We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox flagella
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== | ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== | ||
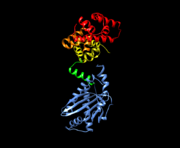
<StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | Flagellar motors are locomotive organelles located in bacterial cell envelopes and push the cell in its environment. These motors are composed of a variety of proteins and consist of a rotary motor, a universal joint, and a helical filament [2]. They are driven by the flow of ions down their concentration gradient with respect to the cytoplasmic membrane through a stator, and are regulated by the chemotaxis pathway. The stator complex serves as a channel to couple the proton flow with a torque generation that occurs at the interface between the stator(s) and a rotor. The torque generation and stator assembly around the rotor require highly conserved charged residues to be present [1,3]. | |
| - | + | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | == | + | == Structure == |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 18:38, 9 December 2015
This page is setup for Beatriz to build her senior project for OU CHEM 4923
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||