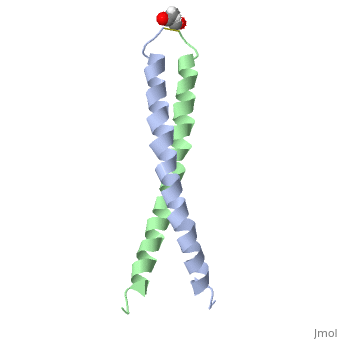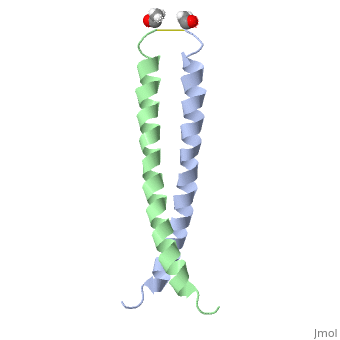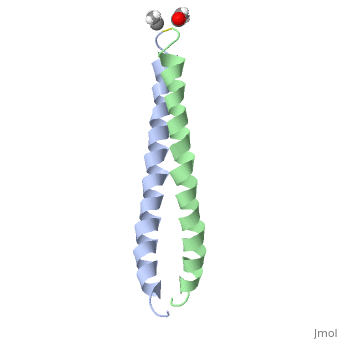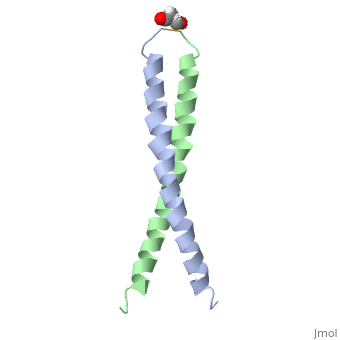
Image:1jun.png Figure 1. A 3-D representation of the two alpha helices which form a coiled coil complex with acetate (PDB code
1jun)
[1] Introduction
The c-Jun protein is a member of transcription factors which consist of a basic region leucine zipper region [1]. Originally identified by its homology to v-jun, the oncogene from the avian sarcomoa virus [2]. All these leucine zipper factors bind to DNA in one of two states: homo or heterodimers [3]. In conjunction with the c-Fos protein these two proteins bind to specific regions of DNA strands. Together these two proteins form the c-fos/c-jun complex which help regulate cell growth and differentiation [1]. The members of the jun and fos families include three Jun proteins and four Fos proteins (c-Jun, JunB, JunD,c-Fos, Fos-B, Fra1, and Fra2) [1]. Regulation of the complex iteslf is done by interactions between the protein and DNA in addition to the protein-protein interactions between each of the leucine zipper domains [1]. See Transcription and RNA Processing.
Structure Overview
The structure of c-Jun is comprised of a leucine zipper as previously stated. This dimerization motif may be in one of two classes, both of which are required for DNA-binding transcription factors; the basic-domain leucine zipper proteins (bZIP) and the basic helix loop-helix-leucine zipper proteins(bHLH-ZIP) [3]. The strand becomes an elongated coiled coil. This is formed by residues at the a and d positions in each of the two monomers, whereby they create hydrophobic centers which conform to the "knobs into holes" model by Crick. [3]. Amino acids at these a and d positions are each surrounded by 4 additional residues from adjacent a-helix monomer [3].
The a and d residues each exhibit varying types of packing in terms of this "knobs into holes" theory. According to Harbury et al.(24) the leucines at the a positions are packed "parallel" in such a way that the C-alpha-C-beta bond vector lies in a parallel manner to the C-alpha-C-alpha vector at the base of the acceptor hole on adjacent helix [1]. Whereas the opposite is true for the leucines in the d positions. Here the residues are packed in a "perpendicular" nature [1]. The bond vector of the C-alpha-C-beta pack approximately perpendicular to the C-alpha-C-alpha vector at the base of the hole of the second helix in which it packs [1]. Therefore only the leucine side chains in the a positions, which point away from the boundary, make van der Waals interactions [1].
Protein Function
The primary function of c-Jun is in regards to DNA transcription. Specifically, the protein is involved in proliferation, apoptosis, oncogenic transformation and various cellular processes [4]. For instance cells which lack an allele for c-jun have been shown to stunt growth both in vitro and in vivo [2]. Whereas a prolonged and therefore strong induction of c-jun has been in response to such things as tumor necrosis factor or stress inducing stimuli such as ultra violet radiation [2].
Protein Regulation
Changes made in the phosphorylation state of specific amino acids is one means by which c-Jun regulates transcription [5]. To date two seperate sites of phosphorylation have been identified. One is located at the N-terminal end in which the amino acids Ser63 and Ser73 are phosphorylated in response to ras expression. When ras is expressed, and Ser63 and Ser73 are phosphorylated,and transcriptional activity of c-Jun increases. The second site is located at the C-terminal which is very close in proximity to the DNA binding domain. Here the residues are Thr214, Ser226, and Ser 232 [5]. Unlike the two serines at the N-terminal end, phosphorylation at the C-terminal end inhibits DNA binding to c-Jun [5]. Therefore with the expression of such oncogenes as ras dephsphorylation of these three residues occurs.
Psychological Influences
The stress-induced signaling cascade may also active c-Jun by phosphorylation. The N-ternminal protein kinase phosphorylates Ser63 and Ser73 [6] . Another mechanism for the activation however is interestingly through intracellular calcium concentrations. Increasing these concentrations by opening the L-type voltage gated calcium channels leads to serines phosphorlation.
It was found that the N-terminus contains both calcium and stress-regulated transcriptional activation domains [6]. According to the study,distinct mechanisms of c-Jun control function by calcium and stress signals [6].
Additional Resources
To See Additional information, see: Transcription and RNA Processing