User:Rana Saad/The human GABAb receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
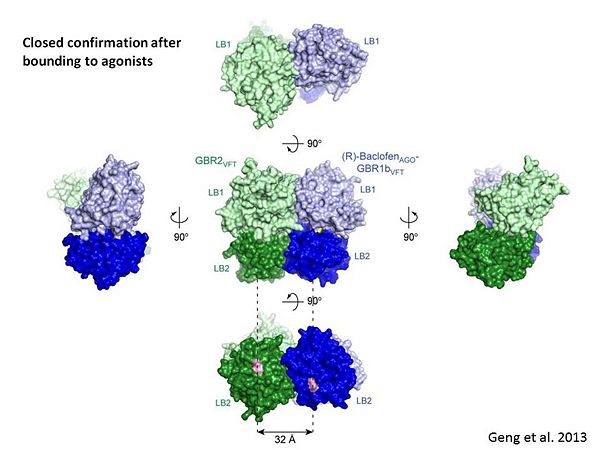
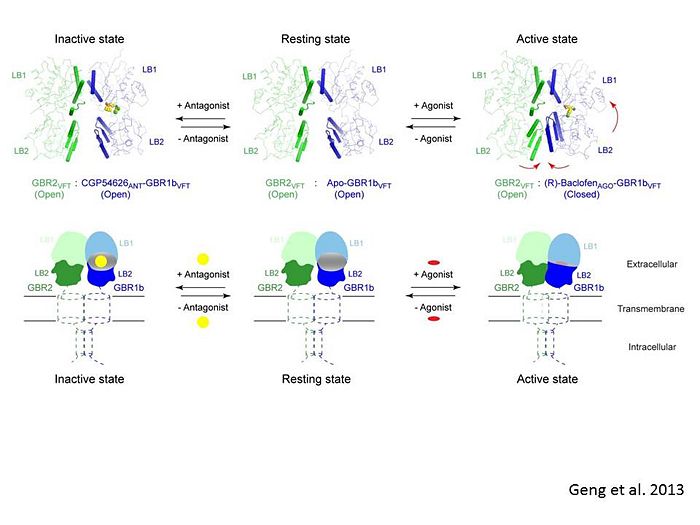
The agonist binding induces the formation of an additional heterodimer interface between the LB2 domains of GBR1bVFT and GBR2VFT subunits. The LB2-LB2 interface buries over 1,300 Å2 of solvent accessible surface area, has poor shape complementarity, and is dominated by polar interactions. The LB2-LB2 interaction is mediated by two strand-loop-helix motifs from each LB2 domain. <scene name='70/701448/Lb2-lb2_interaction/3'> The neighboring strands f and g are part of the central β-sheet in LB2, and helices F and G flank the β-sheet</scene>. (GBR1:LB2 :- strand f-red, strand g-blue, helix F-orange, helix G-darkochid. GBR2:LB2 :- strand f-dimgray, strand g-yellow, helix F-hotpink, helix G-brown). | The agonist binding induces the formation of an additional heterodimer interface between the LB2 domains of GBR1bVFT and GBR2VFT subunits. The LB2-LB2 interface buries over 1,300 Å2 of solvent accessible surface area, has poor shape complementarity, and is dominated by polar interactions. The LB2-LB2 interaction is mediated by two strand-loop-helix motifs from each LB2 domain. <scene name='70/701448/Lb2-lb2_interaction/3'> The neighboring strands f and g are part of the central β-sheet in LB2, and helices F and G flank the β-sheet</scene>. (GBR1:LB2 :- strand f-red, strand g-blue, helix F-orange, helix G-darkochid. GBR2:LB2 :- strand f-dimgray, strand g-yellow, helix F-hotpink, helix G-brown). | ||
| - | LB1 and LB2 resdues of GBR1 interact with the GABA<sub>B</sub> agonsits such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-Aminobutyric_acid GABA],[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baclofen baclofen]. as a results of this interacting '''closed conformation''' will be stabilized when <scene name='70/701448/Gaba_ligand/4'> GBR1 subunit bound to GABA</scene> (PDB 4MS3) or <scene name='70/701448/Baclofen/3'>bound to baclofen</scene> (PDB 4MS4) and other agonists. | + | LB1 and LB2 resdues of GBR1 interact with the GABA<sub>B</sub> agonsits such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-Aminobutyric_acid GABA],[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baclofen baclofen]. as a results of this interacting '''closed conformation''' will be stabilized when <scene name='70/701448/Gaba_ligand/4'> GBR1 subunit bound to GABA</scene> (PDB [[4ms3|4MS3]]) or <scene name='70/701448/Baclofen/3'>bound to baclofen</scene> (PDB [[4ms4|4MS4]]) and other agonists. |
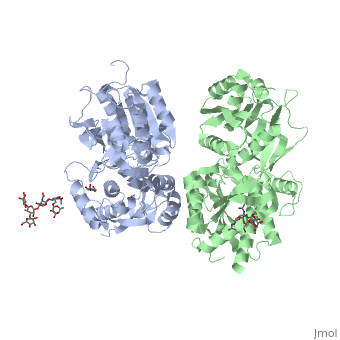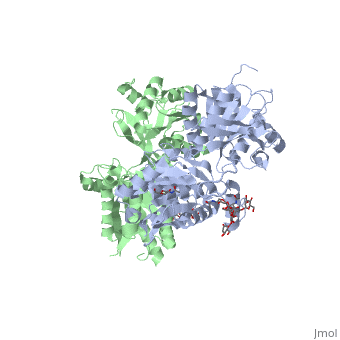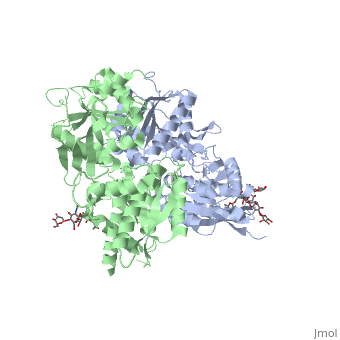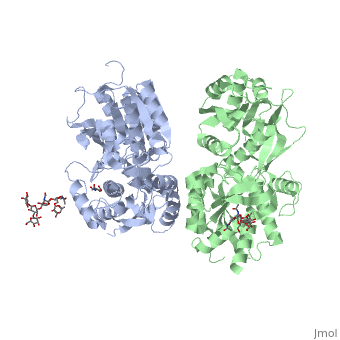
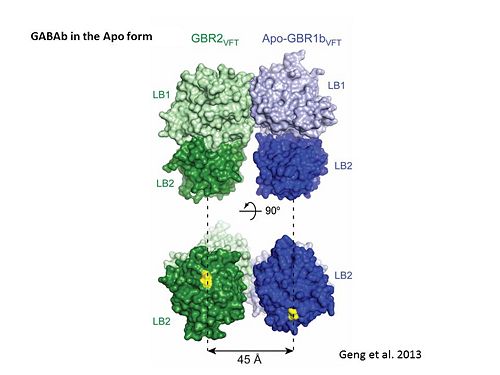
[[Image:GABAb receptor in the Apo form.jpg|center|500px|[[4mqe]]]] | [[Image:GABAb receptor in the Apo form.jpg|center|500px|[[4mqe]]]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
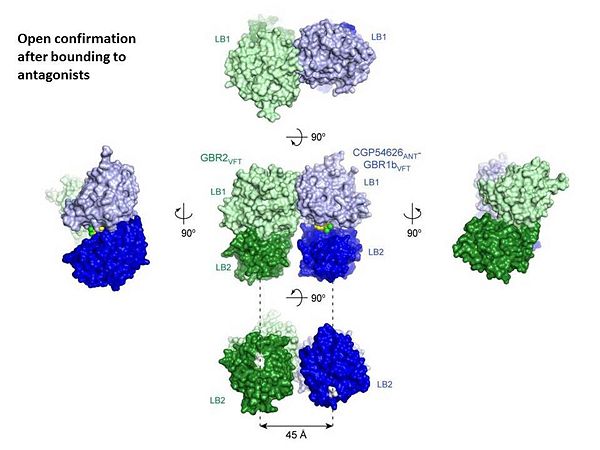
GABA<sub>B</sub> antgonists such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saclofen saclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-46381.html CGP46381], [http://www.hellobio.com/phaclofen.html?picat=&q=phaclofen phaclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-35348.html?picat=&q=CGP+35348 CGP35348] and [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-54626-hydrochloride.html?picat=&q=CGP+54626 CGP54626], mostly intercat with LB1 resduses of GBR1. both ends of the antagonist bind the LB1, which produce '''open confirmation''' of GBR1. | GABA<sub>B</sub> antgonists such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saclofen saclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-46381.html CGP46381], [http://www.hellobio.com/phaclofen.html?picat=&q=phaclofen phaclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-35348.html?picat=&q=CGP+35348 CGP35348] and [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-54626-hydrochloride.html?picat=&q=CGP+54626 CGP54626], mostly intercat with LB1 resduses of GBR1. both ends of the antagonist bind the LB1, which produce '''open confirmation''' of GBR1. | ||
it is very easy to notice the '''open confirmation''' when : | it is very easy to notice the '''open confirmation''' when : | ||
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Saclofen_ant/2'>GBR1 subunit bound to saclofen</scene> (PDB 4MQF). | + | <scene name='70/701448/Saclofen_ant/2'>GBR1 subunit bound to saclofen</scene> (PDB [[4mqf|4MQF]]). |
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Cgp46381_ant/2'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP46381</scene> (PDB 4MS1). | + | <scene name='70/701448/Cgp46381_ant/2'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP46381</scene> (PDB [[4ms1|4MS1]]). |
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Phaclofen_ant/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to phaclofen</scene> (PDB 4MRM). | + | <scene name='70/701448/Phaclofen_ant/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to phaclofen</scene> (PDB [[4mrm|4MRM]]). |
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_cg835348/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP35348</scene> (PDB 4MR8). | + | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_cg835348/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP35348</scene> (PDB [[4mr8|4MR8]]). |
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_CGP54626/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP54626</scene> (PDB 4MR7). | + | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_CGP54626/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP54626</scene> (PDB [[4mr7|4MR7]]). |
[[Image:GABAb.bound.to.antagonist.jpg|center|thumb|600px|The ligand-binding cleft of GBR1bVFT stays open with each bound antagonist. In addition, GBR2VFT remains wide open with an empty interdomain cleft. This open-open configuration of the apo and antagonist-bound structures corresponds to the | [[Image:GABAb.bound.to.antagonist.jpg|center|thumb|600px|The ligand-binding cleft of GBR1bVFT stays open with each bound antagonist. In addition, GBR2VFT remains wide open with an empty interdomain cleft. This open-open configuration of the apo and antagonist-bound structures corresponds to the | ||
resting (or inactive) state of the heterodimeric receptor (Geng et al 2013).]] | resting (or inactive) state of the heterodimeric receptor (Geng et al 2013).]] | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==='''''The intercellular dimerization motif'''''=== | ==='''''The intercellular dimerization motif'''''=== | ||
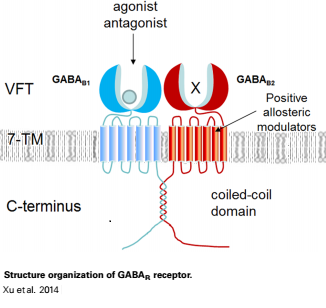
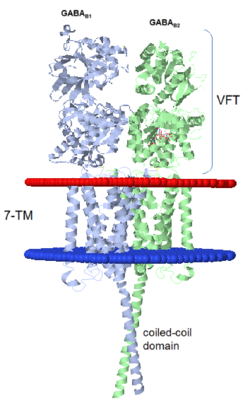
| - | When the GBR1 subunit is expressed alone, it is trapped in vesicles within the cell, whereas the GBR2 alone is expressed on the cell surface, but cannot bind GABA or activate G proteins. When both receptor subunits are expressed in the same cell, the receptor interact through <scene name='70/701448/C_termenal_coild_coil_domain/1'>coiled-coil domain</scene><ref>PMID:24778228</ref><ref>PMID:12209124</ref> (PDB 4PAS) in their carboxyl tails. Then they are expressed on the cell surface, bind GABA and activate G proteins. | + | When the GBR1 subunit is expressed alone, it is trapped in vesicles within the cell, whereas the GBR2 alone is expressed on the cell surface, but cannot bind GABA or activate G proteins. When both receptor subunits are expressed in the same cell, the receptor interact through <scene name='70/701448/C_termenal_coild_coil_domain/1'>coiled-coil domain</scene><ref>PMID:24778228</ref><ref>PMID:12209124</ref> (PDB [[4pas|4PAS) in their carboxyl tails. Then they are expressed on the cell surface, bind GABA and activate G proteins. |
This domain is shaped by <scene name='70/701448/Coild-coil_domain/1'>polar interactions within the hydrophobic core</scene> and is stabilized by <scene name='70/701448/C_termenal_coild_coil_domain/3'>hydrogen-bonding interactions</scene><ref>PMID:24778228</ref>. | This domain is shaped by <scene name='70/701448/Coild-coil_domain/1'>polar interactions within the hydrophobic core</scene> and is stabilized by <scene name='70/701448/C_termenal_coild_coil_domain/3'>hydrogen-bonding interactions</scene><ref>PMID:24778228</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 08:20, 12 August 2015
| |||||||||||