Tyrone Evans Hox Proteins sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
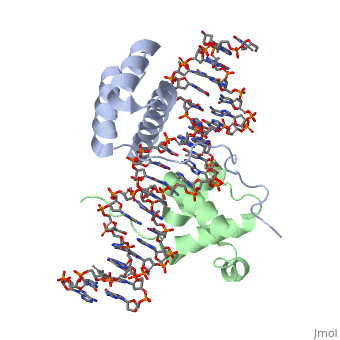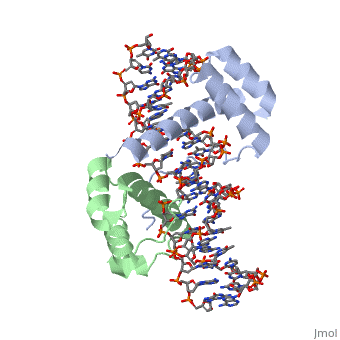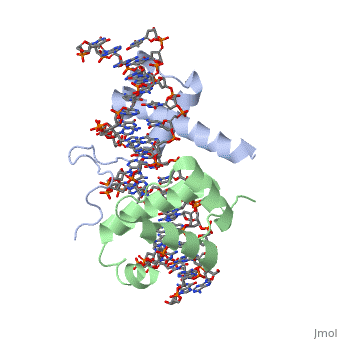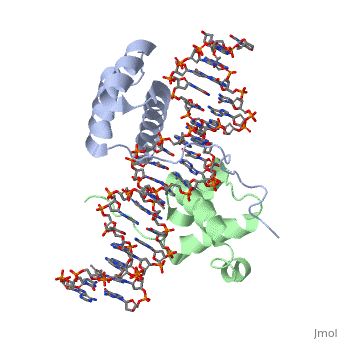
A homeodomain is an essential part that all Hox proteins possess. The homeodomain can be found within the homeobox, a DNA sequence found within genes that are responsible of morphogenesis of living organisms. This sequence codes for homeodomain protein products, 60 amino-acid segments, which have specific folding patterns (helix-turn-helix) that allows them to bind with DNA through a <scene name='71/714951/Taaat_sequence/1'>5’-TAAAT-3’</scene> core motif. This domain consist of three helical regions folded into a tight spherical structure (need picture of structure). There are two antiparallel N-terminal helices and one C-terminal helix within this domain. The C-terminal helix binds directly with DNA through the use of <scene name='71/714951/H_bond_between_gln_and_p/1'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and hydrophobic interactions between side chains and the outer bases and thymine methyl groups within the major groove of a DNA helix. The <scene name='71/714951/Recognition_helix/1'>Recognition helix</scene> within homeodomain binds within the <scene name='71/714951/Dna_major_groove/1'>major groove</scene> of a DNA helix, while the <scene name='71/714951/Amino-terminal_tail/1'>Amino-Terminal tail</scene> binds within the <scene name='71/714951/Dna_minor_groove/1'>minor groove</scene> of a DNA helix. | A homeodomain is an essential part that all Hox proteins possess. The homeodomain can be found within the homeobox, a DNA sequence found within genes that are responsible of morphogenesis of living organisms. This sequence codes for homeodomain protein products, 60 amino-acid segments, which have specific folding patterns (helix-turn-helix) that allows them to bind with DNA through a <scene name='71/714951/Taaat_sequence/1'>5’-TAAAT-3’</scene> core motif. This domain consist of three helical regions folded into a tight spherical structure (need picture of structure). There are two antiparallel N-terminal helices and one C-terminal helix within this domain. The C-terminal helix binds directly with DNA through the use of <scene name='71/714951/H_bond_between_gln_and_p/1'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and hydrophobic interactions between side chains and the outer bases and thymine methyl groups within the major groove of a DNA helix. The <scene name='71/714951/Recognition_helix/1'>Recognition helix</scene> within homeodomain binds within the <scene name='71/714951/Dna_major_groove/1'>major groove</scene> of a DNA helix, while the <scene name='71/714951/Amino-terminal_tail/1'>Amino-Terminal tail</scene> binds within the <scene name='71/714951/Dna_minor_groove/1'>minor groove</scene> of a DNA helix. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='71/714951/Hydrophobic_interaction/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
== Human Hox Genes == | == Human Hox Genes == | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 22 October 2015
Hox Proteins
| |||||||||||