We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1051
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Biological Role== | ==Biological Role== | ||
| - | The cell wall of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium mycobacteria] is primarily composed of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peptidoglycan peptidoglycans], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arabinogalactan arbinogalactans], and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycolic_acid mycolic acids]. | + | The unusually thick and waxy cell wall of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium mycobacteria] is primarily composed of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peptidoglycan peptidoglycans], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arabinogalactan arbinogalactans], and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycolic_acid mycolic acids]. The mycolic acids, which have very long carbon chains and exhibit extreme hydrophobicity, are responsible for forming the outermost layer of the cell wall, thus creating a hydrophobic envelope surrounding the mycobacterium. The antigen 85 (Ag85) complex in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''] is composed of three intracellular membrane proteins: Ag85A, B, and C. Each protein catalyzes the transfer of mycolic acids. NEED REFERENCE! IMPORT DETAILS FROM BLAKE/ZIMMERMAN |
===Clinical Relevance=== | ===Clinical Relevance=== | ||
Revision as of 20:14, 12 May 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Antigen 85C from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Introduction
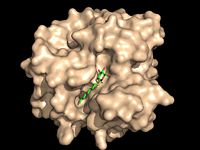
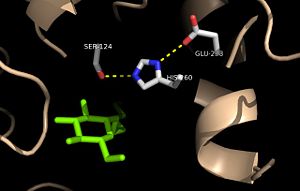
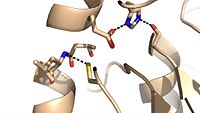
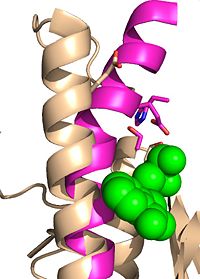
Antigen 85C is one of three distinct protein components of the Ag85 complex in the cell wall of M. tuberculosis. This serine hydrolase catalyzes the transfer of mycoyl groups, unique components of the cell wall of mycobacteria. Several three dimensional structures of Ag85C have been solved, including the wild type enzyme as well as active site variants due to site-directed mutagenesis and covalent modification.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Jackson M, Raynaud C, Laneelle MA, Guilhot C, Laurent-Winter C, Ensergueix D, Gicquel B, Daffe M. Inactivation of the antigen 85C gene profoundly affects the mycolate content and alters the permeability of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell envelope. Mol Microbiol. 1999 Mar;31(5):1573-87. PMID:10200974
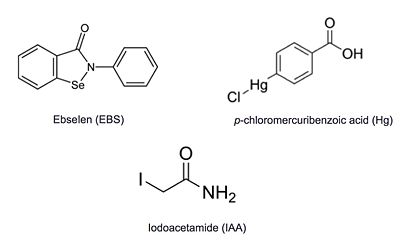
- ↑ Favrot L, Lajiness DH, Ronning DR. Inactivation of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Antigen 85 complex by covalent, allosteric inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 14. pii: jbc.M114.582445. PMID:25028518 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.582445
- ↑ Ronning DR, Klabunde T, Besra GS, Vissa VD, Belisle JT, Sacchettini JC. Crystal structure of the secreted form of antigen 85C reveals potential targets for mycobacterial drugs and vaccines. Nat Struct Biol. 2000 Feb;7(2):141-6. PMID:10655617 doi:10.1038/72413