Regulator of G protein signaling
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
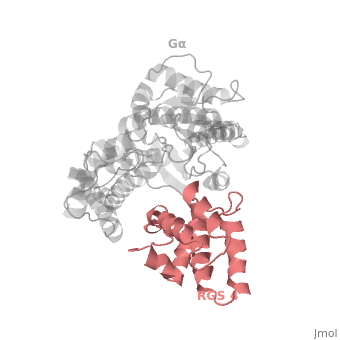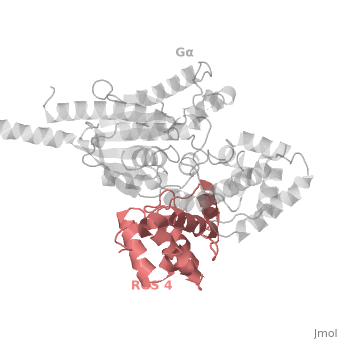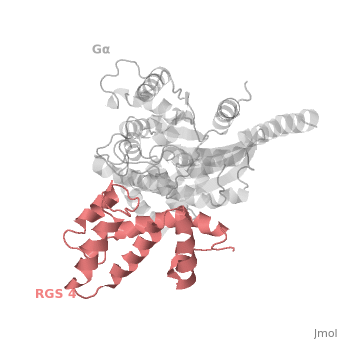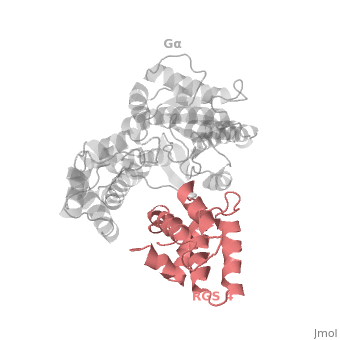
==Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) interactions with G proteins – RGS4-Gα<sub>i</sub> as a model structure.== | ==Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) interactions with G proteins – RGS4-Gα<sub>i</sub> as a model structure.== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1agr' size='340' side='right' caption='RGS4-Gα complex' scene='70/701447/Gi-rgs4/9' pspeed= | + | <StructureSection load='1agr' size='340' side='right' caption='RGS4-Gα complex' scene='70/701447/Gi-rgs4/9' pspeed='8'> |
== RGS proteins == | == RGS proteins == | ||
Regulator of G-proteins signaling (RGS) proteins play a critical role in many G protein-dependent signaling pathways. Thus, RGS proteins have been implicated in a wide range of pathologies, including cancer, hypertension, arrhythmias, drug abuse and schizophrenia. RGS proteins ‘turn off’ heterotrimeric (αβγ) G-proteins and thereby determine the duration of G protein–mediated signaling events. Therefore, RGS proteins function as GTPase Activating Proteins (GAPs), and this GAP activity is mediated by allosteric interactions. | Regulator of G-proteins signaling (RGS) proteins play a critical role in many G protein-dependent signaling pathways. Thus, RGS proteins have been implicated in a wide range of pathologies, including cancer, hypertension, arrhythmias, drug abuse and schizophrenia. RGS proteins ‘turn off’ heterotrimeric (αβγ) G-proteins and thereby determine the duration of G protein–mediated signaling events. Therefore, RGS proteins function as GTPase Activating Proteins (GAPs), and this GAP activity is mediated by allosteric interactions. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
Image:Kosloff-NSMB2011-Fig1b.jpg|350px|family of canonical RGS proteins | Image:Kosloff-NSMB2011-Fig1b.jpg|350px|family of canonical RGS proteins | ||
| - | poly 131 45 213 41 210 110 127 109 | + | poly 131 45 213 41 210 110 127 109 |
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
Phylogenetic tree of 19 human RGS domains. | Phylogenetic tree of 19 human RGS domains. | ||
Revision as of 08:04, 14 May 2015
Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) interactions with G proteins – RGS4-Gαi as a model structure.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Kosloff M, Travis AM, Bosch DE, Siderovski DP, Arshavsky VY. Integrating energy calculations with functional assays to decipher the specificity of G protein-RGS protein interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 19;18(7):846-53. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2068. PMID:21685921 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2068
- ↑ Tesmer JJ, Berman DM, Gilman AG, Sprang SR. Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF4--activated G(i alpha1): stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell. 1997 Apr 18;89(2):251-61. PMID:9108480
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ali Asli, Denise Salem, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky