This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Chymotrypsin
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
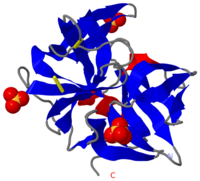
<StructureSection load='7gch' size='450' side='right' scene='38/387136/Bovine_chymotrypsin_overview/1' caption='Bovine γ-chymotrypsin complex with inhibitor (PDB code [[7gch]]) '> | <StructureSection load='7gch' size='450' side='right' scene='38/387136/Bovine_chymotrypsin_overview/1' caption='Bovine γ-chymotrypsin complex with inhibitor (PDB code [[7gch]]) '> | ||
[[Image:2ea3.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of ''Cellulomonas Bogoriensis'' Chymotrypsin [[2ea3]]]] | [[Image:2ea3.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of ''Cellulomonas Bogoriensis'' Chymotrypsin [[2ea3]]]] | ||
| - | [[Chymotrypsin]] (Chy or α-Chy) is a digestive enzyme containing an active serine residue, which helps to digest proteins in our food. Other related proteases are crucial for blood clotting ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=stryer&part=A1378&rendertype=figure&id=A1401 thrombin and other proteases]), for the AIDS virus metabolism ([http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Hiv_protease HIV protease]) and for many other processes relevant to human health and agriculture. Chymotrypsin cleaves peptide bonds of proteins where the amide side of the bond is an aromatic amino acid like tyrosine, phenylalanine or tryptophan. Bovine Chy is found in 2 forms: A and B. The 2 forms have different proteolytic characteristics. The image at the left is the crystal structure of chymotrypsin from ''Cellulomonas Bogoriensis'' ([[2ea3]]) with sulfate ions. Below is description of the structure of bovine chymotrypsin. Some additional details in<br /> | + | [[Chymotrypsin]] (Chy or α-Chy) is a digestive enzyme containing an active serine residue, which helps to digest proteins in our food. Other related proteases are crucial for blood clotting ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=stryer&part=A1378&rendertype=figure&id=A1401 thrombin and other proteases]), for the AIDS virus metabolism ([http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Hiv_protease HIV protease]) and for many other processes relevant to human health and agriculture. Chymotrypsin cleaves peptide bonds of proteins where the amide side of the bond is an aromatic amino acid like tyrosine, phenylalanine or tryptophan. Bovine Chy is found in 2 forms: A and B. The 2 forms have different proteolytic characteristics. '''γ-Chy''' is a covalent acyl adduct of α-Chy.The image at the left is the crystal structure of chymotrypsin from ''Cellulomonas Bogoriensis'' ([[2ea3]]) with sulfate ions. Below is description of the structure of bovine chymotrypsin. Some additional details in<br /> |
*[[Molecular Playground/Chymotrypsin]]<br /> | *[[Molecular Playground/Chymotrypsin]]<br /> | ||
*[[Serine Proteases]]. | *[[Serine Proteases]]. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
**[[1yph]] – bChyA chain A - bovine<br /> | **[[1yph]] – bChyA chain A - bovine<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4cha]], [[5cha]] – | + | **[[4cha]], [[5cha]] – BtChyA<br /> |
**[[1kdq]] – rChyB, chain B (mutant) - rat<br /> | **[[1kdq]] – rChyB, chain B (mutant) - rat<br /> | ||
**[[2ea3]] – Chy – ''Cellulomonas bogoriensis''<br /> | **[[2ea3]] – Chy – ''Cellulomonas bogoriensis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ab9]], [[8gch]], [[1gct]], [[2gct]], [[3gct]], [[2gch]] - gamma BtChy<br /> | ||
* Chymotrypsin + polypeptide inhibitors | * Chymotrypsin + polypeptide inhibitors | ||
| Line 42: | Line 41: | ||
**[[1ca0]] – bChy+APPI <br /> | **[[1ca0]] – bChy+APPI <br /> | ||
**[[1gl1]] – bChy + PMP-C<br /> | **[[1gl1]] – bChy + PMP-C<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1ab9]], [[8gch]], [[1gct]], [[2gct]], [[3gct]], [[2gch]] - bChyA + peptide<br /> |
| - | **[[1cho]], [[1hja]] – | + | **[[1acb]] – bChy+Elgin C <br /> |
| + | **[[1cho]], [[1hja]] – bChyA+turkey ovomucoid third domain <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4h4f]] – hChyC +Elgin C - human<br /> | ||
* Chymotrypsin + inhibitors | * Chymotrypsin + inhibitors | ||
| Line 50: | Line 51: | ||
**[[2p8o]] - bChyA chain A+benzohydroxamic acid/vanadate <br /> | **[[2p8o]] - bChyA chain A+benzohydroxamic acid/vanadate <br /> | ||
**[[1eq9]] – Chy+PMSF – fire ant <br /> | **[[1eq9]] – Chy+PMSF – fire ant <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2cha]] – | + | **[[2cha]] – bChyA+p-sulfinotoluene<br /> |
| + | **[[6cha]] – bChyA+phenylethane boronic acid <br /> | ||
* γ-Chymotrypsin + inhibitors | * γ-Chymotrypsin + inhibitors | ||
| Line 57: | Line 59: | ||
**[[1ggd]] – γ-bChy+N-acetyl-phenylalanine trifluoromethyl aldehyde <br /> | **[[1ggd]] – γ-bChy+N-acetyl-phenylalanine trifluoromethyl aldehyde <br /> | ||
**[[1afq]] - γ-bChy+synthetic inhibitor<br /> | **[[1afq]] - γ-bChy+synthetic inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3gch]], [[4gch]], [[5gch]] - γ- | + | **[[3gch]], [[4gch]], [[5gch]] - γ-bChyA+cinnamate <br /> |
| - | **[[6gch]], [[7gch]] - γ- | + | **[[6gch]], [[7gch]] - γ-bChyA+trifluoromethy ketone <br /> |
| - | + | **[[1gmc]], [[1gmd]] – γ-bChyA+hexane – transition state inhibitor<br /> | |
| - | **[[1gmc]], [[1gmd]] – γ- | + | |
**[[2gmt]] - γ-bChy+N-acetyl-alanyl-phenylalanyl-chloroethyl ketone<br /> | **[[2gmt]] - γ-bChy+N-acetyl-alanyl-phenylalanyl-chloroethyl ketone<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1gmh]], [[1gcd]] - γ- | + | **[[1gmh]], [[1gcd]] - γ-bChyA+organophosphoryl <br /> |
| - | **[[1gha]], [[1ghb]] - γ- | + | **[[1gha]], [[1ghb]] - γ-bChyA+ N-acetyl-tryptophan<br /> |
**[[1vgc]], [[2vgc]], [[3vgc]], [[4vgc]] – γ-bChy + boronic acid inhibitor<br /> | **[[1vgc]], [[2vgc]], [[3vgc]], [[4vgc]] – γ-bChy + boronic acid inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | * γ-Chymotrypsin + reaction transition state inhibitors | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[6cha]] – γ-bChy+phenylethane boronic acid <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1gmc]], [[1gmd]] – γ-bChy+hexane | ||
| - | |||
| - | * δ-Chymotrypsin + inhibitors | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1dlk]] – δ-bChy+peptidyl chloromethyl ketone | ||
* Native Chymotrypsinogen | * Native Chymotrypsinogen | ||
| - | **[[2cga]], [[1chg]], [[1ex3]] – | + | **[[2cga]], [[1chg]], [[1ex3]] – bChygenA<br /> |
| - | **[[2jet]] – | + | **[[2jet]] – rChygenB chain A,B <br /> |
* Chymotrypsinogen + inhibitors | * Chymotrypsinogen + inhibitors | ||
**[[1gl0]], [[1gli]] – ChygenA+PMP_D2v – ''Locusta migratoria''<br /> | **[[1gl0]], [[1gli]] – ChygenA+PMP_D2v – ''Locusta migratoria''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1k2i]] - | + | **[[1k2i]] - bChygenA+7-hydroxycoumarin<br /> |
**[[2y6t]] – bChygenA + ecotin<br /> | **[[2y6t]] – bChygenA + ecotin<br /> | ||
**[[3t62]] - bChygenA + Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitor SHPI-1<br /> | **[[3t62]] - bChygenA + Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitor SHPI-1<br /> | ||
Revision as of 09:52, 5 November 2015
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Chymotrypsin
Updated on 05-November-2015
The Chy precursor is the inactive chymotrypsinogen (Chygen) which gets cleaved 3 times by trypsin and chymotrypsin losing a 4 amino acid long peptide to become the active Chy. γ-Chy is a covalent acyl adduct of α-Chy. δ-Chy results when Chygen is cleaved only twice.
Further reading
You can learn more about chymotrypsin structure, function and regulation in this publicly available chapter of the Biochemistry textbook by Berg, Tymoczka and Stryer.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Karsten Theis, Alice Harmon, Alexander Berchansky