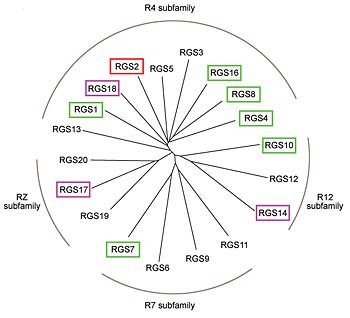
Regulator of G protein signaling
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
== RGS-G proteins interactions == | == RGS-G proteins interactions == | ||
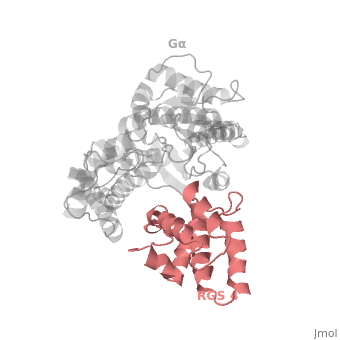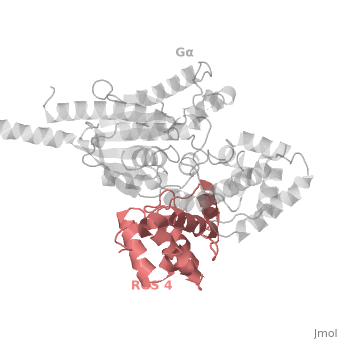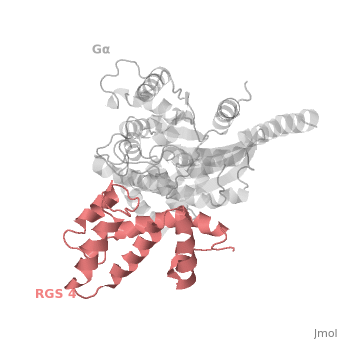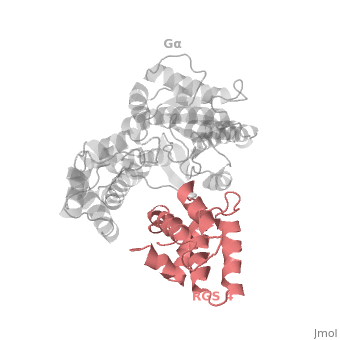
| - | There are many RGS protein residues in the vicinity of the <scene name='70/701447/Rgs4-ga_interface/3'>RGS domain–Gα interface</scene> that contribute to RGS-G proteins interaction,RGS protein shown as wheat cartoon and Gα<sub>i1</sub> subunit shown as white surface. These residues classified into two major groups. First group is Significant & Conserved residues shown as red spheres that located mainly in the center of the RGS domain–Gα interface and have the primary role in accelerating Gα GTPase by stabilizing Gα in a conformation optimal for GTP hydrolysis. Whereas the second group is putative Modulatory residues shown as purpule spheres that located mostly at the periphery of this interface where they contribute to Gα subunit recognition.<ref>PMID: 21685921</ref> | + | There are many RGS protein residues in the vicinity of the <scene name='70/701447/Rgs4-ga_interface/3'>RGS domain–Gα interface</scene> that contribute to RGS-G proteins interaction, RGS protein shown as wheat cartoon and Gα<sub>i1</sub> subunit shown as white surface. These residues classified into two major groups. First group is Significant & Conserved residues shown as red spheres that located mainly in the center of the RGS domain–Gα interface and have the primary role in accelerating Gα GTPase by stabilizing Gα in a conformation optimal for GTP hydrolysis. Whereas the second group is putative Modulatory residues shown as purpule spheres that located mostly at the periphery of this interface where they contribute to Gα subunit recognition.<ref>PMID: 21685921</ref> |
Gα subunits participate in a range of interactions with a variety of other proteins. Therefore, they have interfaces than interact selectively with receptors, effector subfamilies and RGS proteins. However the <scene name='70/701447/Gi-rgs4_interface/1'>Gα residues</scene> that interact specifically with RGS proteins are highly conserved shown as red spheres. Gα Residues located on the three Gα switch regions interact with Significant & Conserved RGS residues. This makes sense because of the pivotal role of the switch regions in GTP hydrolysis that is catalyzed by RGS proteins. On the other hand, Gα residues located in switch regions II and III and multiple residues in the Gα all-helical domain interact with Modulatory RGS residues. | Gα subunits participate in a range of interactions with a variety of other proteins. Therefore, they have interfaces than interact selectively with receptors, effector subfamilies and RGS proteins. However the <scene name='70/701447/Gi-rgs4_interface/1'>Gα residues</scene> that interact specifically with RGS proteins are highly conserved shown as red spheres. Gα Residues located on the three Gα switch regions interact with Significant & Conserved RGS residues. This makes sense because of the pivotal role of the switch regions in GTP hydrolysis that is catalyzed by RGS proteins. On the other hand, Gα residues located in switch regions II and III and multiple residues in the Gα all-helical domain interact with Modulatory RGS residues. | ||
Revision as of 13:26, 24 May 2015
Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) interactions with G proteins – RGS4-Gαi as a model structure.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Kosloff M, Travis AM, Bosch DE, Siderovski DP, Arshavsky VY. Integrating energy calculations with functional assays to decipher the specificity of G protein-RGS protein interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 19;18(7):846-53. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2068. PMID:21685921 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2068
- ↑ Milligan G, Kostenis E. Heterotrimeric G-proteins: a short history. Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;147 Suppl 1:S46-55. PMID:16402120 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706405
- ↑ Tesmer JJ, Berman DM, Gilman AG, Sprang SR. Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF4--activated G(i alpha1): stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell. 1997 Apr 18;89(2):251-61. PMID:9108480
- ↑ Kosloff M, Travis AM, Bosch DE, Siderovski DP, Arshavsky VY. Integrating energy calculations with functional assays to decipher the specificity of G protein-RGS protein interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 19;18(7):846-53. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2068. PMID:21685921 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2068
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ali Asli, Denise Salem, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky