We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
FMDV 3C
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Foot and Mouth Disease 3C Protease'''. | '''Foot and Mouth Disease 3C Protease'''. | ||
'''By, Erica Martel''' | '''By, Erica Martel''' | ||
| - | The viral | + | |
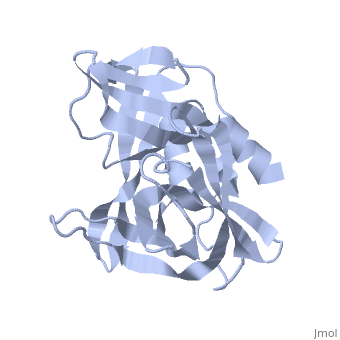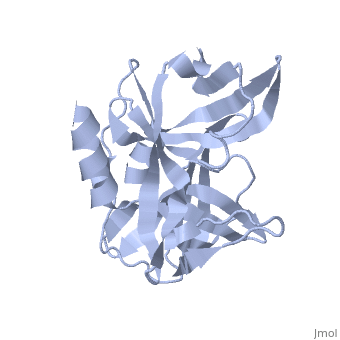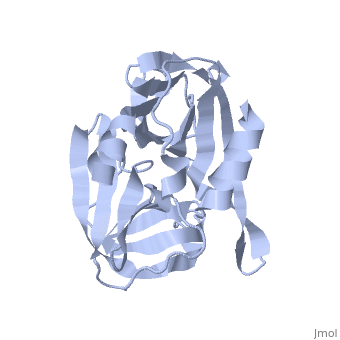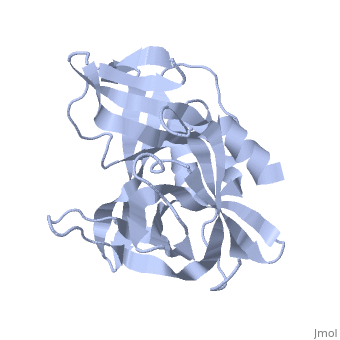
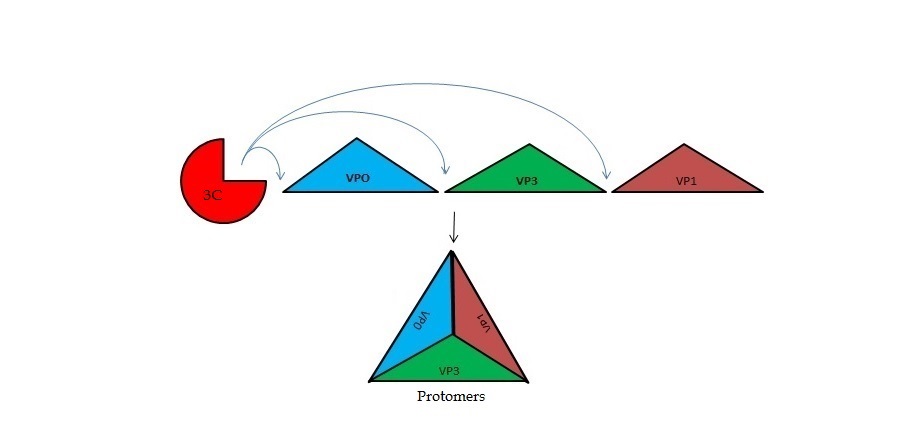
| + | The FMDV viral genome is translated as a single polypeptide precursor that must be cleaved into functional proteins by virally encoded proteases. The FMDV 3C protease is responsible for most cleavages of the viral polyprotein (10 out of the 13 cleavages) and has a highly conserved amino acid sequence across different viral serotypes, making the enzyme an attractive target for inhibitor design and antiviral drugs. The 3C protease cuts itself out of the poly protein and is responsible for processing the P1 peptide into three viral peptides, VP0 VP3, and VP1. The VP0 peptide is further processed into VP4 and VP2 by an unknown mechanism. To form the FMDV capsid fully processed VPs assemble into a triangular protomer, Figure below. Five protomers come together to make a pentamer, twelve pentamers conjoin to complete the virus shell. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:FMDV_3C_Prot.jpeg]] | [[Image:FMDV_3C_Prot.jpeg]] | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | FMDV 3C has | + | FMDV 3C has also been shown to have a number of reported functions on the host cell. This includes inhibition of host cell protein synthesis by cleavage of translation initiation factors eIF4A, eIF4G, as well as proteolytic cleavage Histone H3, NEMO, SAM68, and microtubulin associated proteins. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
FMDV, the etiologic agent of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD), affects a variety of cloven-hoofed animals in different parts of the world, but to date is not present in North America or Australia. FMDV is extremely infectious and displays high adaptability as well as short incubation times. This virus exists in the form of seven different serotypes (A, O, C, Asia-1, and South African Territories - SAT - 1, 2, and 3) and it has innumerable subtypes. These factors, in conjunction with ecological dynamics of livestock, result in a rapid, widespread, and devastating disease that causes exorbitant economic losses for the agricultural industry. FMDV outbreaks impact local and global food-animal markets as trade regulations restrict exportation of products from FMDV endemic areas, stressing the need for a reliable diagnostic tool and effective, yet safe, vaccinations. FMDV is also on the “A” list of infectious diseases of animals of the OIE, the world organization for animal health which means that it is a transmissible disease that has the potential for very rapid spread and is of serious socioeconomic importance. | FMDV, the etiologic agent of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD), affects a variety of cloven-hoofed animals in different parts of the world, but to date is not present in North America or Australia. FMDV is extremely infectious and displays high adaptability as well as short incubation times. This virus exists in the form of seven different serotypes (A, O, C, Asia-1, and South African Territories - SAT - 1, 2, and 3) and it has innumerable subtypes. These factors, in conjunction with ecological dynamics of livestock, result in a rapid, widespread, and devastating disease that causes exorbitant economic losses for the agricultural industry. FMDV outbreaks impact local and global food-animal markets as trade regulations restrict exportation of products from FMDV endemic areas, stressing the need for a reliable diagnostic tool and effective, yet safe, vaccinations. FMDV is also on the “A” list of infectious diseases of animals of the OIE, the world organization for animal health which means that it is a transmissible disease that has the potential for very rapid spread and is of serious socioeconomic importance. | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | Vaccines against FMDV are used where the disease is endemic | + | |
| - | + | Vaccines against FMDV exist and are used where the disease is endemic. The primary vaccine utilized in endemic areas is inactivated FMDV. The inactive FMDV vaccine has drawbacks such as difficulty telling vaccinated from infected animals and it carries the risk that a FMDV outbreak will be caused by incomplete inactivation of the vaccine virus. As a result, there has been interest in producing empty virus like particles (VLPs) for use as vaccines against FMD. Due to the FMDV 3C protease activity on host cell proteins producing large amounts of VLPs has been difficult. | |
| - | + | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<scene name='70/702408/Fmdv_3c_protease_type_a10/6'>FMDV 3C Protease</scene> | <scene name='70/702408/Fmdv_3c_protease_type_a10/6'>FMDV 3C Protease</scene> | ||
Revision as of 15:38, 28 July 2015
FMDV 3C Protease
| |||||||||||
References
references [1]