We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Beta-2 microglobulin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
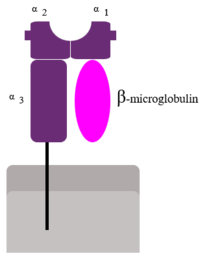
[[Beta-2 microglobulin]] ('''B2M''') is a component of MHC class I system. B2M associates with MHC class I α chain, CD1 and Qa. Loss of B2M function causes iron excess. For more details, see: [[Human beta two microglobulin]]. | [[Beta-2 microglobulin]] ('''B2M''') is a component of MHC class I system. B2M associates with MHC class I α chain, CD1 and Qa. Loss of B2M function causes iron excess. For more details, see: [[Human beta two microglobulin]]. | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Disease == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Elevated B2M levels are found in patients of live cirhossis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | |||
| + | B2M is used as a marker for certain types of blood cell cancer. It can indicate the spread and severity of myeloma. | ||
== 3D Structures of β-2 microglobulin == | == 3D Structures of β-2 microglobulin == | ||
Revision as of 09:29, 10 November 2015
Beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) is a component of MHC class I system. B2M associates with MHC class I α chain, CD1 and Qa. Loss of B2M function causes iron excess. For more details, see: Human beta two microglobulin.
Disease
Elevated B2M levels are found in patients of live cirhossis.
Relevance
B2M is used as a marker for certain types of blood cell cancer. It can indicate the spread and severity of myeloma.
3D Structures of β-2 microglobulin
Updated on 10-November-2015
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner