User:Rana Saad/The human GABAb receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
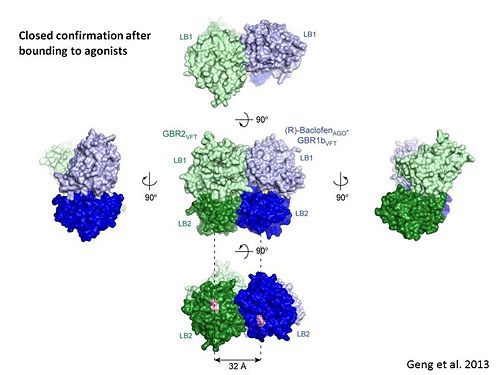
LB1 and LB2 resdues of GBR1 interact with the GABA<sub>B</sub> agonsits such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-Aminobutyric_acid GABA],[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baclofen baclofen]. as a results of this interacting '''closed conformation''' will be stabilized when <scene name='70/701448/Gaba_ligand/4'> GBR1 subunit bound to GABA</scene> (PDB 4MS3) or <scene name='70/701448/Baclofen/3'>bound to baclofen</scene> (PDB 4MS4) and other agonists. | LB1 and LB2 resdues of GBR1 interact with the GABA<sub>B</sub> agonsits such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-Aminobutyric_acid GABA],[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baclofen baclofen]. as a results of this interacting '''closed conformation''' will be stabilized when <scene name='70/701448/Gaba_ligand/4'> GBR1 subunit bound to GABA</scene> (PDB 4MS3) or <scene name='70/701448/Baclofen/3'>bound to baclofen</scene> (PDB 4MS4) and other agonists. | ||
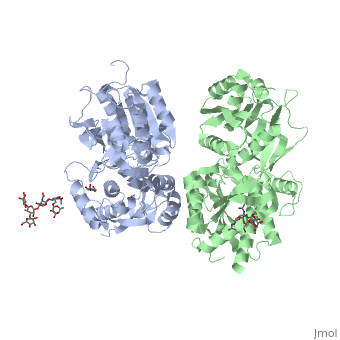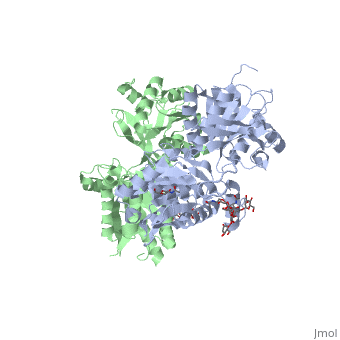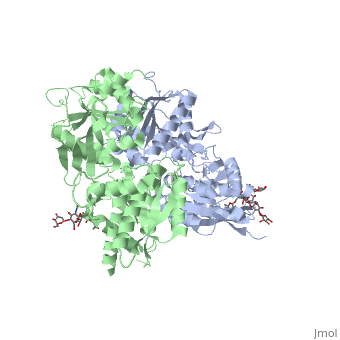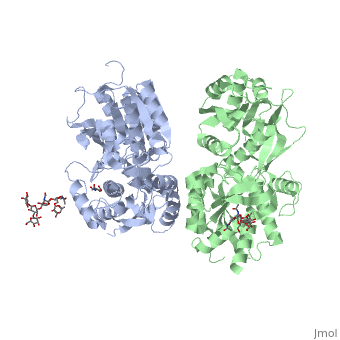
| - | [[Image:GABAb receptor in the Apo form.jpg|center| | + | [[Image:GABAb receptor in the Apo form.jpg|center|500px]] |
| - | [[Image:GABAb bound to agonist.jpg|center| | + | [[Image:GABAb bound to agonist.jpg|center|500px]] |
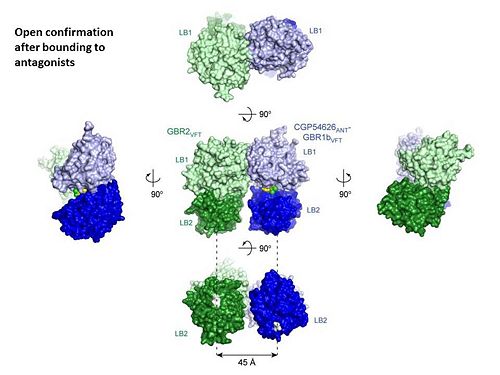
GABA<sub>B</sub> antgonists such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saclofen saclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-46381.html CGP46381], [http://www.hellobio.com/phaclofen.html?picat=&q=phaclofen phaclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-35348.html?picat=&q=CGP+35348 CGP35348] and [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-54626-hydrochloride.html?picat=&q=CGP+54626 CGP54626], mostly intercat with LB1 resduses of GBR1. both ends of the antagonist bind the LB1, which produce '''open confirmation''' of GBR1. | GABA<sub>B</sub> antgonists such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saclofen saclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-46381.html CGP46381], [http://www.hellobio.com/phaclofen.html?picat=&q=phaclofen phaclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-35348.html?picat=&q=CGP+35348 CGP35348] and [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-54626-hydrochloride.html?picat=&q=CGP+54626 CGP54626], mostly intercat with LB1 resduses of GBR1. both ends of the antagonist bind the LB1, which produce '''open confirmation''' of GBR1. | ||
it is very easy to notice the '''open confirmation''' when : | it is very easy to notice the '''open confirmation''' when : | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
<scene name='70/701448/Ant_cg835348/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP35348</scene> (PDB 4MR8). | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_cg835348/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP35348</scene> (PDB 4MR8). | ||
<scene name='70/701448/Ant_CGP54626/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP54626</scene> (PDB 4MR7). | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_CGP54626/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP54626</scene> (PDB 4MR7). | ||
| - | [[Image:GABAb.bound.to.antagonist.jpg|center| | + | [[Image:GABAb.bound.to.antagonist.jpg|center|500px]] |
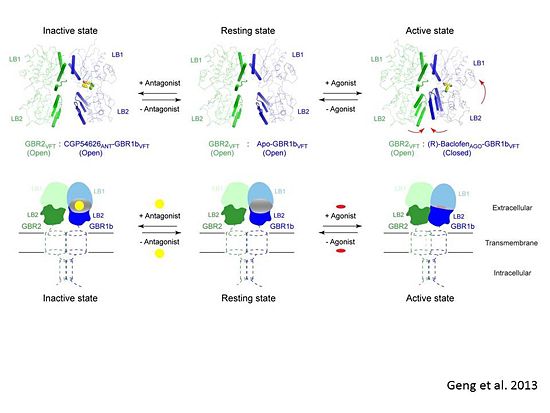
In short, the apo and antagonist-bound structures represent the resting state of the receptor; the agonist-bound complex corresponds to the | In short, the apo and antagonist-bound structures represent the resting state of the receptor; the agonist-bound complex corresponds to the | ||
active state. Both subunits, GBR1 and GBR2 adopt an open conformation at rest, and only GBR1 closes upon agonist-induced receptor activation. | active state. Both subunits, GBR1 and GBR2 adopt an open conformation at rest, and only GBR1 closes upon agonist-induced receptor activation. | ||
| - | [[Image:Summery for the mechanism.jpg|center| | + | [[Image:Summery for the mechanism.jpg|center|550px]] |
==='''''The intercellular dimerization motif'''''=== | ==='''''The intercellular dimerization motif'''''=== | ||
Revision as of 13:00, 8 August 2015
| |||||||||||