Ivan Koutsopatriy estrogen receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Like other steroid hormones estrogen effects the transcription of a large number of genes via its interactions with its intracellular receptors, estrogen receptors. Estrogen receptors are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (Example of an estrogen; 17β-estradiol). | Like other steroid hormones estrogen effects the transcription of a large number of genes via its interactions with its intracellular receptors, estrogen receptors. Estrogen receptors are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (Example of an estrogen; 17β-estradiol). | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | == Disease == | ||
| - | |||
| - | == Relevance == | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| Line 19: | Line 14: | ||
ER is a modular protein composed of a ligand binding domain, a DNA binding domain and a transactivation domain. ER is a DNA-binding transcription factor. Unbound ER normally exists loosly around the nucleus; this is subject to change depending on a multitude of factors including cell type, progress through cell cycle and reception of cellular signals. When estrogen enters the cell and binds ER, ER will trans-locates and undergoes a conformational shift.(1) Ligand bound estrogen receptor associates more tightly with the nucleus. | ER is a modular protein composed of a ligand binding domain, a DNA binding domain and a transactivation domain. ER is a DNA-binding transcription factor. Unbound ER normally exists loosly around the nucleus; this is subject to change depending on a multitude of factors including cell type, progress through cell cycle and reception of cellular signals. When estrogen enters the cell and binds ER, ER will trans-locates and undergoes a conformational shift.(1) Ligand bound estrogen receptor associates more tightly with the nucleus. | ||
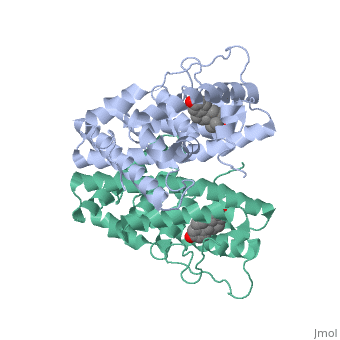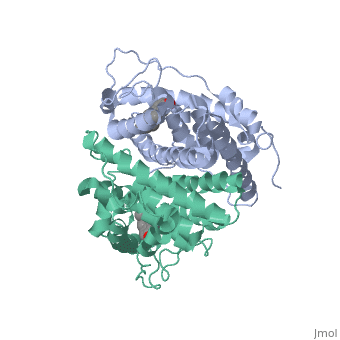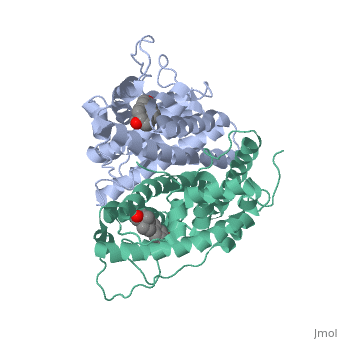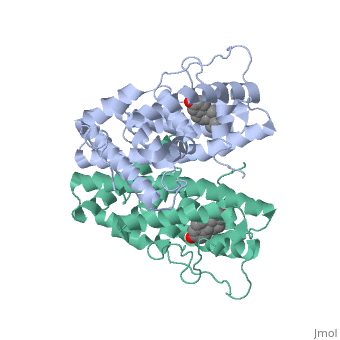
<scene name='71/714947/Agonist_estradiol_bound_er/1'>Agonist_estradiol_bound_er</scene> | <scene name='71/714947/Agonist_estradiol_bound_er/1'>Agonist_estradiol_bound_er</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The specific conformation of this tight loop creates part of the activation signal that will stimulate normal growth, as estradiol is a normal ligand for ER. | ||
<scene name='71/714947/Agonist_ferutinine_bound_er/1'>Agonist_ferutinine_bound_er</scene> | <scene name='71/714947/Agonist_ferutinine_bound_er/1'>Agonist_ferutinine_bound_er</scene> | ||
| - | + | Ferutinine also causes ER to form a tight loop allowing stimulation of normal growth. | |
| - | The | + | <scene name='71/714947/Partial_agonist_genistein_er/1'>Partial_Agonist_genistein_bound_Er</scene> |
| + | |||
| + | The conformation of ER bound to genistein has a loop which is not as tight as those found on ER with a complete agonist ligand. | ||
<scene name='71/714947/Antagonist_tamoxifen_bound_er/1'>Antagonist_tamoxifen_bound_er</scene> | <scene name='71/714947/Antagonist_tamoxifen_bound_er/1'>Antagonist_tamoxifen_bound_er</scene> | ||
Tamoxifen is a drug created to bind ER and inhibit the transcription factor activity of ER. Tamoxifen is larger than the normal hormone ER binds (estradiol); for this reason the activation loop is pushed into an inactive conformation. This blocks ER from giving the signal to grow. | Tamoxifen is a drug created to bind ER and inhibit the transcription factor activity of ER. Tamoxifen is larger than the normal hormone ER binds (estradiol); for this reason the activation loop is pushed into an inactive conformation. This blocks ER from giving the signal to grow. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==DNA Protein Interaction and ER Regulation== | ||
<scene name='71/714947/Er_bound_to_dna/1'>ER_bound_to_dna</scene> | <scene name='71/714947/Er_bound_to_dna/1'>ER_bound_to_dna</scene> | ||
| - | + | ER is functional as a ligand-dependent transcription factor. (3) ER responds to both agonist and antagonist ligands and can associate with the nuclear matrix. The location of the receptor bound and unbound to ligand varies amongst different cell types. In general, an antagonist ligand will cause partial accumulation in the cytoplasm of a cell. The agonist ligand causes the translocation to the nucleus described above. | |
| + | A group bound GFP to ER and studied the location of GFP-ER upon binding of agonists and antagonist ligands. (3) GFP-ER activates the reporter gene in a dose-dependent manner and shows additional activation in the presence of agonist ligand 17-bestradiol. ICI 182780, a pure antagonist for ER, completely inhibited GFP-ER activation of the reporter gene. | ||
| + | The group found that in the absence of ligand, the unoccupied ER is loosely associated with the nucleus. | ||
| + | Ligand causes a biochemical transformation into a complex that associates more tightly with the nucleus. | ||
| + | Before ER binds its hormone the receptor is part of a complex that has many chaperones that maintain the receptor in a steroid binding configuration. Post hormone binding the receptor dissociates from its original complex and binds to hormone responsive elements in chromatin. Gene expression is then regulated by interaction of DNA bound receptors with sequence specific transcription factors and general transcription factors which are mediated by co-activators and co-repressors. The arrangement of cis regulatory elements in a specific promoter or enhancer region and the current state of DNA sequences in nucleosomes determines the system of receptor interactions. Contingent upon the interactions occurring, the result may be induction or repression of transcription. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ERα-regulated gene expression involves interactions with cointegrators (ex. p300/CBP, P/CAF) that have the capacity to modify core histone acetyl groups. 2 ER’s DNA binding domain is ordered around two zinc ions that allow the receptors to bind as homodimers to palindromic DNA sequences in such a way that each homodimer links to one half of the palindrome. | ||
Revision as of 17:50, 10 October 2015
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644