User:Rana Saad/The human GABAb receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
GABA is the major inhibitory [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neurotransmitter neurotransmitter] in the central nervous system (CNS). It plays a key role in modulating neuronal activity since it binds to specific transmembrane receptors ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GABAA_receptor GABA<sub>A</sub>],GABA<sub>B</sub> and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GABAA-rho_receptor GABA<sub>C</sub>]) in the plasma membrane of both pre- and postsynaptic neuronal level. | GABA is the major inhibitory [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neurotransmitter neurotransmitter] in the central nervous system (CNS). It plays a key role in modulating neuronal activity since it binds to specific transmembrane receptors ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GABAA_receptor GABA<sub>A</sub>],GABA<sub>B</sub> and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GABAA-rho_receptor GABA<sub>C</sub>]) in the plasma membrane of both pre- and postsynaptic neuronal level. | ||
===GABA<sub>B</sub> receptors=== | ===GABA<sub>B</sub> receptors=== | ||
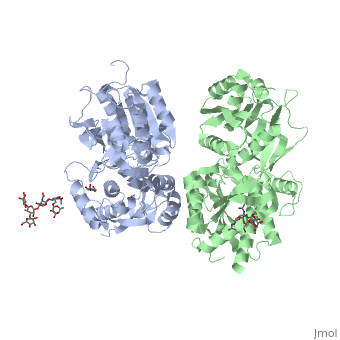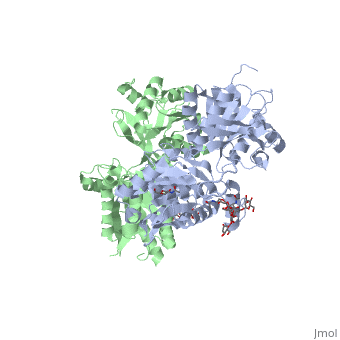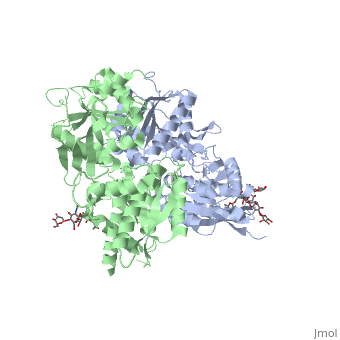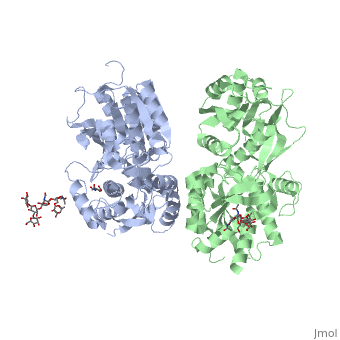
| - | Mammalian GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is a class C [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/G_protein-coupled_receptor#3D_Structures_of_G_protein-coupled_receptors G-protein coupled receptor]<ref>PMID:23237917</ref>. Its structure is similar to [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Metabotropic_glutamate_receptor | + | Mammalian GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is a class C [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/G_protein-coupled_receptor#3D_Structures_of_G_protein-coupled_receptors G-protein coupled receptor]<ref>PMID:23237917</ref>. Its structure is similar to [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Metabotropic_glutamate_receptor metabotropic glutamate receptor] (mGluR) ligand binding domain. GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is central to inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain and so is considered a good candidate for treatments against alcoholism, stress and number of brain diseases<ref>PMID:19913201</ref>. |
[[Image:GABAb.receptor.cartoon2.png|thumb|200px]] | [[Image:GABAb.receptor.cartoon2.png|thumb|200px]] | ||
=='''''Structure'''''== | =='''''Structure'''''== | ||
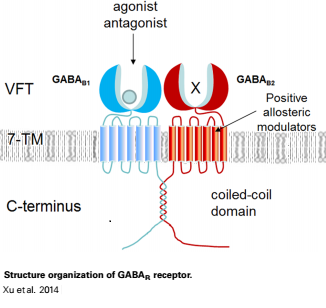
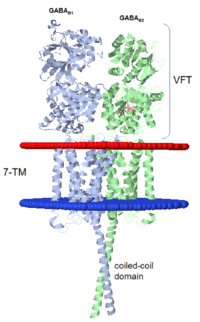
| - | GABA<sub>B</sub> functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of GABA<sub>B1</sub> (GBR1) and GABA<sub>B2</sub> (GBR2). GBR1 is responsible for ligand-binding. GBR2, on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunits. The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is one of only a few obligate receptor heterodimers currently known. There is no crystal or NMR structure of the complete protein, but the extracellular and intracellular domains of it . | + | GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of GABA<sub>B1</sub> (GBR1) and GABA<sub>B2</sub> (GBR2). GBR1 is responsible for ligand-binding. GBR2, on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunits. The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is one of only a few obligate receptor heterodimers currently known. There is no crystal or NMR structure of the complete protein, but the extracellular and intracellular domains of it . |
===GBR1 and GBR2 subunits structure=== | ===GBR1 and GBR2 subunits structure=== | ||
Each subunit is a domain of seven-transmembrane helixes, composed of a large extracellular domain - venus flytrap (VFT), its called like that becouse its like the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venus_flytrap venus flytrap] while binding agonists and antagonists. | Each subunit is a domain of seven-transmembrane helixes, composed of a large extracellular domain - venus flytrap (VFT), its called like that becouse its like the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venus_flytrap venus flytrap] while binding agonists and antagonists. | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 8 July 2015
| |||||||||||