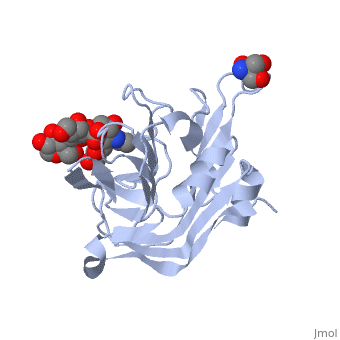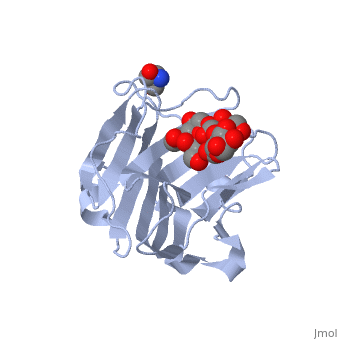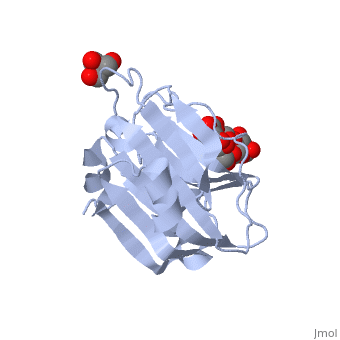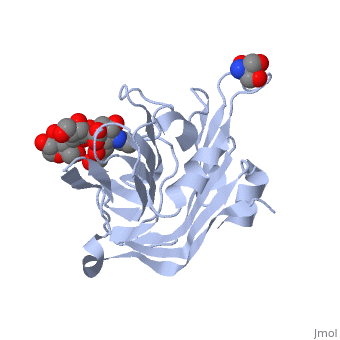
Carbohydrate binding domain from Streptococcus pneumoniae NanA sialidase complexed with 3'-sialyllactose
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<Structure load='4c1w' size='380' frame='true' align='left' caption='Insert caption here' /> | <Structure load='4c1w' size='380' frame='true' align='left' caption='Insert caption here' /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | This is a default text for your page '''Carbohydrate binding domain from Streptococcus pneumoniae NanA sialidase complexed with 3'-sialyllactose'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
| - | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | This sialidase was designed and tested to protect mice from H1N1 by masking cell surface sialic acid receptors recognized by influenza virion, preventing viral binding and entry into the host cells. | |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 02:38, 10 October 2015
Contents |
Carbohydrate binding domain from Streptococcus pneumoniae NanA sialidase complexed with 3'-sialyllactose
|
Function
This sialidase was designed and tested to protect mice from H1N1 by masking cell surface sialic acid receptors recognized by influenza virion, preventing viral binding and entry into the host cells.
Relevance
Influenza binds to sialic acid receptors present on the respiratory epithelium, eventually gaining access through endocytosis.[1] By potentially concealing sialic acid receptors, it has been proposed that a sialic acid binding protein would aid in prevention of influenza infection. [2]
Structural highlights
The carbohydrate binding molecule (CBM) has a ligand chemical component identified with Tris(Hydroxymethyl)Aminomethane, an organic amine proton acceptor. It is used in the synthesis of surface-active agents and pharmaceuticals. This interaction can be see through the . Lactose sialic acid is another identifier and ligand of the CBM . Close interaction between lactose sialic acid and the carbohydrate binding molecule can be seen through and .
</StructureSection>
References
- ↑ SkehelJJ, Wiley DC (2000) Receptor binding and Membrane fustion in virus entry: The influenza hemagglutinin. Annu Rev Biochem 69:531-569
- ↑ Connaris H, Govorkova EA, Ligertwood Y, Dutia BM, Yang L, Tauber S, et al. Prevention of influenza by targeting host receptors using engineered proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(17):6401–6406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404205111