This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
3hts
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:3hts.jpg|left|200px]] | + | [[Image:3hts.jpg|left|200px]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | '''HEAT SHOCK TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR/DNA COMPLEX''' | + | {{Structure |
| + | |PDB= 3hts |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>3hts</scene>, resolution 1.75Å | ||
| + | |SITE= | ||
| + | |LIGAND= <scene name='pdbligand=GOL:GLYCEROL'>GOL</scene> | ||
| + | |ACTIVITY= | ||
| + | |GENE= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''HEAT SHOCK TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR/DNA COMPLEX''' | ||
| + | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 16: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 3HTS is a [ | + | 3HTS is a [[Single protein]] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kluyveromyces_lactis Kluyveromyces lactis]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3HTS OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| - | A new use for the 'wing' of the 'winged' helix-turn-helix motif in the HSF-DNA cocrystal., Littlefield O, Nelson HC, Nat Struct Biol. 1999 May;6(5):464-70. PMID:[http:// | + | A new use for the 'wing' of the 'winged' helix-turn-helix motif in the HSF-DNA cocrystal., Littlefield O, Nelson HC, Nat Struct Biol. 1999 May;6(5):464-70. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10331875 10331875] |
[[Category: Kluyveromyces lactis]] | [[Category: Kluyveromyces lactis]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category: transcription regulation]] | [[Category: transcription regulation]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Mar 20 19:05:21 2008'' |
Revision as of 17:05, 20 March 2008
| |||||||
| , resolution 1.75Å | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
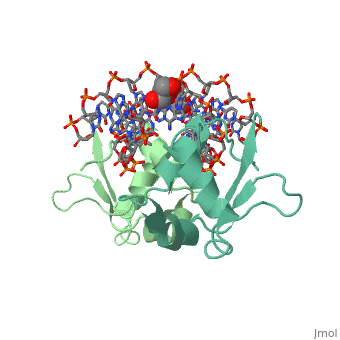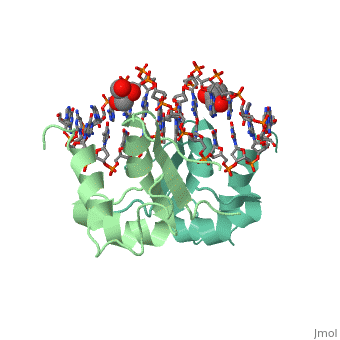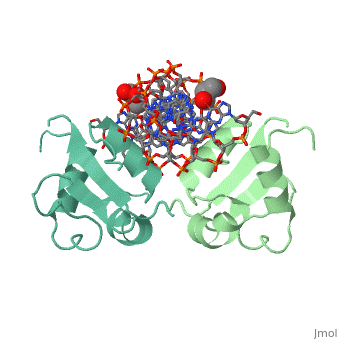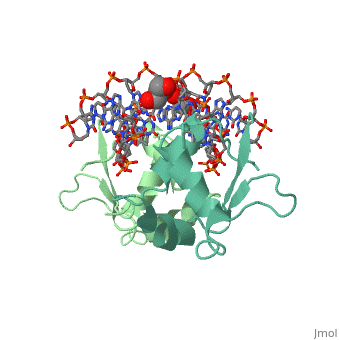
HEAT SHOCK TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR/DNA COMPLEX
Overview
The 1.75 A crystal structure of the Kluyveromyces lactis heat shock transcription factor (HSF) DNA-binding domain (DBD) complexed with DNA reveals a protein-DNA interface with few direct major groove contacts and a number of phosphate backbone contacts that are primarily water-mediated interactions. The DBD, a 'winged' helix-turn-helix protein, displays a novel mode of binding in that the 'wing' does not contact DNA like all others of that class. Instead, the monomeric DBD, which crystallized as a symmetric dimer to a pair of nGAAn inverted repeats, uses the 'wing' to form part of the protein-protein contacts. This dimer interface is likely important for increasing the DNA-binding specificity and affinity of the trimeric form of HSF, as well as for increasing cooperativity between adjacent trimers.
About this Structure
3HTS is a Single protein structure of sequence from Kluyveromyces lactis. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
A new use for the 'wing' of the 'winged' helix-turn-helix motif in the HSF-DNA cocrystal., Littlefield O, Nelson HC, Nat Struct Biol. 1999 May;6(5):464-70. PMID:10331875
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Mar 20 19:05:21 2008