RGS proteins
Regulator of G-proteins signaling (RGS) proteins play a critical role in many G protein-dependent signaling pathways. Thus, RGS proteins have been implicated in a wide range of pathologies, including cancer, hypertension, arrhythmias, drug abuse and schizophrenia. RGS proteins ‘turn off’ heterotrimeric (αβγ) G-proteins and thereby determine the duration of G protein–mediated signaling events. Therefore, RGS proteins function as GTPase Activating Proteins (GAPs), and this GAP activity is mediated by allosteric interactions.
RGS proteins are selective for binding to the transition state of Gα(GTP → GDP + Pi), which can be mimicked by Gα-GDP bound with the planar ion aluminum tetrafluoride (AlF4−).
Like many signaling proteins, RGS proteins comprise a large and diverse family. In human genome, Thirty-seven RGS proteins are encoded by gene loci; this collection of related proteins has been divided into 10 different subfamilies based on the relatedness of their RGS domain sequence and their multiple domain architectures. About 20 ‘canonical’ RGS proteins can in theory downregulate any of the 16 activated Gα subunits, although in practice they interact only with members of the Gi and Gq families.
In these proteins, the ~120-residue RGS homology domain functions as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for GTP-bound Gα subunits.
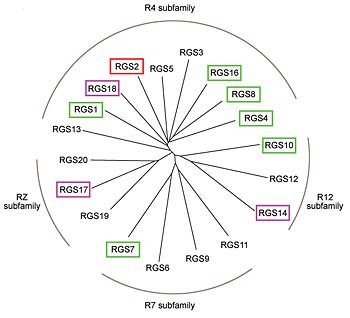
Phylogenetic tree of 19 human RGS domains.
RGS proteins whose activity was tested are colored. RGS proteins with high GAP activity (green), RGS proteins with low but discernible activities (purple) and RGS2 had no measurable activity (red).
[1]
In addition to these domains, diverse proteins subfamilies that include the ~120-residue RGS homology domain bear additional protein-protein interaction domains beyond their signature RGS domain with Gα GAP activity.
Heterotrimeric G-proteins family
Human heterotrimeric G-proteins are derived from 35 genes: 16 encoding α subunits, 5 β and 14 γ subunits. The α subunits function as guanine nucleotide on-off switches, mechanistically similar to other G-proteins that are enzymatic GTPases (Milligan and Kostenis 2006).
G-proteins interact with diverse protein partners, such as G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), downstream effectors, and other proteins. One important G-protein interaction is with members of the RGS protein family. This interaction occurs when the G-protein alpha subunit is activated, and depends on the Gα class, which in turn depends on their sequence that classifies them into several sub-types.
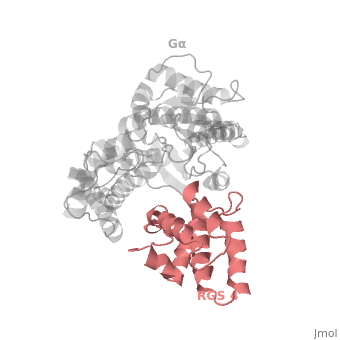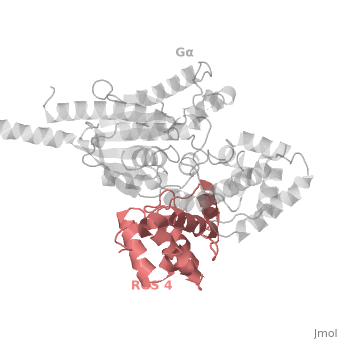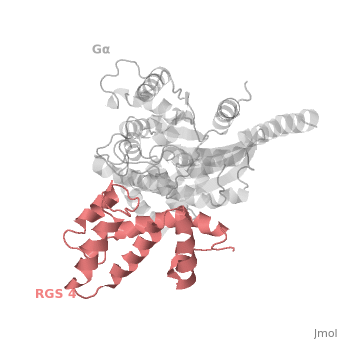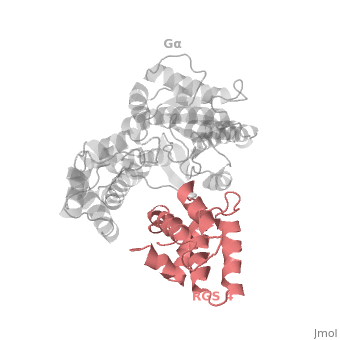
Structural highlights
1AGR is a tetramer structure of two identical duplicate crystal complex of (tetramer excess stability of crystal structure).
in darkmagenta cartoon diagram: The RGS4 domain corresponds to an array of nine α-helices that fold into two small subdomains. The terminal subdomain contains the N and C termini of the box and is formed by α1, α2, α3, α8, and α9. Helices α1 and α9 lie in antiparallel orientation, juxtaposing the N and C termini of the box. The larger bundle subdomain, formed by α4, α5, α6, and α7, is a classic right-handed, antiparallel four-helix bundle. Both subdomains are required for GAP activity.
Gαi1 subunits adopt a conserved fold composed of α helical domain (light gray cartoon), a helical domain of six α helices and a GTPase domain (dark gray cartoon).The GTPase domain hydrolyzes GTP and provides most of Gα's binding surfaces for Gβγ, receptors, effectors and RGS proteins. The GTPase domain contains three flexible regions designated presented as blue sticks, presented as magenta sticks and presented as green sticks that change conformation in response to GTP binding and hydrolysis. The three switch regions of Gαi1: residues 176–184, 201–215, and 233–241, respectively (red cartoon). GDP–Mg+2+2, bound in the active site of Gαi1 is shown as a ball-and-stick model. For clarity, AlF4 is omitted from the figure.[2]