their large, cyclic side chains do not fit within the straight run of α-helix. |
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
'''PROXIMAL AND DISTAL HISTIDINES''': The iron atom sits either side of the side chains of two <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Heme/4'>histidine residues</scene>. | '''PROXIMAL AND DISTAL HISTIDINES''': The iron atom sits either side of the side chains of two <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Heme/4'>histidine residues</scene>. | ||
One of these (coloured cyan) is attached to the iron atom, and is known as the ''proximal'' histidine. The other (green) is called the ''distal'' histidine. | One of these (coloured cyan) is attached to the iron atom, and is known as the ''proximal'' histidine. The other (green) is called the ''distal'' histidine. | ||
| + | Note how the iron is pulled out slightly to one side of the plane of the heam group as a result of it's co-ordination with the side chain of the proximal histidine. | ||
'''OXYGEN''': | '''OXYGEN''': | ||
The space between the iron and the distal histidine is where the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Heme/6'>oxygen</scene> (pink) binds. | The space between the iron and the distal histidine is where the <scene name='User:Michael_Roberts/BIOL115_Myo/Heme/6'>oxygen</scene> (pink) binds. | ||
| + | Note the angled orientation of the oxygen relative to the plane of the heam. The natural binding of oxygen to heam in solution would be the O2 molecule perpendicular to the plane. In myoglobin (and haemoglobin) the presence of the distal His forces to O2 to one side, reducing the affinity of the heam-O2 binding, thus allowing release of oxygen when pO2 is low. The same effect of the distal His also reduces the affinity of heam for carbon monoxide. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 12:20, 27 April 2015
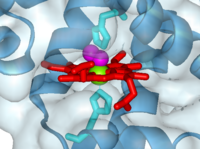
Myoglobin with oxygen bound to heme (1a6m)
The heme group and oxygen binding in myoglobin.
Myoglobin is a protein whose function is to store oxygen in muscle tissues. Like heamoglobin, it is red in colour, and it is myoglobin that gives muscle its strong red colour.
Myoglobin was the first globular protein for which the 3-dimensional structure was solved, back in the late 1950s. It gives its name to the 'globin fold', a common alpha domain motif. An alpha domain is a structural region composed entirley of alpha-helix.
Click on the 'green links' in the text in the scrollable section below to examine this molecule in more detail.
| |||||||||||
