Regulator of G protein signaling
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
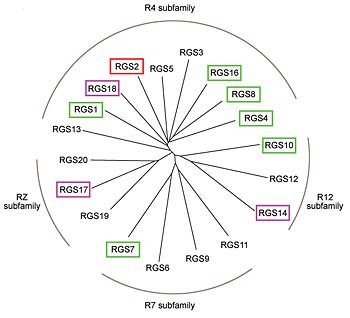
RGS proteins whose activity was tested are colored by their GAP activity, RGS proteins with high GAP activity (green), RGS proteins with low but discernible activities (purple) and RGS2 had no measurable activity (red). | RGS proteins whose activity was tested are colored by their GAP activity, RGS proteins with high GAP activity (green), RGS proteins with low but discernible activities (purple) and RGS2 had no measurable activity (red). | ||
<ref>PMID: 21685921</ref> | <ref>PMID: 21685921</ref> | ||
| + | |||
In addition to these domains, diverse proteins subfamilies that include the ~120-residue RGS homology domain bear additional protein-protein interaction domains beyond their signature RGS domain with Gα GAP activity. R7-subfamily members share a multi-domain protein architecture composed of DEP and GGL domains on the N-terminal side of the RGS domain. R12-subfamily members possess a tandem repeat of Ras binding domains (RBDs) and a single GoLoco motif. | In addition to these domains, diverse proteins subfamilies that include the ~120-residue RGS homology domain bear additional protein-protein interaction domains beyond their signature RGS domain with Gα GAP activity. R7-subfamily members share a multi-domain protein architecture composed of DEP and GGL domains on the N-terminal side of the RGS domain. R12-subfamily members possess a tandem repeat of Ras binding domains (RBDs) and a single GoLoco motif. | ||
Revision as of 12:41, 18 May 2015
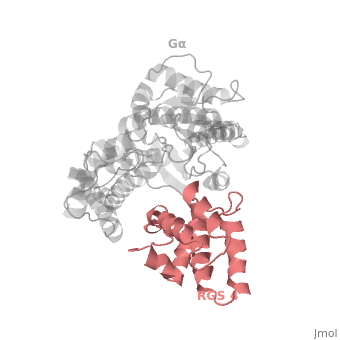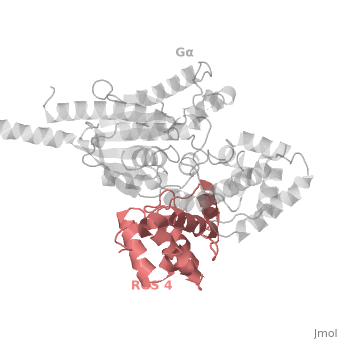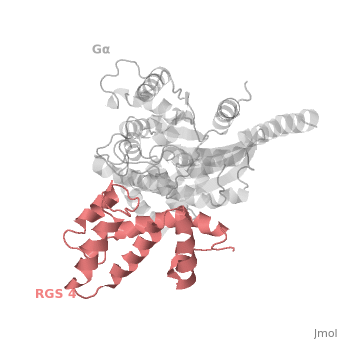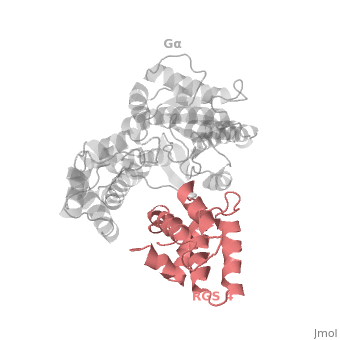
Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) interactions with G proteins – RGS4-Gαi as a model structure.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Kosloff M, Travis AM, Bosch DE, Siderovski DP, Arshavsky VY. Integrating energy calculations with functional assays to decipher the specificity of G protein-RGS protein interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 19;18(7):846-53. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2068. PMID:21685921 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2068
- ↑ Milligan G, Kostenis E. Heterotrimeric G-proteins: a short history. Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;147 Suppl 1:S46-55. PMID:16402120 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706405
- ↑ Tesmer JJ, Berman DM, Gilman AG, Sprang SR. Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF4--activated G(i alpha1): stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell. 1997 Apr 18;89(2):251-61. PMID:9108480
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ali Asli, Denise Salem, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky