We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Aminomutase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''Aminomutases''' catalyze the exchange of hydrogen atom and an amine substituent on a neighboring carbon atom. | '''Aminomutases''' catalyze the exchange of hydrogen atom and an amine substituent on a neighboring carbon atom. | ||
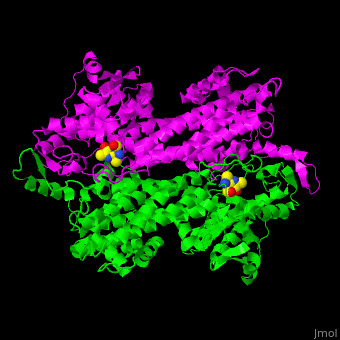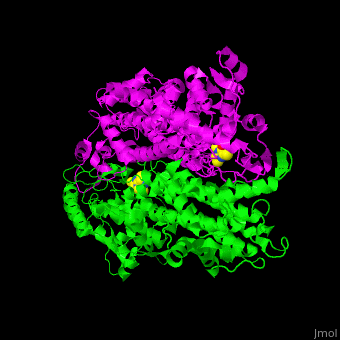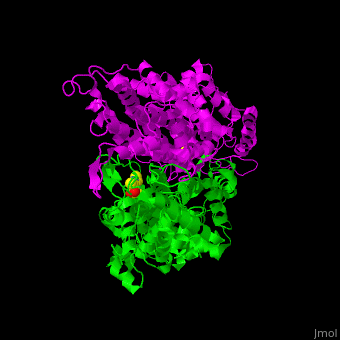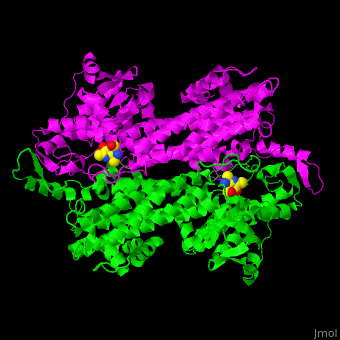
| - | '''Phenylalanine aminomutase''' (PAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of L-phenylalanine to ammonia and trans-cinnamic acid. Ala-Ser-Gly derived chromophore is a cofactor. | + | *'''Phenylalanine aminomutase''' (PAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of L-phenylalanine to ammonia and trans-cinnamic acid. Ala-Ser-Gly derived chromophore is a cofactor. |
| - | '''Tyrosine-2,3-aminomutase''' (TAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of L-tyrosine to 3-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate. Ala-Ser-Gly derived chromophore is a cofactor. | + | *'''Tyrosine-2,3-aminomutase''' (TAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of L-tyrosine to 3-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate. Ala-Ser-Gly derived chromophore is a cofactor. |
| - | '''Ornithine-4,5-aminomutase''' (ORA) catalyzes the reversible conversion of D-ornithine to (2R,4S)-2,4-diaminopropanoate. ORA cofactors are pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), cobamide coenzyme and dithiothreitol. ORA contains subunits S (ORAS) and E (ORAE). The ORAS forms a complex with lysine 5,6-aminomutase. The ORAE contains a balamin-binding motif. | + | *'''Ornithine-4,5-aminomutase''' (ORA) catalyzes the reversible conversion of D-ornithine to (2R,4S)-2,4-diaminopropanoate. ORA cofactors are pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), cobamide coenzyme and dithiothreitol. ORA contains subunits S (ORAS) and E (ORAE). The ORAS forms a complex with lysine 5,6-aminomutase. The ORAE contains a balamin-binding motif. |
| - | '''Lysine-2,3-aminomutase''' (LAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of lysine to beta-lysine. LAM is a S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) radical enzyme. LAM cofactors are PLP, Zn ion and FeS4 cluster. | + | *'''Lysine-2,3-aminomutase''' (LAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of lysine to beta-lysine. LAM is a S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) radical enzyme. LAM cofactors are PLP, Zn ion and FeS4 cluster. |
| - | '''D-lysine-5,6-aminomutase''' (DLAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of D-lysine to 2,5-diaminohexanoate. DLAM cofactor is cobamide | + | *'''D-lysine-5,6-aminomutase''' (DLAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of D-lysine to 2,5-diaminohexanoate. DLAM cofactor is cobamide. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | *'''Glutamate-1-semialdehyde 2,1-aminomutase''' (GSAM) catalyzes the reversible conversion of L-glutamate-1-semialdehyde to 5-aminovulinate. GSAM cofactor is PLP. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 09:11, 2 December 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of aminomutase
Updated on 02-December-2015