DNA-protein interactions
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
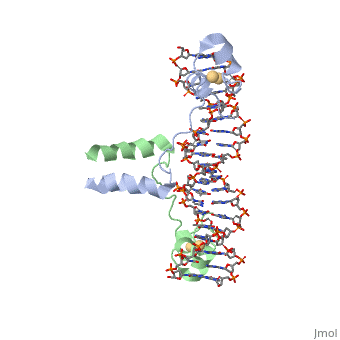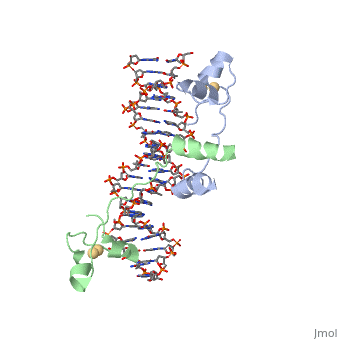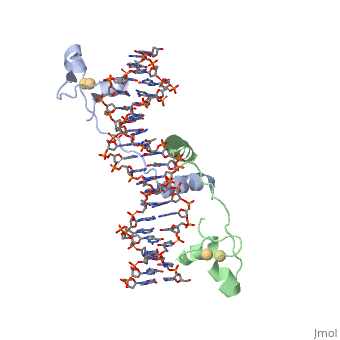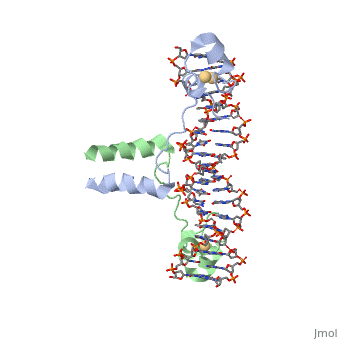
<StructureSection load='1d66' size='340' side='right' caption='Gal4 transcriptional activator interacting with its target DNA=''> | <StructureSection load='1d66' size='340' side='right' caption='Gal4 transcriptional activator interacting with its target DNA=''> | ||
| - | While DNA contains all the genetic material in a cell, proteins play an important role in regulating the transcription of DNA to RNA, not to mention replication, repair and packaging.. The interactions between [[DNA]] and proteins are important in this process. Most sequence specific interactions occur in the major grove, as | + | While DNA contains all the genetic material in a cell, proteins play an important role in regulating the transcription of DNA to RNA, not to mention replication, repair and packaging.. The interactions between [[DNA]] and proteins are important in this process. Most sequence specific interactions occur in the <scene name='71/711660/Grooves/1'>major grove</scene>, as the <scene name='71/711660/Base_exposure/1'>bases are exposed</scene> in this groove. In contrast, the <scene name='71/711660/Grooves/1'>minor grove</scene> contains more of the <scene name='71/711660/Base_exposure/1'>carbohydrate portions</scene> of DNA. |
== Helix-Turn-Helix Interactions with DNA== | == Helix-Turn-Helix Interactions with DNA== | ||
| - | + | The first DNA binding domain characterized was the helix-turn-helix. In helix-turn-helix protein, two α helices are joined by a turn. In most cases, such as in the Cro repressor, the C terminal helix contributes most to DNA recognition, and hence it is often called the "recognition helix". It binds to the major groove of DNA through a series of hydrogen bonds and various Van der Waals interactions with exposed bases.The N-terminal alpha helix stabilizes the interaction between the interaction between protein and DNA, but does not play a particularly strong role in its recognition.[2] The recognition helix and its preceding helix always have the same relative orientation.[ | |
== Leucine zippers == | == Leucine zippers == | ||
Revision as of 23:02, 2 September 2015
DNA-Protein interactions
| |||||||||||
References
This text shows how to insert references: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644