We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Talk:SCF-c-Kit
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction)== | ==Introduction)== | ||
<StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
| - | This is a default text for your page '''RTK activation by dimerization''' | + | This is a default text for your page '''RTK activation by dimerization'''. |
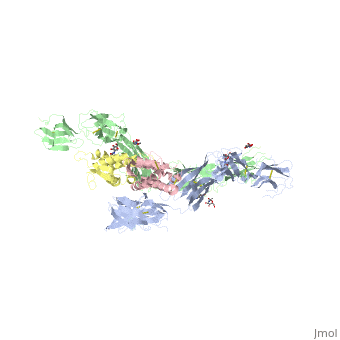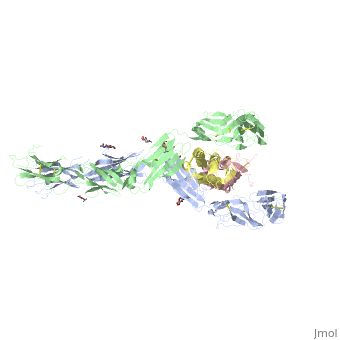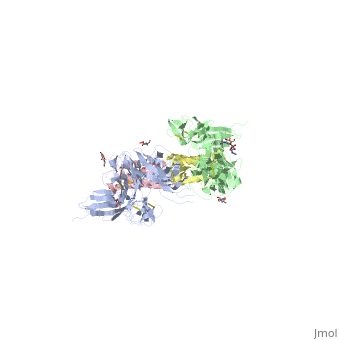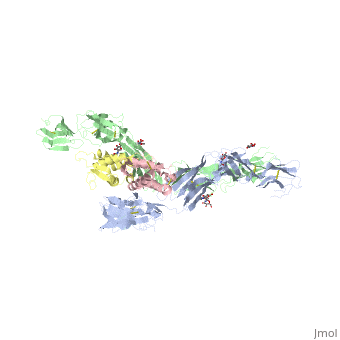
Stem cell factor (SCF) is a cytokine that mediates its diverse cellular responses by binding to and activating the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) KIT (also known as SCF receptor).It was initially discovered as an oncogene in a feline retrovirus. SCF functions as a noncovalent homodimer, and both membrane-anchored and soluble forms of SCF have been described. | Stem cell factor (SCF) is a cytokine that mediates its diverse cellular responses by binding to and activating the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) KIT (also known as SCF receptor).It was initially discovered as an oncogene in a feline retrovirus. SCF functions as a noncovalent homodimer, and both membrane-anchored and soluble forms of SCF have been described. | ||
KIT was initially discovered as an oncogene in a feline retrovirus. | KIT was initially discovered as an oncogene in a feline retrovirus. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
the D1-D2-D3 region of KIT might be a functional unit that is poised for SCF binding, thus leading to subsequent KIT dimerization which is driven by dimeric SCF molecules. In addition, while the overall structure of SCF bound to KIT is similar to the structure of free SCF, there are differences in the angle between the two protomers, in the conformations of the connecting loops, and in the structures of the flexible N terminus of the molecule. | the D1-D2-D3 region of KIT might be a functional unit that is poised for SCF binding, thus leading to subsequent KIT dimerization which is driven by dimeric SCF molecules. In addition, while the overall structure of SCF bound to KIT is similar to the structure of free SCF, there are differences in the angle between the two protomers, in the conformations of the connecting loops, and in the structures of the flexible N terminus of the molecule. | ||
| - | The structure is also characterized by the existence of a large cavity at the center of the complex. Each protomer of SCF binds to a single KIT molecule and that receptor dimerization is driven by SCF dimers, leading to additional receptor-receptor interactions. | + | The structure is also characterized by the existence of a large cavity at the center of the complex. <scene name='70/701458/Scf_bound_to_kit/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> Each protomer of SCF binds to a single KIT molecule and that receptor dimerization is driven by SCF dimers, leading to additional receptor-receptor interactions. |
Current revision
Introduction)
| |||||||||||